Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Context: Recently, India and Saudi Arabia discussed signing a Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty (MLAT) to obtain formal assistance from each other in investigations related to criminal cases.
Details:
- According to the Ministry of Home Affairs, MLAT is a mechanism whereby countries cooperate with one another to provide and obtain formal assistance in the prevention, suppression, investigation and prosecution of crime to ensure that the criminals do not escape or sabotage the due process of law for want of evidence available in different countries.
- The Ministry is the Central Authority of India for dealing with requests for mutual legal assistance in criminal matters.
- India has so far signed MLATs with 45 countries.
Background:
- India needs the Gulf countries, Saudi Arabia in particular, to invest in the country and power its economic recovery. After the diplomatic backlash over the remarks on the Prophet earlier this year, the government is proactively seeking to deepen the ties.
- Saudi Arabia is India’s fourth-largest trading partner. More than 18 per cent of India’s crude oil imports are sourced from Saudi Arabia. During FY22 (April-December), bilateral trade was valued at $29.28 billion. During this period, India’s imports from Saudi Arabia were valued at $22.65 billion and exports to Saudi Arabia were worth $6.63 billion.
- The 2.2-million-strong Indian community is the largest expatriate community in Saudi Arabia, according to the Indian embassy.
.jpeg)
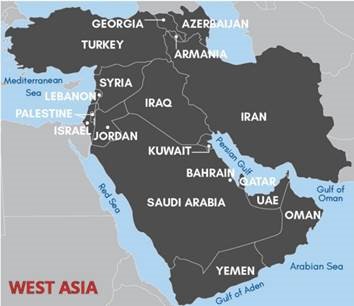
India and West Asia:
- India has economic, political, security and strategic interests with the West Asian countries.
- 70 per cent of India’s imported energy needs come from West Asia.
- India is the largest recipient of foreign remittances from west Asia. 11 million Indians work in West Asia.
Importance:
- To counter radicalization
- Gate way to central Asia
- Geostrategic importance
Issues:
- Political instability in Syria, Yemen, Iraq
- extra-regional players such as the USA and Russia
- Presence of ISIS and other terrorist groups
- GCC-Iran rivalry
- Shia-Sunni conflict
- Saudi-Iran rivalry
- Arab Israel Conflict
- Israel – Palestine Conflict
- US-Iran conflict.
- Influence of Pakistan.
India’s Look West policy:
- Cold war period: India remained a passive player though maintained close economic cooperation with both Saudi Arabia and Iran.
- India adopted Look West policy in 2005.
- India now follows a Secular and Non- Aligned Policy.
- Focus is on business-to-business and people-to-people relationships.
- There is focus on maritime diplomacy.
- Relationship today is driven more by economic calculation than political rhetoric.
Background of India Saudi relations:
- India and Saudi Arabia enjoy cordial and friendly relations reflecting the centuries old economic and socio-cultural ties.
- The establishment of diplomatic relations in 1947 was followed by high-level visits from both sides.
- The historic visit of King Abdullah to India in 2006 resulted in signing of ‘Delhi Declaration’ imparting a fresh momentum to the bilateral relationship.
- The reciprocal visit by Prime Minister Dr. Manmohan Singh to Saudi Arabia in 2010 raised the level of bilateral engagement to ‘Strategic Partnership’ and the ‘Riyadh Declaration’ signed during the visit captured the spirit of enhanced cooperation in political, economic, security and defence realms.
- India is one of the Kingdom’s 8 Strategic Partner Countries under ‘Vision 2030’.
- Saudi Arabia is India’s 4th largest trade partner and is a major source of energy as India imports around 18 % of our crude oil requirement from the Kingdom.
- In 2018-19, the India-Saudi bilateral trade has increased by 23.83 % to US $ 34.03 billion.
- Saudi Aramco and UAE’s ADNOC are jointly participating in the development of US $ 44 billion ‘West Coast Refinery & Petrochemicals Project Limited’ in Raigad, Maharashtra.
- The 2.6 million (as of August 2019) strong Indian community in Saudi Arabia is the largest expatriate community in the Kingdom and is the ‘most preferred community’ due to their expertise, sense of discipline, law abiding and peace loving nature.
- The Hajj Quota was increased by 24, 975 in 2019, enabling 2, 00, 000 Indians performing Hajj in 2019. Around 7, 00, 000 Indians also visit the Kingdom to perform Umrah every year.
https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/india-saudi-arabia-discuss-treaty-on-mutual-assistance-for-criminal-investigations/article66320892.ece













