Description
Context: LiDAR (Aerial Ground) Survey for Delhi - Varanasi High Speed Rail Corridor begins
- High Speed Rail work gathers momentum. With the start of LiDAR (Aerial Ground) Survey.
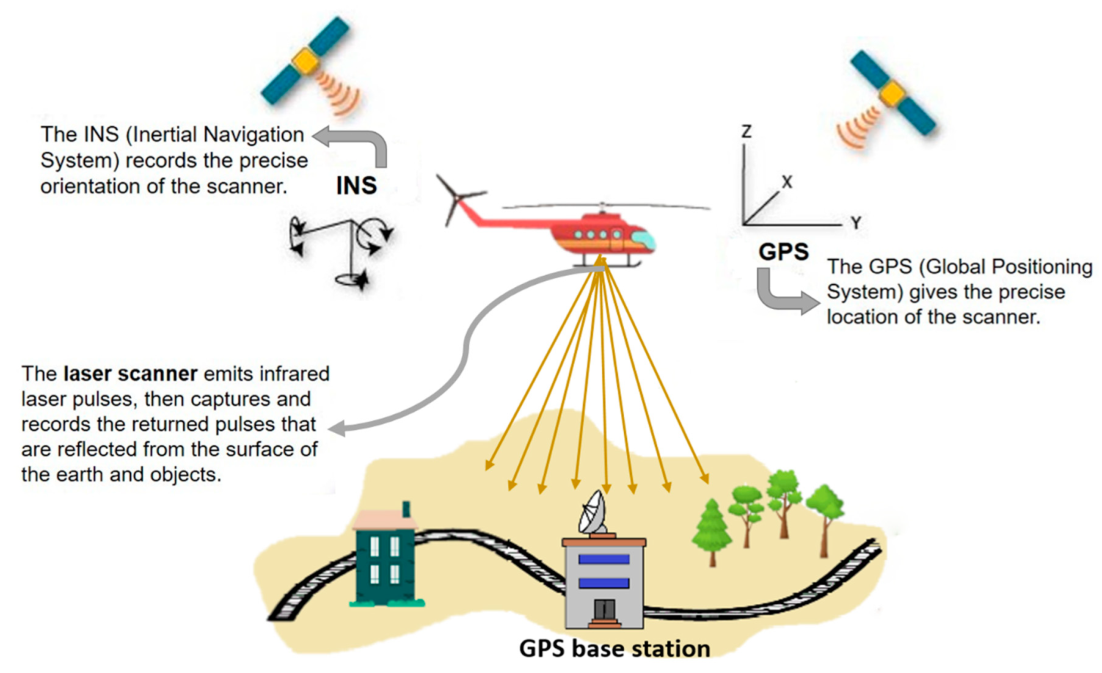
- The ground survey is a crucial activity for any linear infrastructure project as the survey provides accurate details of areas around the alignment.
- This technique uses a combination of Laser data, GPS data, flight parameters and actual photographs to give accurate survey data.
Light Detection and Ranging Survey (LiDAR) technology
- Lidar is a method for measuring distances (ranging) by illuminating the target with laser light and measuring the reflection with a sensor.
- Differences in laser return times and wavelengths can then be used to make digital 3-D representations of the target.
- It has terrestrial, airborne, and mobile applications.
- Lidar sometimes is called 3-D laser scanning, a special combination of a 3-D scanning and laser scanning.
- Lidar is commonly used to make high-resolution maps, with applications in surveying, geodesy, geomatics, archaeology, geography, geology, geomorphology, seismology, forestry, atmospheric physics,[6] laser guidance, airborne laser swath mapping (ALSM), and laser altimetry.
- The technology is also used in control and navigation for some autonomous cars.
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1687515















