Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The discovery of 50,000-year-old magnetic fossils in the Bay of Bengal by scientists from the CSIR-National Institute of Oceanography in Goa provides valuable insights into the Earth's past environments and the behavior of magnetotactic bacteria.
Details
Magnetofossils and Magnetotactic Bacteria
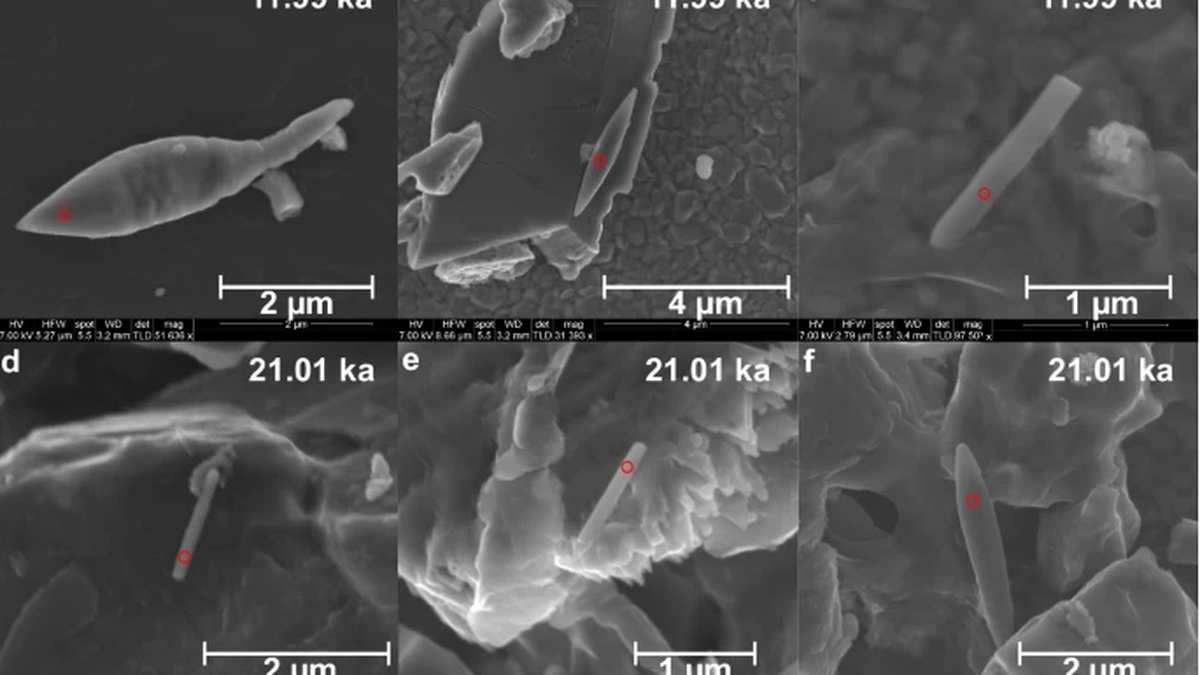
- Magnetofossils are fossilized remains of magnetic particles created by magnetotactic bacteria.
- Magnetotactic bacteria are prokaryotic organisms that align themselves along the Earth's magnetic field using tiny crystals made of iron-rich minerals like magnetite or greigite.
Discovery in the Bay of Bengal
- The sediment core sample extracted from the southwestern Bay of Bengal contained a 50,000-year-old giant magnetofossil, making it one of the youngest to be found.
- This discovery challenges previous notions that giant magnetofossils primarily originated during periods of extreme warming, as this specimen dates to the late Quaternary period.
- The low oxygen concentration in the Bay of Bengal at depths of around 1,000-1,500 m provided a suitable environment for the growth of magnetotactic bacteria.
- Nutrient-rich sediment carried by rivers like the Godavari, Mahanadi, Ganga-Brahmaputra, Cauvery, and Penner supplied reactive iron, which combined with organic carbon to support bacterial growth.
- Fluctuations in monsoon intensity over geological periods influenced sedimentation and weathering, affecting the formation of magnetofossils.

About Magneto fossils
- Magneto fossils, also known as magnetic fossils or biogenic magnetite, are a fascinating aspect of paleontology and geology.
- They provide valuable insights into the Earth's ancient environments, the behavior of ancient organisms, and even the Earth's magnetic field.
Definition and Nature:
- Magneto fossils are remnants of biological materials that contain magnetic minerals, particularly magnetite (Fe3O4) or greigite (Fe3S4).
- These magnetic minerals can preserve the orientation and intensity of the Earth's magnetic field at the time of their formation.
Types of Magneto Fossils:
- Bacterial Magnetite: Some bacteria are capable of producing magnetite within their cells, forming chains of magnetosomes, which act as tiny compass needles.
- Magnetic Crystals in Organisms: Certain organisms, such as some species of mollusks, fish, and even birds, can biomineralize magnetite or greigite within their tissues.
Formation and Preservation:
- Magneto fossils are typically formed through biomineralization processes, where organisms precipitate magnetic minerals either inside their bodies or in their surrounding environment.
- Preservation occurs when these minerals are buried in sediments, protecting them from oxidation and alteration.
Significance:
- Paleomagnetism: Magneto fossils provide a means of reconstructing the Earth's past magnetic field. By studying the orientation and intensity of magnetic minerals in fossils, scientists can infer the ancient orientation of the Earth's magnetic field.
- Paleoenvironmental Reconstruction: The presence of magneto fossils in sedimentary rocks can provide clues about ancient environments, such as the presence of oxygen, temperature, and even the presence of specific organisms.
- Biological Behavior: Studying magneto fossils can offer insights into the behavior and ecology of ancient organisms. For example, the presence of magnetite in certain organisms may indicate their ability to navigate using the Earth's magnetic field.

Methods of Study:
- Rock Magnetism: Techniques such as rock magnetism, which involves measuring the magnetic properties of rocks and fossils, are used to study magneto fossils.
- Paleomagnetic Analysis: Paleomagnetic studies involve measuring the orientation and intensity of magnetization in rocks and fossils to reconstruct the Earth's past magnetic field.
- Microscopy and Imaging: High-resolution microscopy and imaging techniques allow scientists to examine the structure and distribution of magnetic minerals within fossils at the microscopic level.
Conclusion
Magneto fossils represent a unique intersection of biology, geology, and paleomagnetism. They offer valuable insights into Earth's ancient environments, the behavior of ancient organisms, and the evolution of the Earth's magnetic field.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Understanding the distribution and formation of magnetofossils contributes to paleoenvironmental reconstructions and studies of Earth's magnetic history. Discuss. (250 Words)
|
















