Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Context: In what is being seen as a major diplomatic breakthrough, Israel announced a “historic” deal with Lebanon, aimed at resolving a long-running maritime border dispute over Mediterranean waters.
Details of the agreement:
- Analysts believe that this deal may pave the way for reduced tensions between the nations.
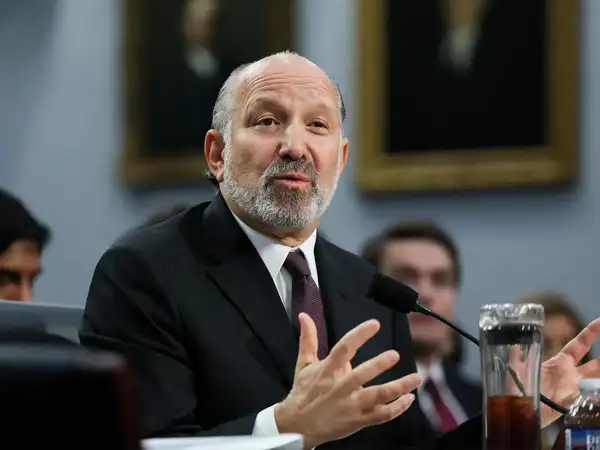
- The draft agreement is floated by US envoy Amos J Hochstein, who is the special envoy and coordinator for international energy affairs and leads the bureau of energy resources (ENR) at the US Department of State
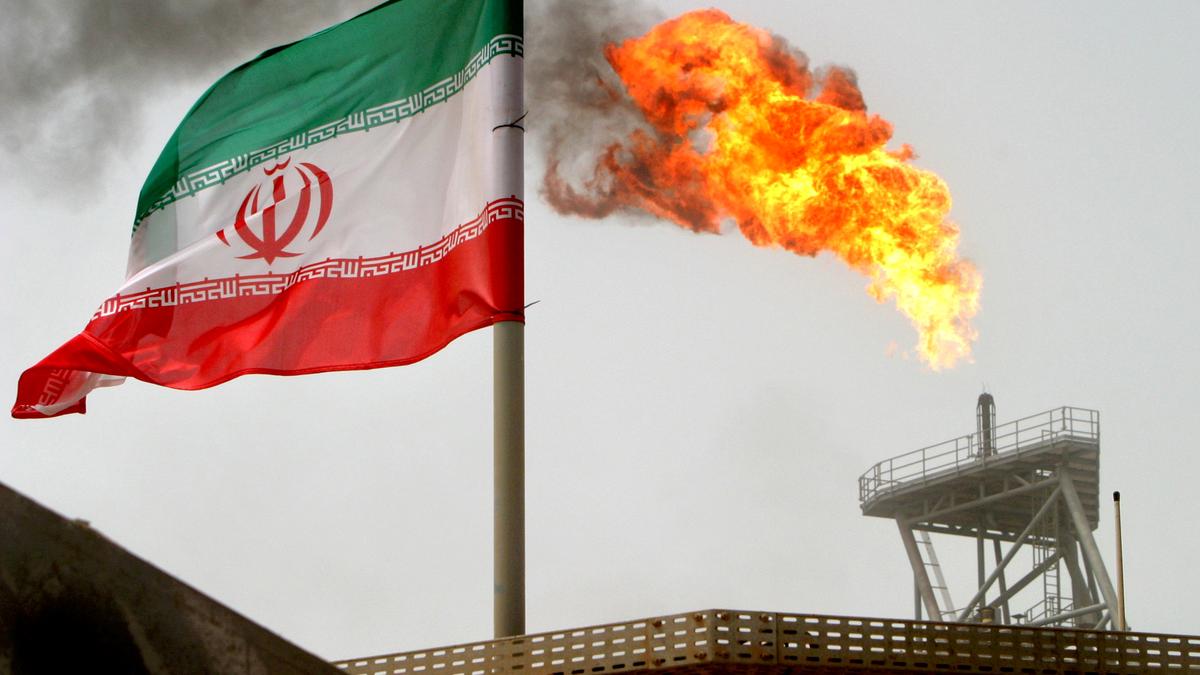
- It aims to settle Israel and Lebanon’s competing claims over offshore gas fields in the region.
- While Israel is already producing natural gas at nearby fields, what this agreement does is that it resolves a territorial dispute in the eastern Mediterranean sea, in an area that Lebanon wants to explore for natural gas.
- It would allow both countries to get royalties from the gas.
- It also sets a border between the maritime waters of Lebanon and Israel for the first time.
- It is also expected to avert the immediate threat of conflict between Israel and Hezbollah militants in Lebanon, after fears of escalation if negotiations fell apart.
- It could also have a potentially wider impact: it would likely provide Europe with a potential new source of gas amid energy shortages caused by the Russian invasion of Ukraine.

Concerns:
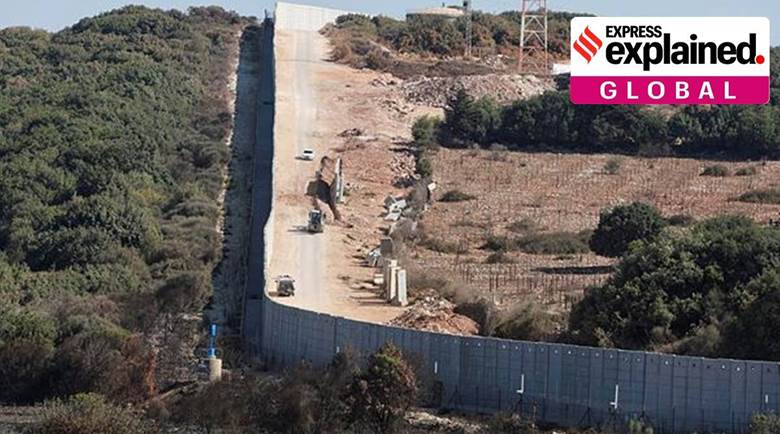
- The agreement does not touch on the shared land border between Israel and Lebanon, which is still disputed, but where both countries are committed to a ceasefire.
- This border is also called the Blue Line, a boundary that was drawn up by the UN after Israel withdrew from southern Lebanon in 2000. This land border is currently patrolled by the United Nations forces.
Background:
- Israel and Lebanon do not have official diplomatic relations and the two countries remain technically at war.
- The issue is a little over a decade old, after the two countries declared overlapping boundaries in 2011 in the Mediterranean Sea.
- Since both countries have been technically at war, the United Nations was asked to mediate.
- The issue gained significance after Israel discovered two gas fields off its coast a decade ago, which experts had believed could help turn it into an energy exporter
Hezbollah-Israel conflict:
About Hezbollah:
- Hezbollah is a Shia militia-cum-political party in Lebanon.
- Hezbollah and Israel have fought two wars before.
- They have been observing a tenuous ceasefire for 14 years.
Main events:
- In 2000, after 18 years of occupation of southern Lebanon, Israel was forced to withdraw mainly due to the fighting of Hezbollah.
- In 2006, Israel invaded Lebanon, aimed at destroying Hezbollah’s military capabilities.
- But after a month of Israeli aerial and land attacks, Hezbollah fired hundreds of short-range rockets into northern Israel.
- Ever since, both sides have been wary of another open conflict.
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-global/historic-deal-between-israel-lebanon-terms-significance-8203111/










