Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- South Eastern Coalfields Ltd (SECL) will undertake a plantation using the Miyawaki method in the coal belt region of Chhattisgarh.

Miyawaki Method
About
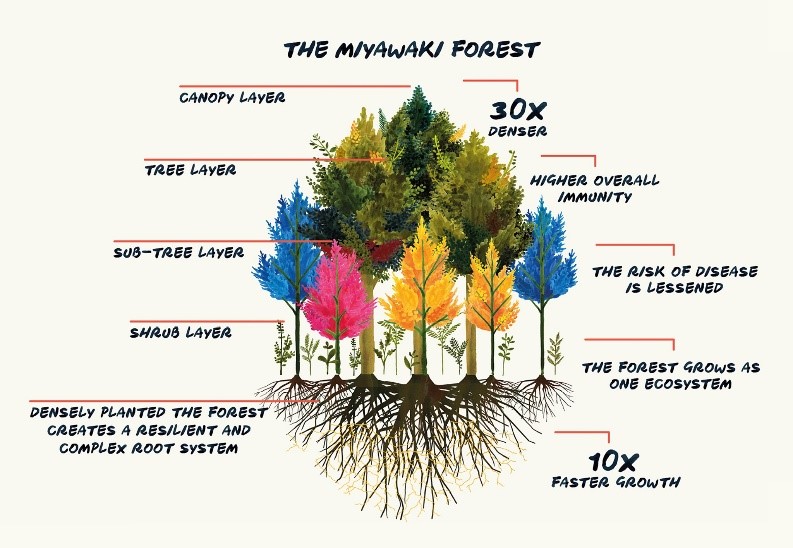
- The Miyawaki method is an afforestation technique for cultivating fast-growing groves of native plants, with the dense, mixed planting intended to simulate the layers of a natural forest.
Development
- It was developed in the early 1970s by the late Japanese forest ecologist Akira Miyawaki.

Steps involved
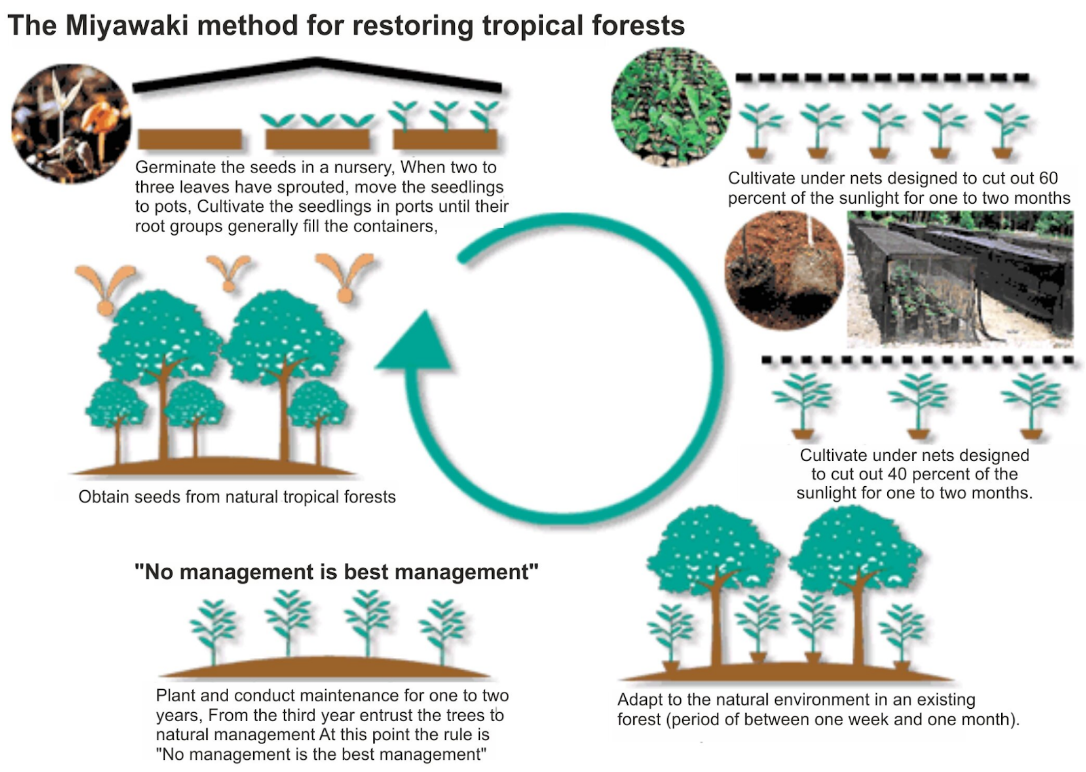
The method involves the following steps:
- determine the plant species native to a given area;
- improve the soil by mixing in organic material;
- plant seedlings of native trees and understory plants in a dense,
- mixed manner (about three seedlings per square meter) meant to simulate a natural forest;
- remove weeds from the site for up to three years after planting, if necessary.
- After that, the grove is left to its own devices. Due to the dense planting, the seedlings grow quickly as they compete for sunlight.
Implementation
- Although originally implemented in Japan, Miyawaki collaborated with Japanese multinational companies to apply his method overseas as well. This led Miyawaki in 1999 to claim that “quasi-natural forests can be built in 15-20 years in Japan and 40-50 years in Southeast Asia.”
- Over the past decade, the Miyawaki method’s popularity has reached new heights, including projects in Jordan and Brazil, among other locations.
The benefits of a Miyawaki forest
- Miyawaki forests grow rapidly, increase soil- and forest biodiversity, increase carbon sequestration, increase forest resilience and reduce maintenance costs.
Ecological benefits
- Miyawaki forests are more resilient than traditionally planted forests.
- Research has found that these forests have a much greater biodiversity – above ground and below.
- Deadwood and leaves are left alone. This provides potential habitat for fungi and invertebrates.
- The diversity of plants is attractive to various types of fauna, providing habitat and food for everything from invertebrates to birds to mammals.
- Miyawaki forests achieve ecological succession within 20 or 30 years, compared to 100-200 years for a traditionally planted forest.
Cost-effective
- Miyawaki forests often require less initial cost of funds, which may include installing a watering system, labor costs for planting and the first few years of development, the price of saplings, and the price of soil additives.
- In the long run after the initial period of growth, investment requirements are little to none.
- Additionally, the growers can increase the economic value of their forests by incorporating high-value native timber trees and creating “Miyawaki Fruit Forests”, by providing forest tours, nature walks and educational sessions.

Carbon sequestration
- Miyawaki technique trees are planted, and they develop much more quickly, accelerating the process of creating forests and absorbing more carbon.
- The best part of the technique is that after three years saplings become maintenance-free or self-sustainable.
- Being capable of rapidly establishing diverse, healthy forests could be crucial in fulfilling international targets and addressing these concerns in light of the current climate change emergency and alarming warnings about worldwide biodiversity loss.
Prevents calamities
- Apart from carbon sequestration, Miyawaki forests have also proven effective when used for a specific purpose, such as providing tsunami protection, stabilizing mine dump slopes, and as typhoon protection systems.

READ MORE ON MIYAWAKI METHOD: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/miyawaki-forests#:~:text=It%20starts%20with%20Identification%20of,using%20compost%20tea%20and%20straw.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Consider the following statements with reference to Miyawaki Method:
1. Miyawaki forests have a much greater biodiversity – above ground and below.
2. In this technique, after three years saplings become maintenance-free or self-sustainable.
3. Miyawaki forests achieve ecological succession within 100 years.
How many of the above statements are correct?
A) Only 1
B) Only 2
C) All 3
D) None
Answer: B) Only 2
Statement 3 is incorrect.
Miyawaki forests achieve ecological succession within 20 or 30 years, compared to 100-200 years for a traditionally planted forest.
|















