Description
Source: IndianExpress
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The International Court of Justice (ICJ) at The Hague, Netherlands, on May 24 ordered Israel to halt its military assault in the city of Rafah, located in the southernmost part of Gaza.
- The 15-judge Bench, however, stopped short of ordering a full ceasefire throughout the enclave.
Details
Background of the Case
- South Africa initiated legal proceedings against Israel in December 2023, accusing Israel of genocide in the Gaza Strip.
- Previous rulings by the ICJ included orders for Israel to prevent acts of genocide against Palestinians and ensure the timely arrival of basic food supplies to Gaza.
South Africa's Fresh Request
- On May 10, 2024, South Africa submitted a fresh request to the ICJ, seeking urgent measures to protect Palestinians in Gaza from Israel's ongoing military assault on Rafah.
- South Africa argued that Israel's actions constituted grave and irreparable violations of Palestinian rights.
The ICJ Ruling
- The ICJ, in a 13:2 majority ruling, ordered Israel to halt its military assault specifically in the city of Rafah, located in the southernmost part of Gaza.
- While a full ceasefire throughout Gaza was not mandated, Israel was directed to open the Rafah crossing between Egypt and Gaza to allow humanitarian aid to flow.
- Israel was also instructed to grant access to any UN fact-finding or investigative missions regarding the allegations of genocide in Gaza.
- Israel was required to report back to the ICJ within a month on the progress of implementing these measures.
Justification for the Ruling:
- The ICJ highlighted the exceptional gravity of the situation, particularly the ongoing displacement of nearly 800,000 people from Rafah due to Israel's military offensive.
- The court emphasized the need to modify provisional measures due to changes in circumstances, as articulated in Article 76 of the Rules of Court.
- Despite Israel's claims of evacuation efforts to enhance civilian security, the ICJ expressed skepticism about their sufficiency to alleviate the immense risks faced by the Palestinian population in Gaza.
Implications of the Ruling:
- While ICJ rulings are legally binding, they lack direct enforcement mechanisms.
- However, experts suggest that this latest order could further isolate Israel diplomatically, deepening its international isolation.
Recent Military Assault in Rafah
Background:
- The recent escalation in Rafah is part of the broader Israel-Hamas conflict that reignited on October 7, 2023, when Hamas and allied militants attacked southern Israel.
- This initial assault resulted in the death of nearly 1,200 people and the capture of over 250 hostages by Hamas.
- Israel responded with a total blockade of Gaza, heavy bombing, and a ground invasion, triggering a severe humanitarian crisis.
The Offensive:
- Objective:The Israeli military aimed to eliminate Hamas brigades reported to be in Rafah, a city in southern Gaza that had become a refuge for approximately 1.4 million displaced Palestinians.
- Ceasefire Attempts:Despite a ceasefire proposal accepted by Hamas and brokered by Egypt and Qatar, Israel rejected the terms and continued its operation, emphasizing the need to eradicate Hamas and secure the release of hostages.
Humanitarian Impact:
- Displacement:About 800,000 Palestinians were evacuated to areas described as unsafe and lacking essential supplies.
- Casualties:The offensive has resulted in the deaths of approximately 210 Palestinians and injuries to 280 more.
- Medical Crisis:Hospitals in Rafah are overwhelmed and under-resourced, struggling due to continuous Israeli airstrikes and the blockade, which has cut off essential supplies and medical aid.
- Infrastructure Damage:The closure of the Rafah and Kerem Shalom crossings has further strained the humanitarian situation, preventing the flow of aid and exacerbating the crisis.
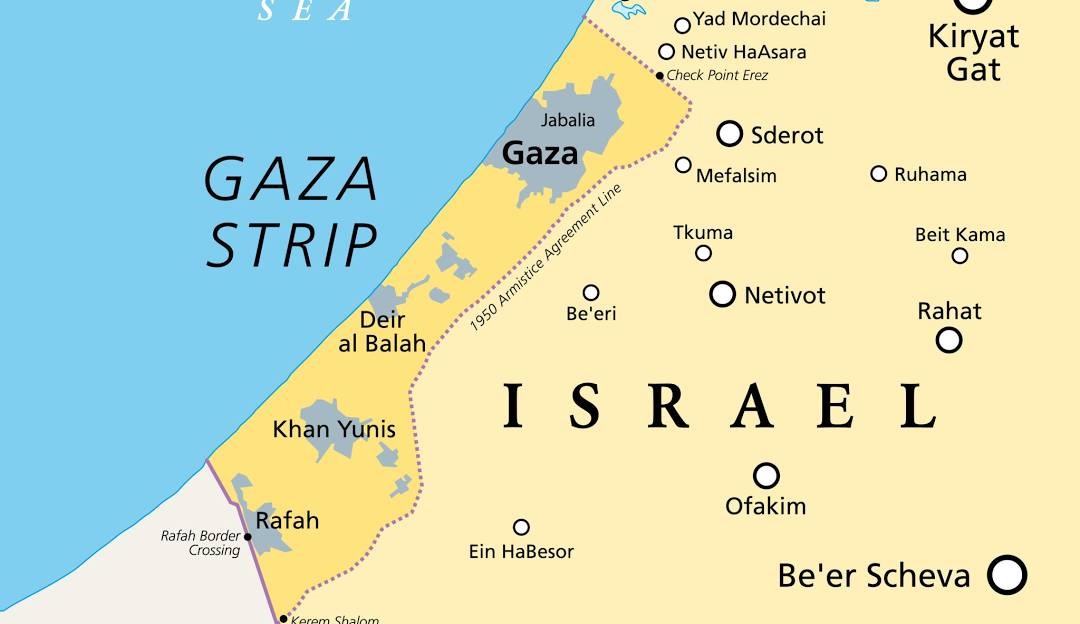
About Rafah
- Location: Rafah is a city in the southern part of the Gaza Strip, near the border with Egypt. It is divided into two parts: Rafah in the Gaza Strip and the Egyptian side of Rafah in the Sinai Peninsula.
- Population: Rafah has a population of approximately 250,000 residents. It has a high population density, with many residents living in crowded conditions.
- Significance: Rafah is known for its strategic importance due to the Rafah Border Crossing, the main point of entry between Egypt and the Gaza Strip. This crossing is vital for the movement of people and goods, especially given the restrictions imposed by the Israeli blockade.
- Historical Background: Rafah has a long history, with evidence of habitation dating back to ancient times. It has been a significant location throughout various periods, including the Byzantine, Islamic, and Ottoman eras.
- Modern History: In the 20th century, Rafah became a focal point during the Arab-Israeli conflict. Following the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, Rafah became part of the Gaza Strip under Egyptian administration. After the Six-Day War in 1967, Israel occupied Rafah until the establishment of the Palestinian Authority in the 1990s.
Sources:
IndianExpress
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. The assault on Rafah underscores the severe humanitarian and geopolitical challenges in the Israel-Hamas conflict. Discuss. (250 Words)
|















