





Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/sc-halts-90-acre-project-in-kumaon-himalayas-on-a-plea-challenging-single-window-clearances/article68201001.ece
Context: The Supreme Court of India has temporarily halted the construction of a 90-acre hotel and township project in the Kumaon hills of Uttarakhand.
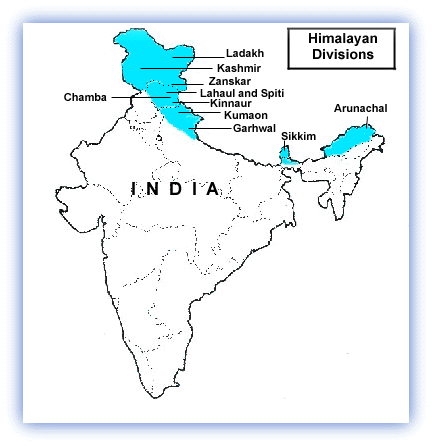
About Kumaon Hills
|
History of Kumaon Region |
●Ancient Rulers: The region was initially inhabited by Kol tribals, followed by waves of migrations by groups such as Kiratas and Khasas. The Katyuri dynasty, of Khasha origin, established the Kurmanchal kingdom, extending its influence from Sikkim to Kabul. ●Chand Dynasty: The Chand dynasty, established in the 10th century, displaced the Katyuri kings and ruled over Kumaon. They established their capital in Champawat and made significant contributions to the region's cultural and architectural heritage. ●British Era: Following the Anglo-Nepalese War and the Treaty of Sugauli in 1816, Kumaon became a British territory. The British administration introduced administrative reforms, infrastructure development, and established hill stations like Nainital. |
|
Culture of Kumaon Region |
●Women adorn Pichaura, a traditional attire, often worn during religious ceremonies and festivals. Men wear the Kumaoni cap, reflecting the region's cultural identity. ●Aipan, an intricate form of art, is practised in Kumaon. It involves creating geometric patterns using rice flour and has cultural significance on auspicious occasions. |
|
Economy of Kumaon Region |
●The region is known for cultivating crops such as Basmati rice, wheat, and fruits. Tea cultivation in areas like Berinag and Chyura oil production contributes to the agricultural economy. ●Kumaon's picturesque landscapes, including lakes, national parks, and hill stations, attract tourists from around the world. The tourism sector generates revenue and employment opportunities for the local population. ●Haldwani and Rudrapur serve as economic hubs, driving commercial and industrial activities. Rudrapur, in particular, has witnessed industrial growth, supported by infrastructure development and connectivity. |
Source:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Consider the following statements: 1. The Kumaon Himalayas are primarily formed by the collision of the Indian Plate with the Eurasian Plate. 2. Nanda Devi is the highest peak entirely within the Kumaon Himalayas. Select the correct answer using the codes given below: A) 1 only B) 2 only C) Both 1 and 2 D) None Answer: C |






© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved