Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
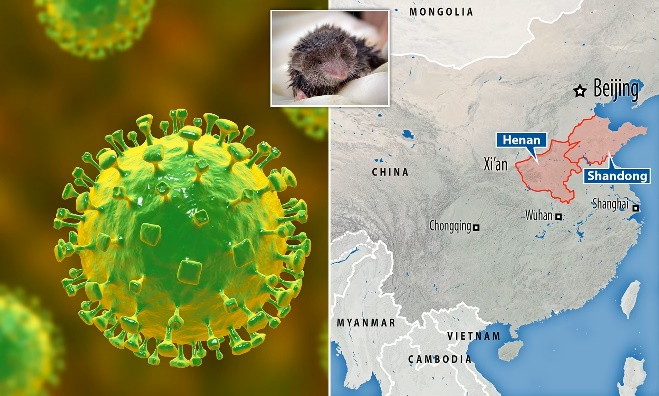
- A new virus that can jump from animals to humans has been detected in China with 35 people already infected. It has been called Langya henipavirus (LayV) - and has been found across two provinces in eastern China.
What is Langya Virus?
- LayV is an example of a Zoonotic Henipavirus. The virus is in the Henipavirus family. Two species have been identified before; the Hendra virus - first detected in the Brisbane suburb of the same name - and Nipah virus, both cause severe infections and are sometimes fatal.
- The World Health Organisation classifies Henipavirus as a biosafety Level 4 threat. Case fatality rates range between 40 and 75 per cent, data suggests.
What makes a virus zoonotic?
- A zoonotic disease is defined as an infectious disease transmitted between species; either from animals to humans, or from humans to animals.
- Examples of zoonotic viruses include, COVID-19, monkeypox and Hendra virus (HeV).
What is the origin of the Langya Virus?
Test results from more than two dozen wild animals suggests the shrew - a small mole-like mammals - might be a natural reservoir of LayV.
Existing patients had a history of contact with animals.

What are the symptoms of Langya Virus?
- Symptoms of LayV include: fever, fatigue, a cough, loss of appetite, muscle pain, nausea, headache and vomiting.
Has Langya Virus been detected outside of China?
- No cases outside of China have been reported. The study also said human-to-human transmission of LayV has not been observed.
https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/health/novel-langya-henipavirus-infection-may-have-spread-through-rodent-like-mammals-84237
















