Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended
Context
- Geological Survey of India (GSI), Ministry of Mines in collaboration with the British Geological Survey (BGS) under the National Environmental Research Council (NERC), UK funded, multi-consortium LANDSLIP project has developed a prototype regional Landslide Early Warning System (LEWS) for India, and the same is currently being evaluated and tested by GSI in two pilot areas in India(Darjeeling district. West Bengal, and the Nilgiris district, Tamil Nadu)
About
- GSI through the LANDSLIP project is engaged in developing an experimental regional Landslide Early Warning System (LEWS) based on rainfall thresholds since 2017.
- The LANDSLIP research has developed a prototype model in 2020 based on the terrain-specific rainfall thresholds for two test areas (Darjeeling district, West Bengal, and the Nilgiris district, Tamil Nadu)
Landslide
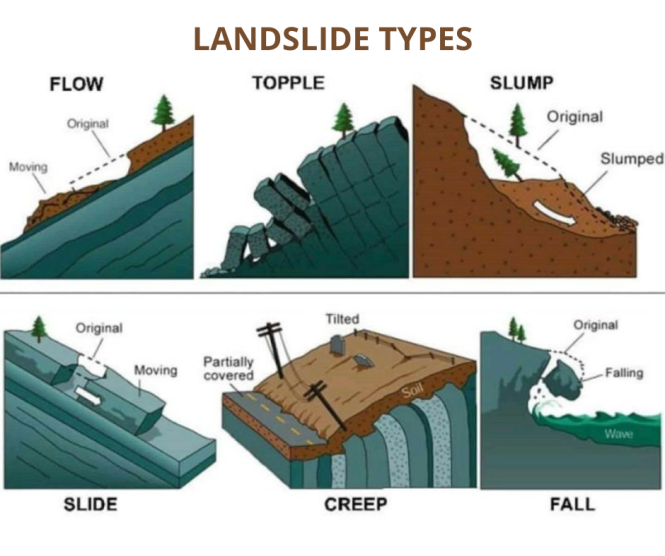
- Landslides, also known as landslips, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, deep-seated slope failures, mudflows, and debris flows.
- Gravity is the primary driving force for a landslide to occur, but there are other factors affecting slope stability that produce specific conditions that make a slope prone to failure.
- In many cases, the landslide is triggered by a specific event (such as a heavy rainfall, an earthquake, a slope cut to build a road, and many others), although this is not always identifiable.
Natural Causes of Landslides
- Climate: A significant upsurge in precipitation or ground saturation would dramatically increase the level of ground water. When sloped areas are completely saturated with water, landslides can occur.
- Earthquakes
- Weathering
- Erosion
- Volcanoes
- Forest fires
- Gravity
- Human causes of landslides
- Mining
- Clear cutting: Clear cutting is a technique of timber harvesting that eliminates all old trees from the area. This technique is dangerous since it decimates the existing mechanical root structure of the area.
Effects of Landslides
- Lead to economic decline
- Decimation of infrastructure
- Loss of life
- Affects beauty of landscapes
- Impacts river ecosystems
Indian examples of devastating landslides
- In past years, there have been some serious and fatal landslides in India. Here is a list of worst landslides :
- 1948 Guwahati landslide, Assam
- 1938 Darjeeling landslide, West Bengal
- 2000 Mumbai landslide, Maharashtra
- 2013 Kedarnath landslide, Uttarakhand
Landslide mitigation
There are a wide range of technologies available for landslide mitigation. These include:
- equipments for emergency response,
- geological reconnaissance of landslide-prone areas,
- local monitoring services,
- site investigation with borings and test pits,
- slope stability analyses,
- seismic analysis of slopes,
- technical assistance in construction of buildings, roads, pipes, etc,
- design assistance for drainage systems, and erosion modelling (Landslide Technology, 2017).
- India’s National Disaster Management Agency (NDMA) has a focus on site-specific landslide mitigation that involves making geological investigations on selected sites (NDMA, 2015).
- Its approach is based on co-operation with various government agencies such as the Geological Survey of India to designate certain areas as landslide-prone areas.
- India has not as yet witnessed a comprehensive hands-on technological approach to landslide mitigation.
- However, technology for this is available, and the problem is a matter of managing costs with the possibility of a high failure rate.
- On the other side however, a few timely evacuations might open a new vista for the NDMA in terms of disaster preparedness.
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1777174














.jpg)