Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
The water levels in two important reservoirs.
Details
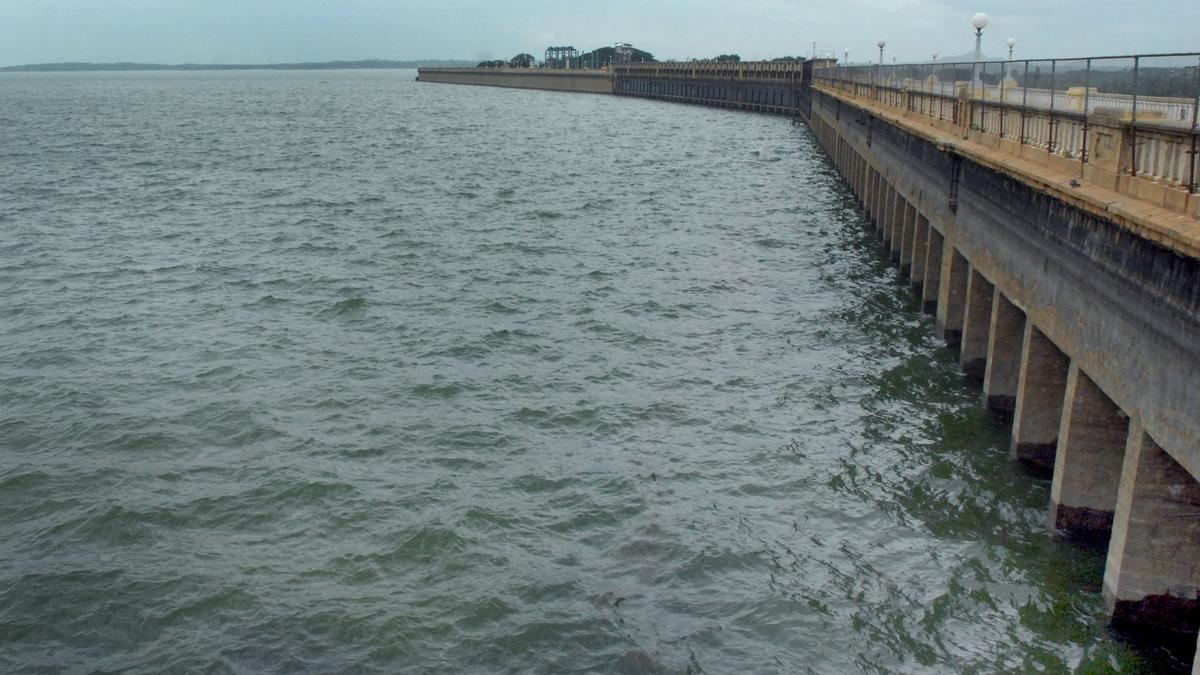
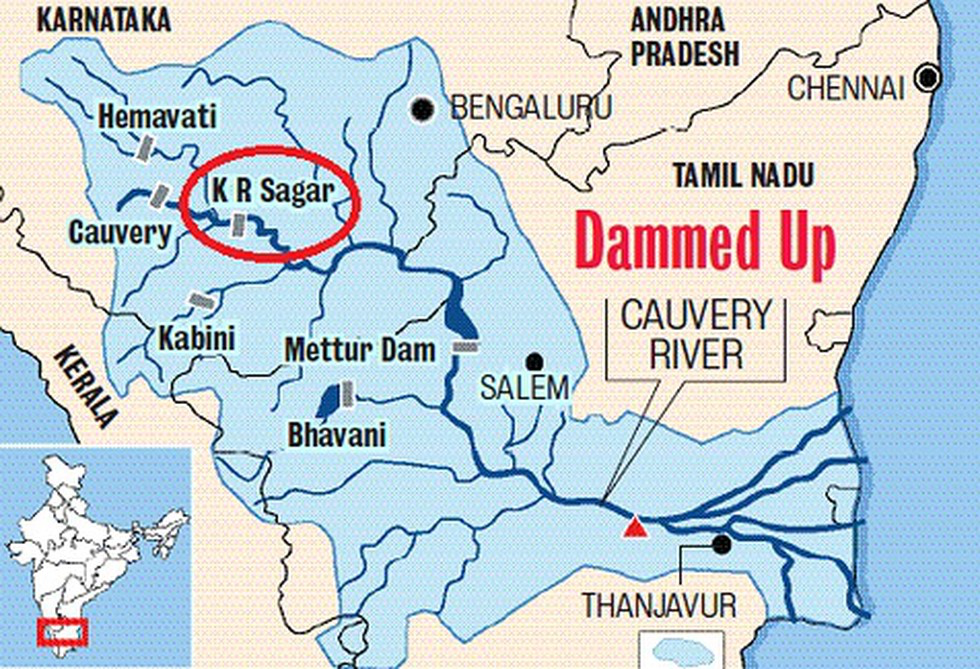
- Krishnaraja Sagar (KRS) water level breaches 100-ft mark and reaches 102.35 ft due to heavy rainfall in the catchment area.
- Increase in inflow and live storage in the dam, but it's still at 46% of the gross capacity.
- Inflow at 48,025 cusecs in the morning, increased to 49,280 cusecs at night.
- Outflow rate at 5,449 cusecs.
- Future trends depend on rainfall in Kodagu and discharge from Harangi reservoir.
Water Level in Kabini Reservoir
- Kabini reservoir in H.D. Kote taluk of Mysuru district nears full reservoir level (FRL).
- Heavy inflow from rain in the catchment area in Wayanad, Kerala, leads to rise in water level.
- Inflow at 25,485 cusecs, water level at 2,281.27 ft on Tuesday.
- Outflow increased from 15,000 cusecs to 20,000 cusecs, with the possibility of Bidarahalli bridge being partially submerged.
- Kabini typically fills up early in the monsoon season, but this year had scanty rain.
About Krishnaraja Sagar
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
- Krishnaraja Sagar is located in the Mandya district of Karnataka, India.
- It is one of the major reservoirs in the Cauvery basin and plays a vital role in managing water resources for various purposes.
Construction and Purpose
- The reservoir was constructed during the early 20th century, between 1911 and 1931.
- The primary purpose of building KRS was to store water from the Cauvery River to support agricultural activities in the surrounding regions.
Capacity and Size
- Krishnaraja Sagar has a significant capacity to store water.
- The reservoir spans an area of several square kilometers and has a considerable storage volume.
Water Supply
- The water stored in KRS is used for irrigation, providing crucial water resources to the agriculturally rich areas in Karnataka.
- The canal system connected to the reservoir distributes water to farmlands, contributing to the region's agricultural prosperity.
Drinking Water Supply
- Apart from irrigation, Krishnaraja Sagar also serves as a major source of drinking water for the nearby cities and towns.
- It plays a crucial role in meeting the water requirements of cities like Mysuru and Bengaluru.
Hydropower Generation
- Krishnaraja Sagar also houses a hydropower plant that generates electricity.
- The flow of water from the reservoir is used to generate hydroelectric power, contributing to the state's energy needs.
Impact of Rainfall
- The water level in Krishnaraja Sagar is heavily influenced by the rainfall in its catchment area.
- During periods of heavy rainfall, the water level rises, replenishing the reservoir and ensuring adequate water supply for various purposes.
Management and Conservation
- The management of Krishnaraja Sagar is overseen by the Karnataka government and the irrigation department.
- Conservation efforts are undertaken to ensure sustainable water use and to mitigate the impact of droughts.
Role in Regional Economy
- Krishnaraja Sagar's water resources have a significant impact on the regional economy, contributing to agricultural growth and overall development.
Tourist Attraction
- Besides its functional importance, Krishnaraja Sagar is also a popular tourist attraction.
- The picturesque surroundings and the architectural beauty of the dam attract visitors from different parts of the state and beyond.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q) Examine the challenges faced in effective management of Krishnaraja Sagar and the steps taken for sustainable water use. Also, analyze its impact on the regional economy and its potential as a model for water resource management in other parts of India. (250 words)
|

https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/karnataka/krs-breaches-100-ft-mark-thanks-to-copious-rain-in-kodagu/article67119623.ece












