Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
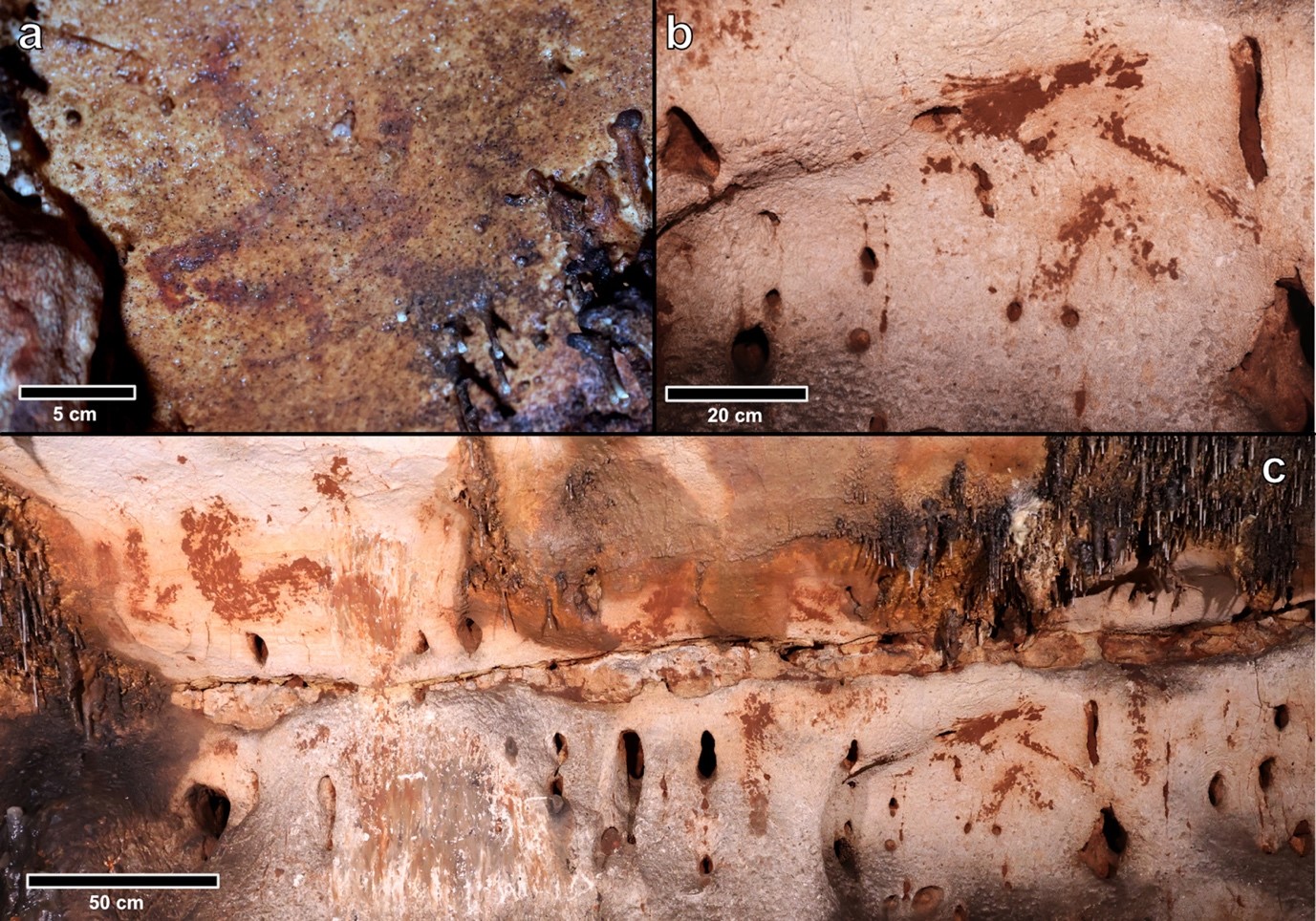
- Archaeologists have made a remarkable discovery at the Cova Dones site on the eastern Iberian Coast in Spain, unearthing more than 100 Paleolithic cave paintings and engravings that date back over 24,000 years.
- This cave, stretching approximately 1,640 feet, has the potential to be the most significant site of its kind in the region.
- Despite being a well-known spot among hikers and locals, the Paleolithic markings remained hidden until their recent revelation by a team of researchers from Spanish and UK universities.
Details
The Cova Dones Cave
- Location and Discovery: The Cova Dones cave, situated on the eastern Iberian Coast, has been a popular destination for hikers and locals. However, it wasn't until June 2021 that archaeologists from Spain's Zaragoza and Alicante universities, in collaboration with the University of Southampton in the UK, stumbled upon the ancient art. Their findings were published in the journal Antiquity recently.
- Vastness and Significance: The cave, measuring around 1,640 feet in length, surprised researchers with its size and complexity. It has now revealed over 100 distinct designs created through various techniques. This discovery positions Cova Dones as one of the most significant Paleolithic cave art sites in the region, rivaling the Atxurra site discovered in northern Spain in 2015.
- Artistic Representation: The newfound paintings depict a range of animals, including hinds, horses, aurochs, and deer. What sets Cova Dones apart from other caves is the prevalent use of clay in the creation of these artistic expressions, a feature that is relatively rare in such ancient art.
Significance of the Discovery
- Spain boasts the largest number of Paleolithic cave art sites, but few have been documented in eastern Iberia.
- The discovery of more than 100 intricate Paleolithic designs at Cova Dones signifies its unique historical and cultural importance in the region.
- These findings shed light on the artistic prowess and cultural significance of early human populations in the area over 24,000 years ago.

About Paleolithic Period
- The Paleolithic Period, often referred to as the Old Stone Age, stands as a defining epoch in human history.
- Spanning nearly 2.5 million years, this era was marked by significant milestones in the development of human society, culture, and technology.
Paleolithic Timeline:
- The Paleolithic Period is typically divided into three phases: the Lower Paleolithic, Middle Paleolithic, and Upper Paleolithic.
- Lower Paleolithic (2.5 million - 200,000 years ago): Characterized by the emergence of early hominins, the use of simple tools, and the mastery of fire.
- Middle Paleolithic (200,000 - 40,000 years ago): Notable for the development of more sophisticated tools, including the handaxe, and the appearance of Homo sapiens.
- Upper Paleolithic (40,000 - 10,000 years ago): Witnessed remarkable advancements in art, technology, and social organization.
Hominin Evolution:
- The Paleolithic Period saw the evolution of various hominin species, including Homo habilis, Homo erectus, and Homo sapiens.
- Homo habilis, known as "handy man," was among the first toolmakers.
- Homo erectus, characterized by its tall stature and use of fire, spread beyond Africa.
- Homo sapiens, anatomically similar to modern humans, emerged around 300,000 years ago.
Cultural Achievements:
- Toolmaking: The Paleolithic period witnessed a significant shift from unmodified stones to crafted tools, including handaxes, spears, and blades.
- Fire Control: The controlled use of fire for warmth, cooking, and protection was a hallmark of Paleolithic societies.
- Art and Symbolism: The Upper Paleolithic period is famous for intricate cave paintings, sculptures, and symbolic artifacts, revealing the emergence of complex symbolic thinking.
- Social Organization: Early humans lived in small groups, engaging in hunting and gathering activities. Social structures became more complex over time.
Subsistence Strategies:
- Hunter-Gatherer Lifestyle: Paleolithic communities primarily relied on hunting game and gathering wild plants for sustenance.
- Adaptation to Environments: Different regions led to diverse subsistence strategies, such as coastal foraging, megafauna hunting, and plant domestication.

Conclusion
The discovery of over 100 Paleolithic cave paintings and engravings at the Cova Dones site in eastern Iberia is a testament to the rich cultural heritage of the region. These ancient artworks, dating back over 24,000 years, provide a glimpse into the artistic and cultural achievements of early human populations and establish Cova Dones as a remarkable site of historical and archaeological significance in Spain.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Examine the significance of the Paleolithic Period in shaping human evolution and the development of early human societies. Discuss the key cultural achievements, subsistence strategies, and the impact of this epoch on our understanding of human history. (150 Words)
|















