Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Thousands of people were marooned across Odisha as the Mahanadi river basin flooded after six days of relentless rain in the catchment areas of Chhattisgarh, besides high water inflow in the Hirakud reservoir.
Course
- The origin of the Mahanadi occurs in the state of Chhattisgarh in the highland region. It flow a total of 860 km by distance before it ends up in the Bay of Bengal. The other states that the river traverses through are Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand. A considerable part of the peninsula is drained by this river. The Gandhi minar has been constructed on one side of the Hirakud dam which stands on one side of the Mahanadi River. Other side has the Ashok minar.
- Near Boudh a township, the river changes course where it flows south rather than south east. A few kilometers on, the river changes direction eastward till it reaches Tikarpara this lies in the Barmul canyon. The river flows though wooded areas from here and forms a gorge that is 22 km long. The height at which the river flows in this region is between 475 to 915 meter. Together with the Brahmani River the Mahanadi forma a very large delta between which the city of Cuttack exists.
- Mangroves and rice cultivation that takes place in this delta region produces quite a large quantum of yield.
Physiography
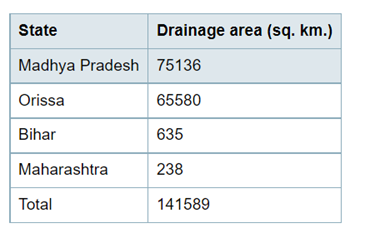
- Mahanadi basin extends over an area of 141,589 sq. km. which is nearly 4.3% of the total geographical area of the country.
- It is bounded on the north by the Central India Hills, on the south and east by the Eastern Ghats and on the west by the Maikala range.
- The basin lies in the States of Madhya Pradesh, Orissa, Bihar and Maharashtra. The State-wise distribution of drainage area is given below:
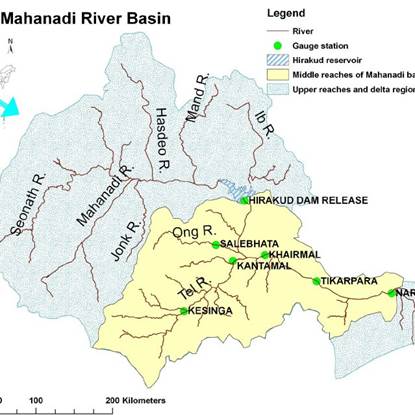
- Physiographically, the basin can be divided into four regions, namely, the Northen Plateau, the Eastern Ghats, the Coastal Plain and the erosional plains of Central Table Land. The first two are hilly regions. The Coastal plain is the fertile delta area.
- The cenral table land is the central inerior region of the basin, traversed by the river and its tributaries.
- The main soil types found in the basin are red and yellow soils, mixed red and black soils, laterite soils,and deltaic soils.

Major Projects
- Hirakud Dam, Ravishankar Sagar, Dudhawa Reservoir, Sondur Reservoir, Hasdeo Bango and Tandula.
Tributaries
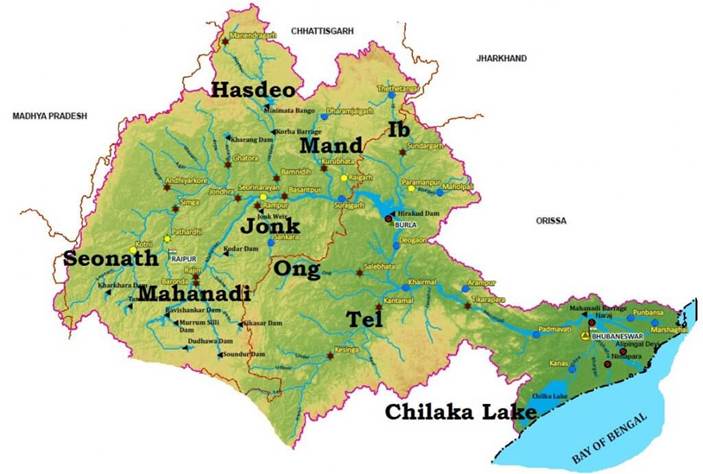
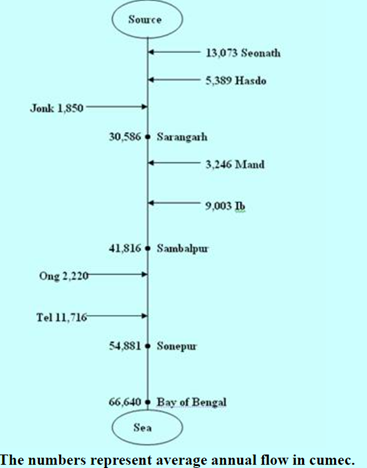
- Its main tributaries are the Seonath, the Jonk, the Hasdeo, the Mand, the ib, the Ong and the Tel.
Urban Centres and Industries
- Three important urban centes in the basin are Raipur, Durg and Cuttack.
- Mahanadi basin, because of its rich mineral resource and adequate power resource, has a favourable industrial climate.
- The Important industries presently existing in the basin are the Iron and Steel plant at Bhilai, aluminium factories at Hirakud and Korba, paper mill near Cuttack and cement factory at Sundargarh.
- Other industries based primarily on agricultural produce are sugar, textile and okl mills. Mining of coal, iron and manganese are other industrial activities.
- The various banks it touches are Raipur, Betul, Bilaspur, Janjgi, Subarnapur, Sambalpur, Anugul, Boudh, Kendrapada, Cuttack, Sonepur, Sambalpur, Subalaya, Birmaharajpur, Boudh.
https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/natural-disasters/thousands-marooned-in-odisha-as-mahanadi-basin-floods-due-to-heavy-rain-84341



















