





Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: bnn.network
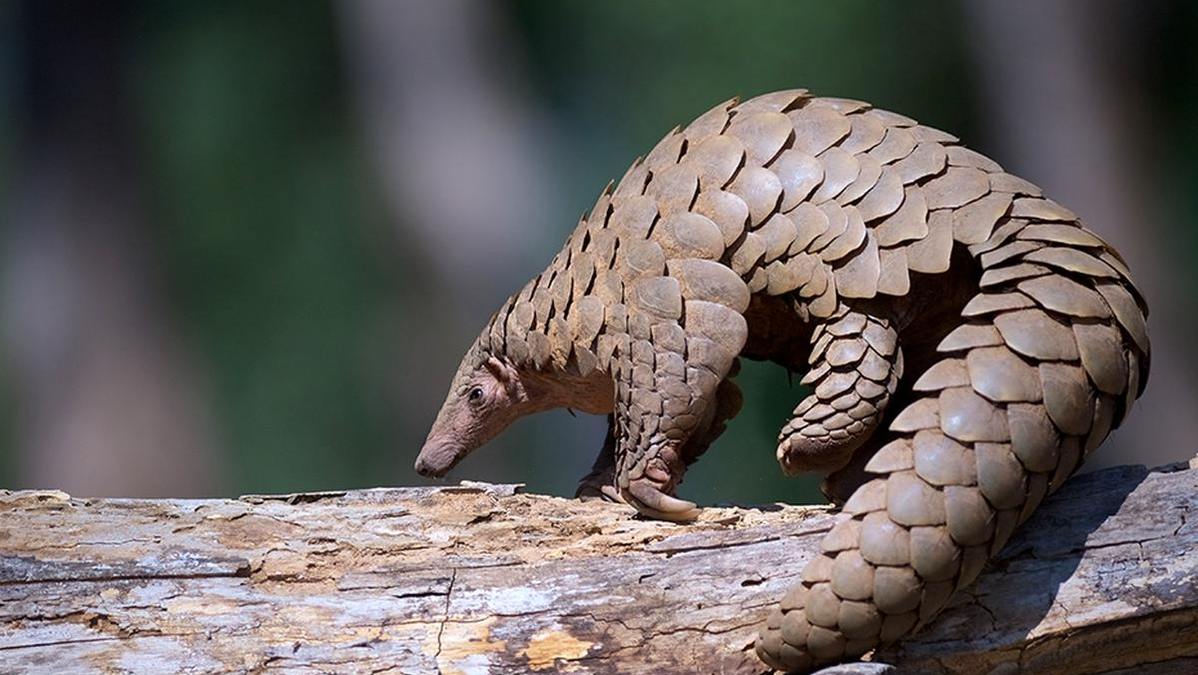
Context: The discovery of a new pangolin species, Manis mysteria, brings both hope and urgency to the forefront of conservation efforts.
Key Highlights about Pangolins
|
Key Description |
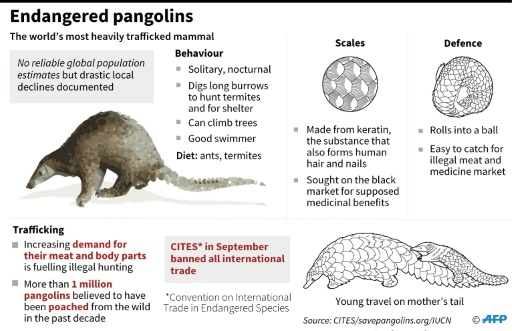
●Pangolins are unique mammals covered in tough, overlapping scales made of keratin. These scales are their most distinctive feature, providing protection against predators. ●They vary in size; some are as small as a house cat, while others can be as long as 3.5 feet. Pangolins have small heads, long tongues, and powerful claws, which they use for digging into termite mounds and ant nests. ●Pangolins are found in parts of Africa and Asia, primarily in forests and grasslands. They are highly elusive, making them challenging to study in the wild. |
|
Behaviour |
●Pangolins are nocturnal creatures, meaning they are most active during the night. They are solitary animals, preferring to live alone and only coming together to mate. ●Their diet consists mainly of ants and termites. Using their long, sticky tongues, they capture insects from mounds and nests. Despite having no teeth, they rely on keratinous spines in their stomachs and gravel to aid in digestion. ●When threatened, pangolins curl into a tight ball, resembling a spiky ball, using their tough scales as armour. This behaviour protects them from predators. |
|
Conservation Status and Threats |
●All eight known pangolin species are listed on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. This designation highlights the critically endangered status of these animals in the wild. ○Manis mysteria is the 9th pangolin species. ●Pangolins are the most trafficked mammals in the world due to the high demand for their scales and meat. Their scales are used in traditional medicine, particularly in some Asian countries, and their meat is considered a delicacy in certain cultures. This illegal trade has significantly contributed to their declining populations. |
Key Highlights about the Manis mysteria
|
Discovery and Research |
●The discovery of Manis mysteria occurred through the analysis of scales seized in China's Yunnan province during anti-trafficking operations in 2015 and 2019. ●Scientists compared the genetic data from these scales with genomes of known pangolin species. This comparison revealed a distinct genetic lineage, indicating the presence of a new species. ●Manis mysteria is believed to have diverged from its Philippine and Malayan relatives approximately five million years ago. This indicates a long evolutionary history unique to this newly discovered species. |
|
Conservation Implications |
●The analysis of genetic data raised concerns about the population of Manis mysteria. Factors like low genetic diversity, high levels of inbreeding, and genetic load in the seized samples suggest that this species might already be facing a decline in numbers. ●The discovery underscores the urgent need for comprehensive research and conservation efforts to protect Manis mysteria. Conservation strategies are vital to ensure the survival of this newly discovered species and its integration into global conservation initiatives aimed at protecting pangolins. |
Conclusion
Must Read Articles:
PANGOLINS: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/pangolins-42
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. The term “Manis mysteria” is frequently mentioned in the news, it is related to: A) Malware B) Virus C) Bacteria D) Defence system E) None of the above Answer: D Explanation: Manis mysteria is a newly discovered pangolin species identified through the analysis of scales seized in China's Yunnan province in 2015 and 2019. This new species is believed to have diverged from its Philippine and Malayan relatives approximately five million years ago. |







© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved