Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://bellona.org/news/ccs/2014-06-lies-store-ccs
Context: The Prime Minister of India addressed the International Energy Agency's (IEA) Ministerial Meeting, commemorating its 50th anniversary and highlighting India's role in energy security and sustainability.
Prime Minister's Address at IEA Ministerial Meeting
- Rapid Economic Growth and Renewable Energy Focus: He highlighted India's impressive economic growth, transitioning from the 11th to the 5th largest economy within a decade. This growth was accompanied by a significant increase in renewable energy capacity, particularly solar (26x) and overall (doubled). He emphasized exceeding Paris Agreement commitments ahead of schedule.
- Low Carbon Emissions Despite Large Population: Despite representing 17% of the global population, India's carbon emissions only account for 4%. This point to India's efforts towards sustainable development.
- Commitment to Climate Action: Modi reaffirmed India's commitment to combating climate change through various initiatives like Mission LiFE (pro-planet lifestyles) and traditional values of reduce-reuse-recycle. He mentioned India's leadership in the International Solar Alliance and Global Biofuels Alliance.
- Call for Inclusivity and India's Contribution: He stressed the importance of inclusivity for institutions like the IEA and highlighted India's potential to contribute talent, technology, and innovation. He expressed confidence that a larger role for India would benefit the IEA.
- Collaboration and Building a Better Future: Modi concluded by wishing for a successful meeting and emphasizing the need to leverage this platform for strengthening existing partnerships and creating new ones, ultimately building a cleaner, greener, and more inclusive world.
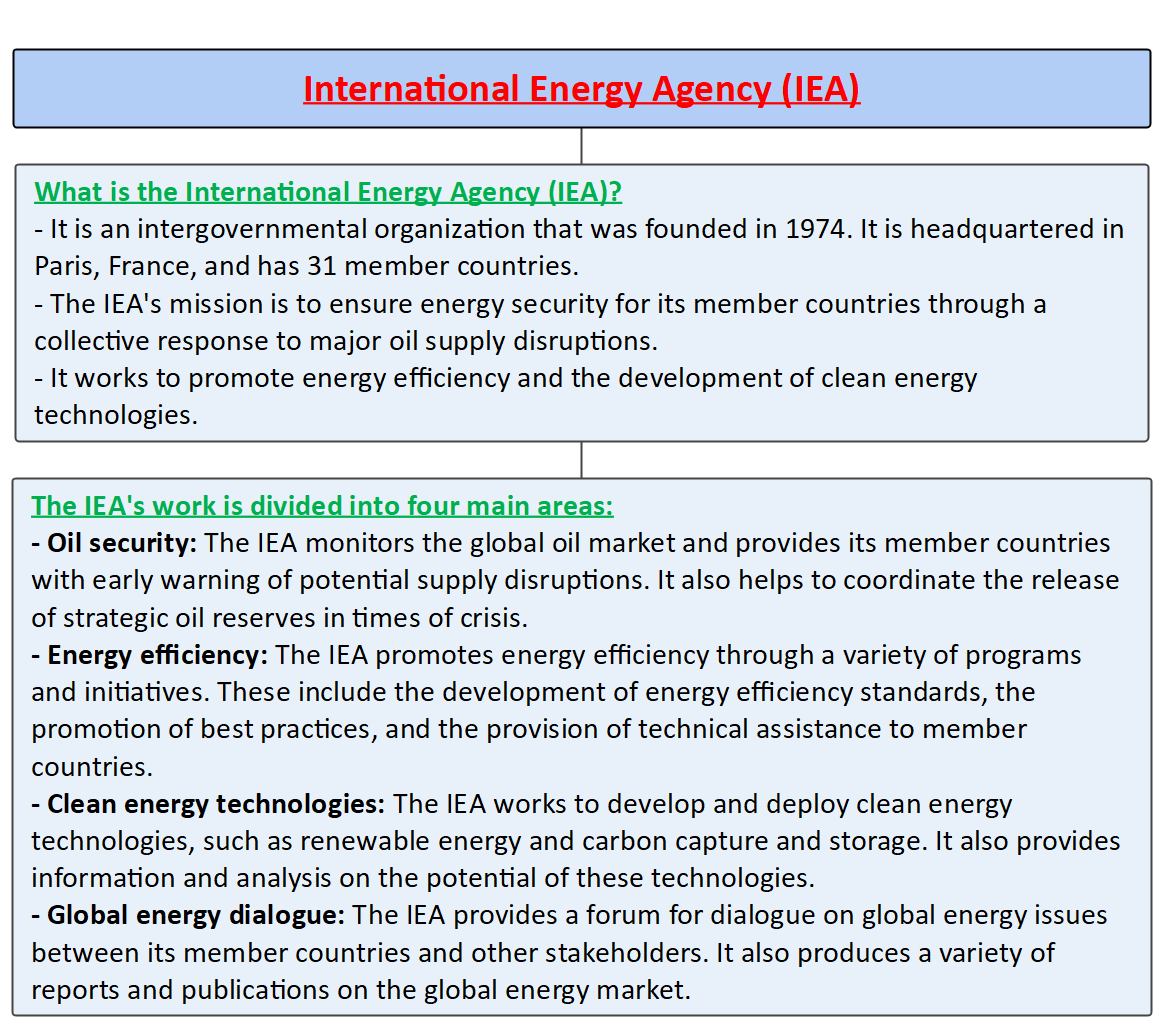
International Energy Agency (IEA)
- It is an intergovernmental organisation that provides policy recommendations, analysis and data on the global energy sector. It was established in 1974 by the members of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in response to the 1973 oil crisis and has since expanded its role to cover the entire spectrum of energy issues, including energy security, clean energy transition, climate change mitigation and energy access.
- The IEA has 31 member countries and 13 association countries, representing 75% of global energy demand.
- The IEA has been a key player in the development of a number of international agreements on energy, including the Paris Agreement on climate change. The agency is also a member of the World Bank Group and the United Nations Environment Programme.
The IEA's main activities include
- Data Collection and Publishing: Collects and publishes data and statistics on the global energy system. Releases reports such as the monthly Oil Market Report, the annual World Energy Outlook, and the Net Zero by 2050 report.
- Policy Advice and Guidance: Provides policy advice and guidance to member states, associated countries, and other stakeholders. Aims to help achieve energy security and sustainability goals through informed policy recommendations.
- Emergency Response Coordination: Coordinates emergency response measures in case of major disruptions in oil or gas supplies. This includes the release of strategic petroleum reserves or the activation of demand restraint measures to address energy supply disruptions.
- Promotion of Energy Efficiency and Innovation: Promotes energy efficiency, conservation, and innovation through various programs and initiatives. Includes the Energy Efficiency Network, Technology Collaboration Programmes, and participation in the Clean Energy Ministerial.
- Support for Clean Energy Transition: Supports global efforts to accelerate the transition to clean energy and mitigate climate change. Works in line with the Paris Agreement and the Sustainable Development Goals to achieve net-zero emissions and prevent global temperatures from rising above 1.5 °C.
- Enhancing Energy Access and Affordability: Works towards improving energy access and affordability, particularly in developing countries and regions. Engages in projects such as the Africa Energy Outlook, and the Energy Access Outlook, and collaborates with organizations like the Clean Cooking Alliance.

The IEA conducts its work through four main bodies
Governing Board
- Comprising senior representatives from each member country.
- Sets the overall policy direction and budget of the IEA.
- This body plays a key role in determining the strategic objectives and priorities of the IEA, ensuring alignment with the energy policy goals of member countries.
Standing Groups
- Composed of experts from member countries.
- Deals with specific aspects of energy policy, including oil markets, gas markets, electricity markets, energy efficiency, renewable energy, and technology cooperation.
- These groups focus on in-depth analysis, research, and recommendations in their respective domains, providing valuable insights to guide energy policies and strategies.
Secretariat
- Based in Paris, headed by the executive director.
- Carries out day-to-day operations, including producing reports, organizing events, managing programs, and providing services to members and partners.
- Acts as the operational arm of the IEA, implementing decisions made by the Governing Board and facilitating communication and collaboration among member countries.
Committees on Energy Research and Technology (CERT) and Global Energy Dialogue (CGED)
- Representatives from member countries, association countries, and other stakeholders.
- Provides advice and input to the IEA on energy research and innovation, shaping the agency's approach to technological advancements in the energy sector.
- Offers advice and input on global energy dialogue and cooperation, fostering international collaboration on energy-related issues.
Conclusion
- The IEA plays a crucial role in shaping global energy policies, fostering innovation, and advancing sustainable development goals related to energy security, affordability, and environmental sustainability. Its activities span data collection, policy advice, emergency response coordination, energy efficiency promotion, clean energy transition support, and efforts to enhance energy access worldwide.
Must Read Articles:
IEA Summit On Clean Energy Minerals: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/iea-summit-on-clean-energy-minerals
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. The International Energy Agency (IEA) mission aims for both energy security and sustainability. How does the agency navigate potential conflicts between these goals, particularly for member countries with diverse energy needs and priorities? Can it truly achieve both objectives without compromising one for the other?
Answer Structure:
●Start with a brief introduction that explains what the IEA is, what its mission is, and why it faces potential conflicts between energy security and sustainability.
●Provide some examples of how these conflicts arise in different contexts, such as fossil fuels versus renewables, climate change versus economic growth, or regional versus global cooperation.
●Analyze how the IEA tries to balance these conflicting goals, using evidence from its reports, policies, and initiatives. Highlight its strengths and weaknesses, as well as the opportunities and challenges it faces.
●Conclude with a summary of the main points and a critical evaluation of whether the IEA can truly achieve both energy security and sustainability without compromising one for the other.
|








