




Source: HINDU
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
ISRO has signed an Implementation Agreement (IA) with the Australian Space Agency (ASA) to enhance collaboration for the mission focusing on crew safety and recovery.
Enables cooperation for search and rescue operations and recovery of crew modules in case of contingencies during the ascent phase near Australian waters.
Strengthens space collaboration between India and Australia as strategic partners.
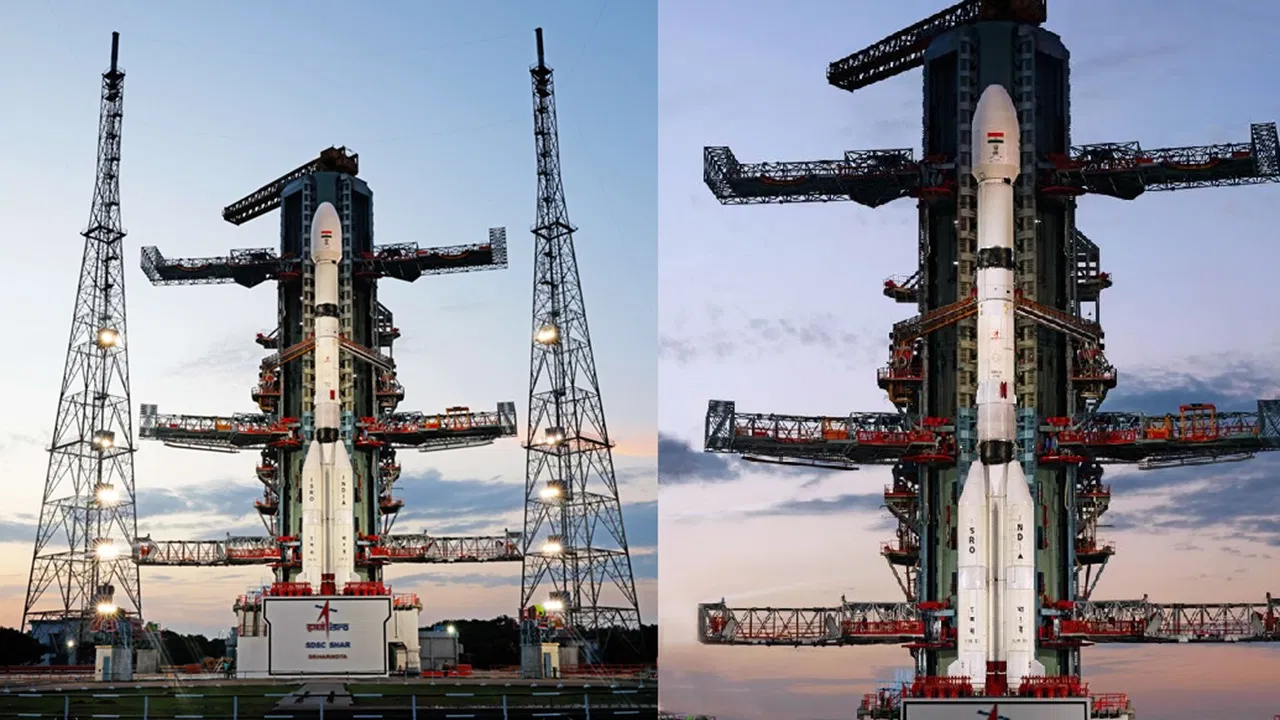
It is an Indian crewed orbital spacecraft intended to be the formative spacecraft of the Indian Human Spaceflight Programme. The spacecraft is being designed to carry three people and a planned upgraded version will be equipped with rendezvous and docking capabilities.
In its maiden crewed mission, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)'s largely autonomous 5.3-metric ton capsule will orbit the Earth at 400 km altitude for up to seven days with a two- or three-person crew on board. The first crewed mission was originally planned to be launched on ISRO's HLVM3 rocket in December 2021.
As of November 2024, it is expected to be launched no earlier than 2026.
Mission Name |
Country |
Year |
Details |
Significance |
|
Vostok 1 |
Soviet Union (USSR) |
1961 |
First human spaceflight; carried Yuri Gagarin into orbit for 108 minutes. |
Made Yuri Gagarin the first human in space, marking the start of human space exploration. |
|
Mercury-Redstone 3 |
USA |
1961 |
First American manned mission; Alan Shepard flew a suborbital flight. |
First American astronaut in space, demonstrating US capability in space travel. |
|
Mercury-Atlas 6 |
USA |
1962 |
John Glenn orbited Earth three times in the Friendship 7 spacecraft. |
First American to orbit Earth, boosting the USA in the space race. |
|
Voskhod 1 |
Soviet Union (USSR) |
1964 |
First multi-person mission; three cosmonauts onboard. |
Demonstrated capability for multiple crew members in a single spacecraft. |
|
Voskhod 2 |
Soviet Union (USSR) |
1965 |
Alexei Leonov conducted the first spacewalk (extravehicular activity). |
Pioneered spacewalking technology, crucial for future missions. |
|
Apollo 11 |
USA |
1969 |
First human Moon landing; Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin walked on the Moon. |
Landmark achievement in space exploration; "One giant leap for mankind." |
|
Skylab Missions |
USA |
1973-1974 |
Series of missions to the first US space station. |
Conducted long-term studies of life in space and Earth's observation. |
|
Soyuz Missions |
Soviet Union/Russia |
1967-Present |
Long-standing series of missions, including trips to space stations and the ISS. |
Backbone of Soviet and Russian human spaceflight programs. |
|
Space Shuttle Program |
USA |
1981-2011 |
Reusable spacecraft missions; carried astronauts and payloads to space, including the ISS. |
Enabled deployment of satellites, ISS construction, and advanced space experiments. |
|
Mir Missions |
Soviet Union/Russia |
1986-2001 |
Manned missions to the Mir Space Station. |
Pioneered long-term human habitation in space. |
|
International Space Station (ISS) |
USA, Russia, and partners |
2000-Present |
Continuous human presence; multinational crew conducting experiments in microgravity. |
Largest international collaboration in space exploration. |
|
Shenzhou 5 |
China |
2003 |
First Chinese manned mission; Yang Liwei spent 21 hours in space. |
Marked China's entry into manned space exploration. |
|
Shenzhou Missions |
China |
2003-Present |
Series of missions, including spacewalks and space station construction. |
Showcased China's growing capability in human space exploration. |
|
SpaceX Crew Dragon |
USA (Private, NASA) |
2020 |
First commercial spacecraft to carry humans (Demo-2 mission). |
Revolutionized commercial space travel; enabled reusable spacecraft. |
|
Artemis II (Planned) |
USA |
2024-2025 |
Upcoming mission to carry humans around the Moon. |
Precursor to Moon landings under the Artemis program. |
Sources:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q.Consider the following statements regarding the Vostok 1 mission:
Options: Answer: B Explanation: Statement 1 is incorrect. Vostok 1 was launched by the Soviet Union not the USA. The mission was part of the USSR's ambitious space program during the Cold War which sought to establish Soviet dominance in space exploration. Statement 2 is correct. Yuri Gagarin from Russia became the first human to travel into outer space on April 12, 1961. This milestone is celebrated annually as Cosmonautics Day in Russia. Statement 3 is correct. The Vostok 1 mission lasted for about 108 minutes during which it completed one full orbit around Earth. This historic flight demonstrated human survival in space and the capability to return safely. |





© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved