Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
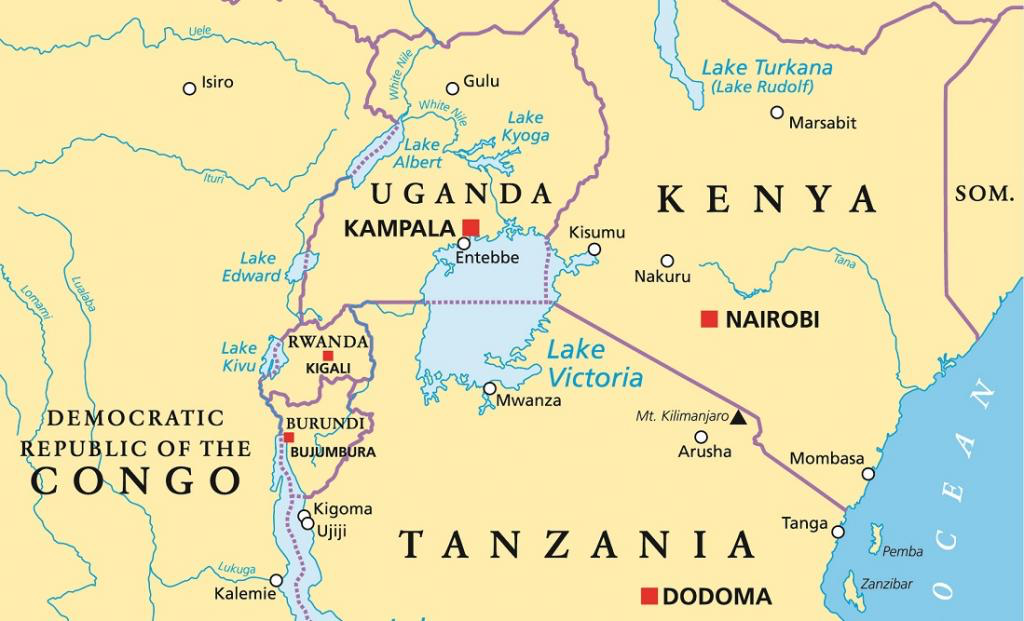
Context: The impact of climate change on the Lake Victoria Basin (LVB) in East Africa.
Details
- Heavy rains, wind storms, and floods pose a threat to the survival and water access of LVB communities.
- Extreme weather events, such as regular flooding, strongly affect the 40 million inhabitants of the LVB.
- Unprecedented high water levels in Lake Victoria in late 2019 and early 2020 resulted in massive flooding and displacement of over 200,000 people in Kenya, Uganda, and Tanzania.
Pressure on Lake Victoria and Surrounding Areas
- Lake Victoria and its wetlands and forests face extreme pressure and degradation.
- Rapid population growth, agricultural expansion, urbanization, and industrialization contribute to the degradation of the region.
- The modified equatorial climate of the LVB, characterized by warm and humid conditions, exacerbates the pressure on the ecosystem.
Role of Regional Rainfall
- Recharge into Lake Victoria mainly comes from regional rainfall, as the lake is fed by 23 rivers.
- The largest river, Kagera, runs through Rwanda and Burundi before emptying into the lake.
- Regional rainfall plays a crucial role in regulating the water levels in Lake Victoria.
Findings from the Scientific Report
- The scientific report titled "Extreme climatic events to intensify over the Lake Victoria Basin under global warming" analyzes future precipitation patterns in the LVB.
- Mean annual and seasonal precipitation values were computed, focusing on the periods of March-May, June-August, and October-December.
- Significant precipitation changes are expected at the sub-seasonal scale rather than seasonal and annual scales.
- There is an overall increase in mean daily precipitation intensity for all seasons, with greater changes projected for the end of the century (potential increase by 16%) compared to the middle of the century (potential increase by six percent).
- By the 2050s, precipitation over the study domain is estimated to increase by about five percent for mean annual and seasonal values compared to the baseline period of 1985-2014.
Implications for the Region
- The projected changes in precipitation will have significant impacts on the LVB, which already experiences water and water resource conflicts.
- The study recommends the use of climate services to minimize the risks associated with the projected changes and enhance the socio-economic well-being of LVB communities.
- The report also highlights the high impacts of climate change on the fish and biodiversity of the LVB.
- The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) warns that 76 percent of the lake's endemic biodiversity faces the threat of extinction.
- Adequate monitoring and conservation actions are necessary to minimize the impacts of climate change on the biodiversity of Lake Victoria.
- Limited understanding and climate models pose a challenge in accurately explaining weather and climate dynamics in the LVB.

About Lake Victoria Basin
- The Lake Victoria Basin is situated in East Africa, shared by five countries: Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Burundi, and Rwanda.
- It covers an extensive area of approximately 250,000 square kilometers.
- It is the largest lake in Africa and the world's second-largest freshwater lake, providing a crucial water source for the region.
- The basin consists of rich wetland areas and forests, which contribute to its ecological diversity and provide numerous ecosystem services.
Human Population and Socio-economic Importance
- The Lake Victoria Basin is home to approximately 40 million people, making it densely populated.
- The basin supports a vibrant fishing industry and is renowned for its abundant fish stocks, providing a critical source of livelihood and food security for local communities.
- The fertile lands surrounding the lake support extensive agricultural activities, including crop cultivation and livestock farming, contributing to the region's economy.
- Lake Victoria serves as a crucial water resource for domestic, industrial, and agricultural purposes, playing a vital role in the region's socio-economic development.
Climate and Extreme Weather Events
- The Lake Victoria Basin experiences a modified equatorial climate characterized by warm and humid conditions.
- The region receives long rains from March to May and short rains from October to December, which contribute to the water levels of Lake Victoria and surrounding rivers.
- The basin is prone to heavy rains, windstorms, and floods, leading to challenges for communities living in the area, including displacement, infrastructure damage, and loss of livelihoods.
Environmental Challenges and Pressures
- Rapid population growth in the basin has exerted pressure on natural resources, leading to deforestation, land degradation, and increased demand for water and energy.
- The expansion of agriculture, including both subsistence and commercial farming, has contributed to the loss of natural habitats and increased water pollution from agrochemicals.
- Urbanization and industrial activities have resulted in pollution, waste generation, and encroachment on sensitive ecosystems, impacting the overall environmental health of the basin.
Climate Change and Biodiversity Threats
- Scientific reports indicate significant changes in precipitation patterns and an increase in extreme climate events, posing risks to the communities and biodiversity of the Lake Victoria Basin.
- The basin harbors rich biodiversity, including numerous endemic species. However, habitat degradation, pollution, and climate change pose significant threats to the survival of many species, with some facing the risk of extinction.
Conservation and Sustainable Management
- There is a need for adequate monitoring and conservation actions to mitigate the impacts of climate change, protect biodiversity, and restore degraded ecosystems in the Lake Victoria Basin.
- The utilization of climate services can help in minimizing risks posed by projected climate changes, assisting communities in adapting to the changing conditions and enhancing their socio-economic well-being.
- Addressing the environmental challenges in the basin requires collaboration between governments, local communities, and international organizations to implement sustainable management practices, promote conservation, and ensure the equitable use of resources.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q) Which of the following statements accurately describe the Lake Victoria Basin?
1) The Lake Victoria Basin is the largest freshwater lake in the world.
2) The Lake Victoria Basin is located in East Africa.
3) The Lake Victoria Basin is primarily inhabited by the Maasai tribe.
4) The Lake Victoria Basin is shared by five countries.
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 2 and 4 only
Ans: D
|
https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/africa/more-robust-measures-needed-to-minimise-disaster-impact-in-lake-victoria-basin-study-90136
















