Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Recently, the National Health Accounts Estimates for India (2019-20) were released.
Highlights of the Report
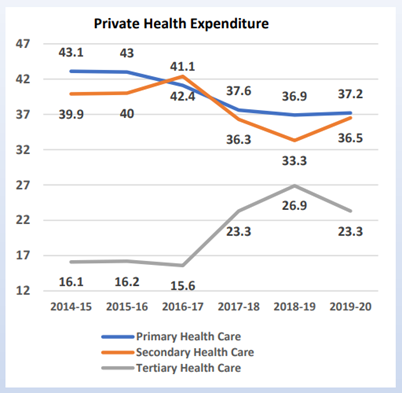
Public spending in Primary Healthcare
- The Report highlights the increased public spending in primary healthcare, which is in line with National Health Policy 2017 which states that two-thirds of public health spending must be in Primary Health systems.
- This is also a result of great developments/initiatives taken at grassroot level such as the opening of over 1.6 lakh Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centres (AB-HWCs) which are providing plethora of health services to the people.
Private Health Insurance Share
- Private health insurance share is also going up.
- This shows a sign of maturity for a country in terms of the insurance arena as those who can afford will afford it from private players too. This complements the government syst em of primary, secondary, and tertiary care.”
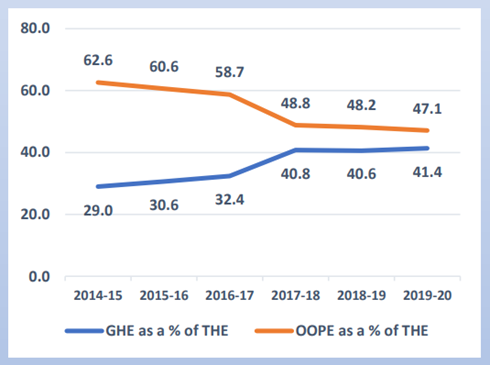
Share of Out-of-Pocket Expenditure
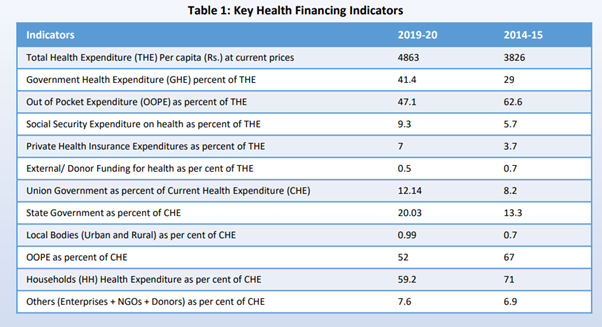
- The share of Out-of-Pocket Expenditure (OOPE) in total Health Expenditure (THE) declined from 62.6% to 47.1%.
- The continuous decline in the OOPE in the overall health spending shows progress towards ensuring financial protection and Universal Health Coverage for citizens.
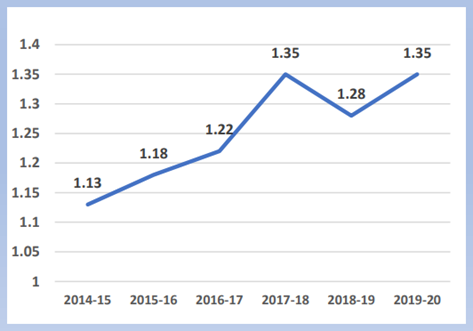
Government Health Expenditure (GHE)
- During this period, the share of Government Health Expenditure (GHE) in the overall GDP of the country has increased from 1.13% in 2014-15 to 1.35% in 2019-20.
- In per capita terms, GHE has doubled from Rs. 1,108 to Rs. 2,014 between 2014-15 to 2019-20.
- The government spending on health between 2018-19 and 2019-20 increased by 12%, more than double the growth rate between 2017-18 and 2018-19 which was at 5%.
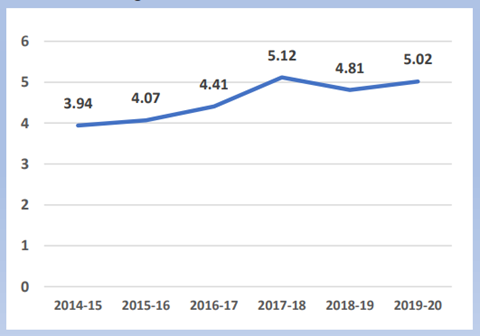
General Government Expenditure
- In General Government Expenditure (GGE), the share of health sector spending has steadily increased from 3.94% to 5.02% between 2014-15 and 2019-20.
- This clearly indicates that healthcare has been the priority for public investment in the country.
Total Health Expenditure (THE)
- The increase in government spending on health has an important implication for the reduction of financial hardship endured by households.
- In the Total Health Expenditure (THE) of the country between 2014-15 and 2019-20, the share of GHE has increased from 29% to 41.4%.
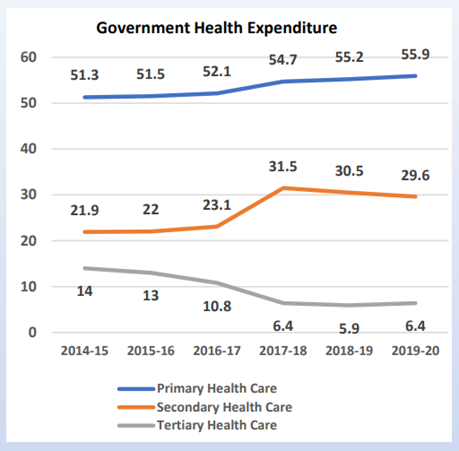
Share of primary healthcare in Current Government Health Expenditure (CGHE)
- The share of primary healthcare in Current Government Health Expenditure (CGHE) has increased from 51.3% in 2014-15 to 55.9% in 2019-20.
- The increased focus on primary healthcare reinforces the government’s decisions to prioritize primary healthcare in the country.
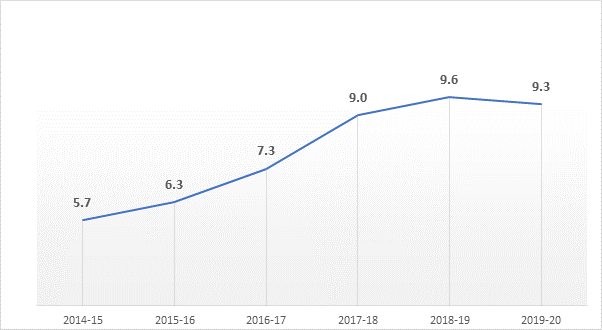
Social Security Expenditure (SSE)
- Another positive trend in the country’s health financing space is the increase in Social Security Expenditure (SSE) on healthcare. This increase in social security has a direct impact on reducing out-of-pocket payments.
- A robust social security mechanism ensures that individuals will not face financial hardship and the risk of poverty as a consequence of accessing essential healthcare services.
- The share of SSE on health, which includes government-funded health insurance, medical reimbursement to government employees, and social health insurance programs, has increased from 5.7% in 2014-15 to 9.3% in 2019-20.
Moving Ahead
- The state governments need to move ahead in healthcare spending as percentage of their total budget to about 8% which is currently 4-5% for many states.
- This spending must be in line with the bigger picture of benefiting the citizens”.
National Health Account (NHA) Estimates
- The National Health Account (NHA) estimates for India 2019-20 is the seventh consecutive NHA estimates report prepared by NHSRC, designated as National Health Accounts Technical Secretariat (NHATS) in 2014 by the Union Health Ministry.
- The NHA estimates are prepared by using an accounting framework based on the internationally accepted standard of System of Health Accounts, 2011, developed by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- With the present estimate of NHA, India now has a continuous series of NHA estimates for the country, from 2013-14 to 2019-20.
- These estimates are not only comparable internationally but also enable the policymakers to monitor the progress in different health financing indicators of the country.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Which of the following statements are correct with reference to National Health Accounts Estimates for India (2019-20)?
a) The NHA estimates are prepared by using an accounting framework based on the internationally accepted standard of System of Health Accounts, 2011, developed by the World Health Organization (WHO).
b) In the Total Health Expenditure (THE) of the country between 2014-15 and 2019-20, the share of GHE has increased from 29% to 41.4%.
c) The share of Out-of-Pocket Expenditure (OOPE) in total Health Expenditure (THE) declined from 62.6% to 47.1%.
d) During this period, the share of Government Health Expenditure (GHE) in the overall GDP of the country has increased from 1.13% in 2014-15 to 1.35% in 2019-20.
1. a and b only
2. b and c only
3. c and d only
4. All of the above.
Correct Answer: Option 4
|

https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1919582#:~:text=The%20government%20spending%20on%20health,%2D15%20and%202019%2D20.























