




Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context:
About:
History:
Production:
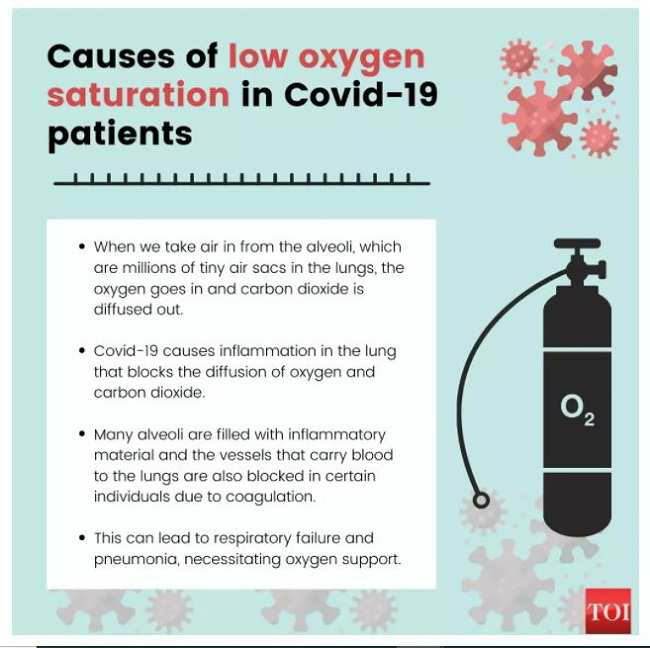
Liquid Oxygen and COVID


https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1716197









© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved