





Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
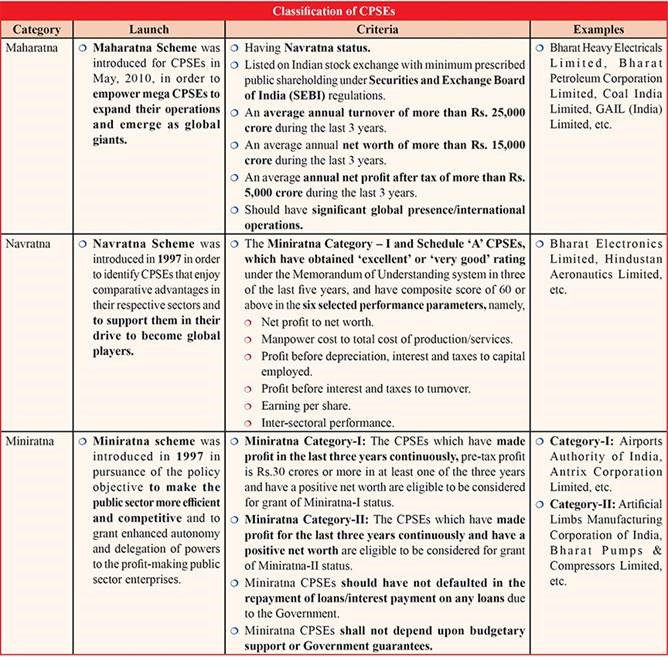
Maharatna, Navratna, and Miniratna
In a nutshell,
Eligibility Criteria for Grant of Maharatna, Navratna and Miniratna Status to CPSEs
The eligibility criteria laid down by the Government for grant of Maharatna, Navratna and Miniratna status to Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs) are following:
Criteria for grant of Maharatna status :-
The CPSEs fulfilling the following criteria are eligible to be considered for grant of Maharatna status.
(i) Having Navratna status.
(ii) Listed on Indian stock exchange with minimum prescribed public shareholding under SEBI regulations.
(iii) Average annual turnover of more than Rs. 25,000 crore, during the last 3 years.
(iv) Average annual net worth of more than Rs. 15,000 crore, during the last 3 years.
(v) Average annual net profit after tax of more than Rs. 5,000 crore, during the last 3 years.
(vi) Should have significant global presence/international operations.
Criteria for grant of Navratna status :-
The Miniratna Category – I and Schedule ‘A’ CPSEs, which have obtained ‘excellent’ or ‘very good’ rating under the Memorandum of Understanding system in three of the last five years, and have composite score of 60 or above in the six selected performance parameters, namely,
(i) net profit to net worth,
(ii) manpower cost to total cost of production/services,
(iii) profit before depreciation, interest and taxes to capital employed,
(iv) profit before interest and taxes to turnover,
(v) earning per share and
(vi) inter-sectoral performance.
Criteria for grant of Miniratna status :-
The CPSEs which have made profits in the last three years continuously and have positive net worth are eligible to be considered for grant of Miniratna status.
MUST READ ARTICLE: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/role-of-public-sector-undertakings
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Discuss the role of Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs) in India's economic development and the challenges they face in the contemporary context. |











© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved