Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Israel’s parliament, passed a key clause of an overarching judicial reform bill that seeks to curtail the powers of the Supreme Court.
Details
- Called the “reasonableness bill”, it seeks to strip the top court of the power to declare government decisions unreasonable.
- The reasonableness doctrine is commonly used by courts there to determine the constitutionality or lawfulness of a given legislation, and allows judges to make sure that decisions made by public officials are “reasonable.”
- The reasonableness bill is just one part of a broader package of reforms to Israel's judicial system by the right-wing coalition.
- Other elements of the overhaul are aiming to give the ruling coalition government more control over the appointment of judges and would remove independent legal advisers from government ministries.
Government’s rationale
- PM Benjamin Netanyahu and his supporters say the move is meant to rebalance powers between the branches of government.
- The prime minister and his supporters argue that the Supreme Court has become an insular, elitist group that does not represent the Israeli people. They say it has overstepped its role, getting into issues it should not rule on.
- Israel, which has no written constitution but only a set of quasi-constitutional basic laws, has had a relatively powerful Supreme Court, which supporters of the changes argue is problematic.

Criticism
- Critics say it poses a threat to Israeli democracy and to the independence of the judiciary.
- Thousands of protesters outside the Supreme Court condemned the approval of the law with chants of “shame” and “democracy or rebellion".
- The Supreme Court is the only check on the power of the Knesset and the government since the executive and legislative branches are always controlled by the same governing coalition.
- Critics say the overhaul will destroy the only avenue available to provide checks and balances in the governing of the country. They also warn it will harm the independence of the Israeli judiciary and will hurt rights not enshrined in Israel’s basic laws, like minority rights and freedom of expression.
Conclusive Remarks
- The reasonableness doctrine is not unique to Israel’s judiciary. The principle is used in a number of countries, including the United Kingdom, Canada, and Australia.
- Changing the Judicial Process will be the most extreme shakeup to Israel’s judiciary since its founding in 1948.
Israel
Location
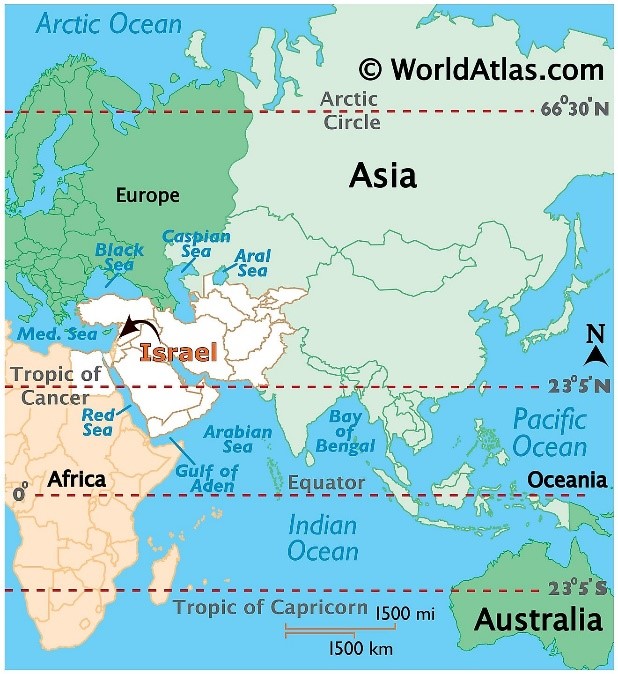
- Israel is located in the Levant area of the Fertile Crescent region.
- Israel is a Middle East country, situated in Western Asia.
- It is located in the Northern and Eastern hemispheres of the Earth.
- Israel is situated on the Southeastern coasts of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern coasts of the Red Sea.
Levant, historically, the region along the eastern Mediterranean shores, roughly corresponding to modern-day Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, and certain adjacent areas.
Borders
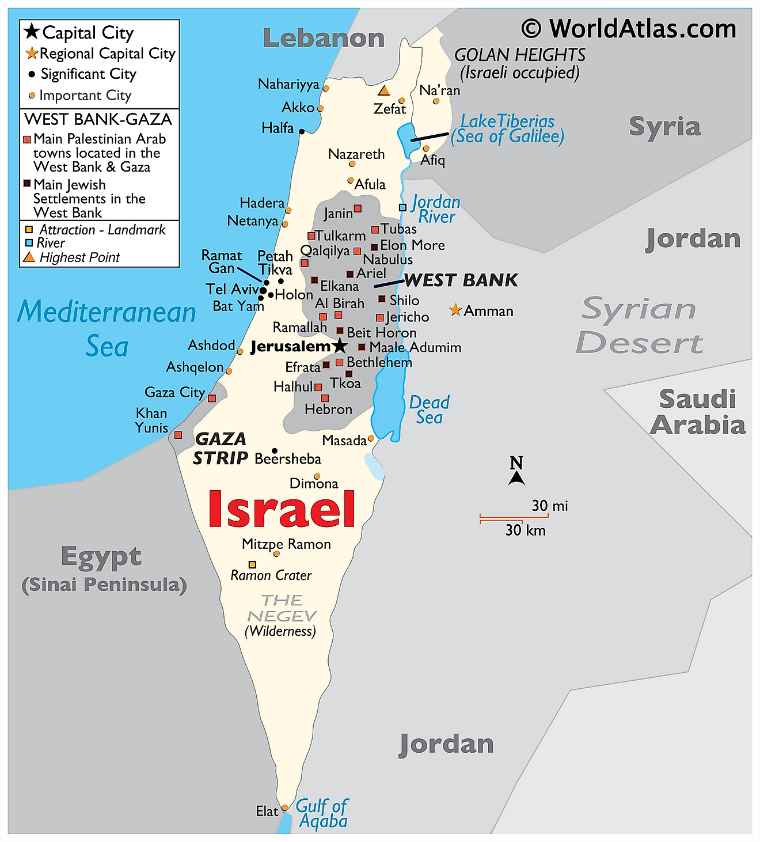
- Israel is bordered by Lebanon in the north, Syria in the northeast, Jordan in the east, Egypt in the southwest; the Palestinian territories (West Bank and Gaza Strip) in the east and west.
Geographical Features
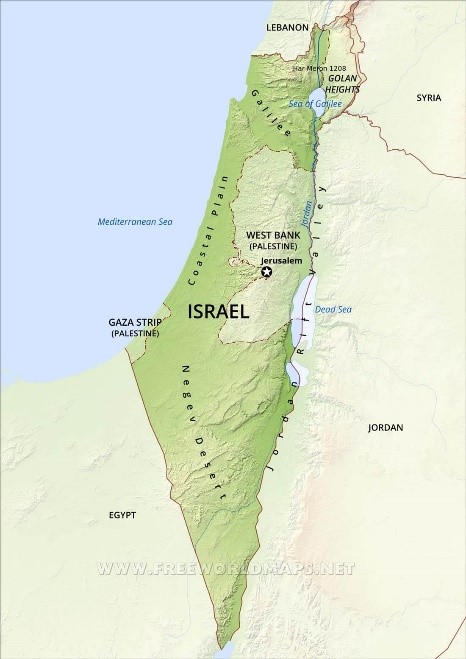
- Israel is home to a variety of geographic features, from the Negev desert in the south to the inland fertile Jezreel Valley, mountain ranges of the Galilee, Carmel and toward the Golan in the north.
- East of the central highlands lies the Jordan Rift Valley, which forms a small part of the 6,500-kilometer Great Rift Valley.
- The Jordan River runs along the Jordan Rift Valley, from Mount Hermon through the Hulah Valley and the Sea of Galilee to the Dead Sea, the lowest point on the surface of the Earth.
- Further south is the Arabah, ending with the Gulf of Eilat, part of the Red Sea. Makhtesh, or "erosion cirques" are unique to the Negev and the Sinai Peninsula.
Ecoregions
- Israel contains four terrestrial ecoregions: Eastern Mediterranean conifer-sclerophyllous-broadleaf forests, Southern Anatolian montane conifer and deciduous forests, Arabian Desert, and Mesopotamian shrub desert.
City and Ports
- Jerusalem is Israel's most important city although most countries have embassies in Tel Aviv-Yafo. Other cities include Haifa and Beer-Sheva.
- Haifa is Israel's main port. Other ports are Ashdod, Ashkelon and Eilat.
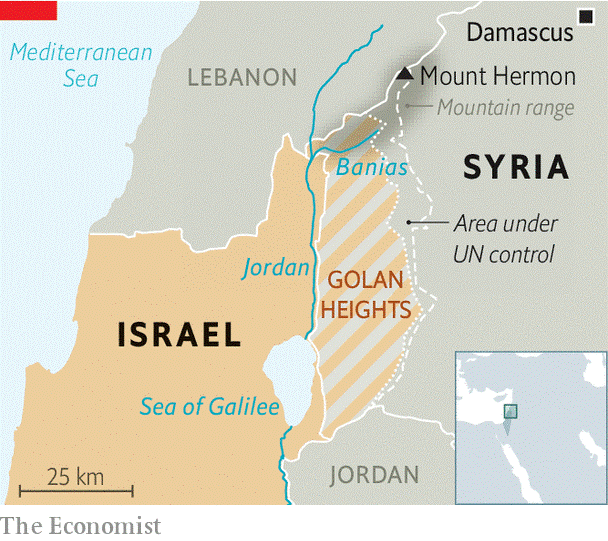
Golan Height:
- It is a basaltic plateau bordered by the Yarmouk River in the south, the Sea of Galilee and Hula Valley in the west.
- It is the area captured from Syria and occupied by Israel during the 1967 Six-Day War, territory which has been administered as part of Israel since 1981.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Consider the following statements.
1. Israel is located in the Levant area of the Fertile Crescent region.
2. Negev desert lies in the north of Israel.
3. Golan Heights is a basaltic plateau bordered by the Yarmouk River in the south.
4. Israel is bordered by Lebanon in the south, Syria in the northeast, and Jordan in the east.
Which of the above statements is/are incorrect?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) None of the above.
Correct Answer: (b) 2 and 4 only
|
.jpg)
https://www.wionews.com/world/israel-passes-controversial-judicial-reform-law-protesters-call-for-mass-rallies-618990

















