Description
Context:
- Adopting Industry 4.0 technologies would make MSMEs more efficient and competitive.
Background
- The term ‘Industry 4.0’ was coined by the German government in 2011.
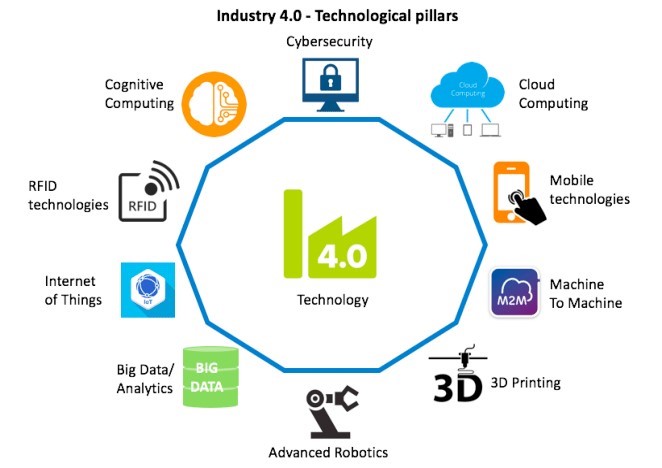
- Additive manufacturing, Internet of Things, Cyber Physical Systems, Augmented Reality/Virtual Reality and data analytics are some of the technologies associated with Industry 4.0.
- Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) are expected to become the backbone of India as the economy grows larger who lack basic focus in the direction of Industry 4.0.
- MSMEs form more than 95% of the industries in India, produce more than 45% of the total manufacturing output and employ more than 40% of the workforce.
- According to the Economic Survey 2020-21, over 6 crore MSMEs employ more than 11 crore people and contribute roughly 30% to the GDP and half of the country’s exports.
- MSMEs are also ancillaries to larger enterprises, leading to a seamless supply chain integration. As a result, making MSMEs more efficient will be advantageous for the whole economy.
Industry 4.0
- Industry 4.0 is the digital transformation of manufacturing/production and related industries and value creation processes.
- Industry 4.0 is used interchangeably with the fourth industrial revolution and represents a new stage in the organization and control of the industrial value chain.
- Cyber-physical systems form the basis of Industry 4.0 (e.g., ‘smart machines’).
- They use modern control systems, have embedded software systems and dispose of an Internet address to connect and be addressed via IoT (the Internet of Things).
- Industry 4.0 refers to the intelligent networking of machines and processes for industry with the help of information and communication technology.
- Industry 4.0 is often used interchangeably with the notion of the fourth industrial revolution. It is characterized by, among others
○ Even more automation than in the third industrial revolution.
○ The bridging of the physical and digital world through cyber-physical systems, enabled by Industrial IoT
○ A shift from a central industrial control system to one where smart products define the production steps,
○ Closed-loop data models and control systems ○ Personalization/customization of products.
Challenges faced
- MSMEs face challenges when it comes to adopting new technologies such as Industry 4.0.
- They lack awareness regarding Industry 4.0 and its benefits.
- They consider such technologies disruptive and have the potential to demolish their existing system.
- Industry 4.0 believes in improving the existing system.
- Scientific literature provides evidence of sensors and WiFi networks being integrated with old machines like lathes and mills to improve their performance.
- MSMEs will need to make major financial investments to adopt Industry 4.0.
- Investing in the right set of technologies will need experts and consultants as well.
- For any new technology to be adopted, an organisation requires a positive organisational culture and the support of people.
- MSMEs need to believe in the advantages that Industry 4.0 technologies can o er.
- The frameworks and steps that can assist MSMEs in adopting Industry 4.0 technologies have been missing.
- In this regard, MSMEs need to understand the data they are producing from all their operational activities.
- Based on such data, their readiness can be evaluated.
- Finally, MSMEs should develop their own vision of Industry 4.0 technologies that they want to adopt and identify the relevant tools and practices they need for such a tailored vision.
Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Classification 2020
|
Size of the Enterprise
|
Investment and Annual Turnover
|
|
Micro
|
Investment less than Rs. 1 crore
Turnover less than Rs. 5 crore
|
|
Small
|
Investment less than Rs. 10 crore
Turnover up to Rs. 50 crore
|
|
Medium
|
Investment less than Rs. 20 crore
Turnover up to Rs. 100 crore
|
Importance of MSMEs for Indian Economy
- Employment:It is the second largest employment generating sector after agriculture. It provides employment to around 120 million persons in India.
- Contribution to GDP:With around 36.1 million units throughout the geographical expanse of the country, MSMEs contribute around 6.11% of the manufacturing GDP and 24.63% of the GDP from service activities.
- MSME ministry has set a target to up its contribution to GDP to 50% by 2025 as India becomes a $5 trillion economy.
- Exports: It contributes around 45% of the overall exports from India.
- Inclusive growth:MSMEs promote inclusive growth by providing employment opportunities in rural areas especially to people belonging to weaker sections of the society.
- For example: Khadi and Village industries require low per capita investment and employs a large number of women in rural areas.
- Financial inclusion:Small industries and retail businesses in tier-II and tier-III cities create opportunities for people to use banking services and products.
- Promote innovation:It provides opportunity for budding entrepreneurs to build creative products boosting business competition and fuels growth.