Description
Copyright infringement not intended.
Context:
- Researchers from Indian Institute of Technology Madras have developed Origami Metamaterials, which could have many such uses.
Metamaterials
- A metamaterial is any material engineered at the atomic level to have a property that is not found in naturally occurring materials.
- They are made from assemblies of multiple elements fashioned from composite materials such as metals and plastics.
- Their precise shape, geometry, size, orientation and arrangement gives them their smart properties capable of manipulating electromagnetic waves: by blocking, absorbing, enhancing, or bending waves.
Meta-materials and Negative Refraction
- Metamaterials are made up of nanoparticle building blocks (typically based on composite metals and plastics) that use extremely small, repetitive patterns to interact with light or other waves to produce dynamic effects.
- The refinement of the refraction can be modified to produce different values and transform positive refraction into negative.
- Negative refraction of light and other wave forms can be a highly desirable property. It bends waves as they enter the structure of the metamaterial, which may allow the materials to exhibit certain properties, including:
- Invisibility or optical camouflage.
- Extreme light magnification.
- Negative electrical permittivity and magnetic permeability.
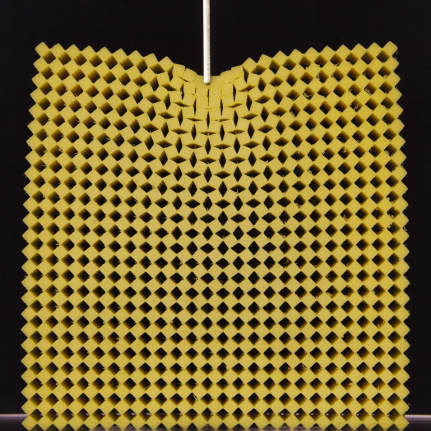
Origami Meta-materials
- There is a keen interest to develop materials that can be sandwiched in the fender system which will absorb the shock and prevent the interiors from being damaged.
- Origami metamaterials developed by Indian Scientists crumple rather than tear, and take the impact, can play an important role in such situations.
- This special class of origami metamaterials shows a constant value of Poisson Ratio when subjected to stress.
- Origami metamaterials combine the Japanese art of paper folding (origami) and the existing material of choice and fold it to obtain desired properties.
|
Poisson's ratio
Poisson's ratio is defined as the ratio of the change in the width per unit width of a material, to the change in its length per unit length, as a result of strain.
In order to be useful, materials need to maintain a constant Poisson ratio when they crumble under pressure. However, they are prone not to do so, and the Poisson ratio varies as they deform.
|
Potential Applications of Metamaterials
- Potential applications of metamaterials are diverse and include optical filters, medical devices, remote aerospace applications, sensor detection and infrastructure monitoring, smart solar power management, crowd control, radomes, high-frequency battlefield communication and lenses for high-gain antennas, improving ultrasonic sensors, and even shielding structures from earthquakes.
https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/a-metamaterial-that-can-make-use-of-origami-to-reduce-shock/article38419736.ece










