Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- On August 15, 2021, Hon’ble Prime Minister announced the launch of National Hydrogen Mission.
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy has accordingly prepared a draft Mission document.
National Hydrogen Mission
- Under National Hydrogen Mission, India is targeting to produce three-fourths of its hydrogen from renewable resources by 2050.
- The Mission under the Ministry of Power, aims to support India in meeting its Sustainable climate goals.
- Hydrogen is seen as the potential fuel to replace fossil fuels in future. It will help India in increasing its renewable energy capacity.
- The Mission aims to aid the government in meeting its climate targets and making India a green hydrogen hub.
- The focus of the mission is lowering the cost of hydrogen production and commercialising green hydrogen.
- This will help in meeting the target of production of 5 million tonnes of Green hydrogen by 2030 and the related development of renewable energy capacity.
- This will help the government in achieving the target of 450 GW Renewable Energy by 2030.
Features of National Hydrogen Mission
- Green Hydrogen / Ammonia manufacturers may purchase renewable power from the power exchange or set up renewable energy capacity themselves or through any other, developer, anywhere. Open access will be granted within 15 days of receipt of application.
- The Green Hydrogen / Ammonia manufacturer can bank his unconsumed renewable power, up to 30 days, with distribution company and take it back when required.
- Distribution licensees can also procure and supply Renewable Energy to the manufacturers of Green Hydrogen / Green Ammonia in their States at concessional prices. This will only include the cost of procurement, wheeling charges and a small margin as determined by the State Commission.
- Waiver of inter-state transmission charges for a period of 25 years will be allowed to the manufacturers of Green Hydrogen and Green Ammonia for the projects commissioned before 30th June 2025.
- The manufacturers of Green Hydrogen / Ammonia and the renewable energy plant shall be given connectivity to the grid on priority basis to avoid any procedural delays.
- The benefit of Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO) will be granted incentive to the hydrogen/Ammonia manufacturer and the Distribution licensee for consumption of renewable power.
- To ensure ease of doing business a single portal for carrying out all the activities including statutory clearances in a time bound manner will be set up by MNRE.
- Connectivity, at the generation end and the Green Hydrogen / Green Ammonia manufacturing end, for the purpose of manufacturing Green Hydrogen / Green Ammonia shall be granted on priority.
- Manufacturers of Green Hydrogen / Green Ammonia shall be allowed to set up bunkers near Ports for storage of Green Ammonia for export / use by shipping.
- The land for the storage for this purpose shall be provided by the respective Port Authorities at applicable charges.
Hydrogen as a fuel
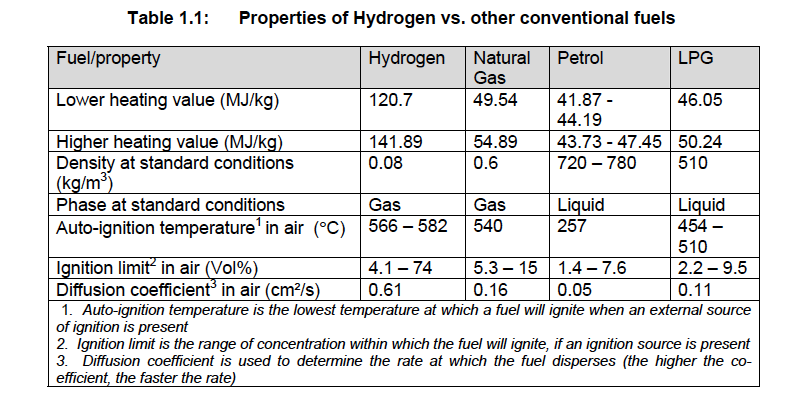
- Hydrogen is a clean fuel and an efficient energy carrier. It is emerging as an important source of energy since it has zero carbon content in contrast to hydrocarbons which have net carbon content between 75 and 85 per cent.
- When burnt, Hydrogen produces water as a by-product and is, therefore, environmentally benign.
- The energy content by weight for Hydrogen is 120.7 MJ/kg, which is the highest for any known fuel.

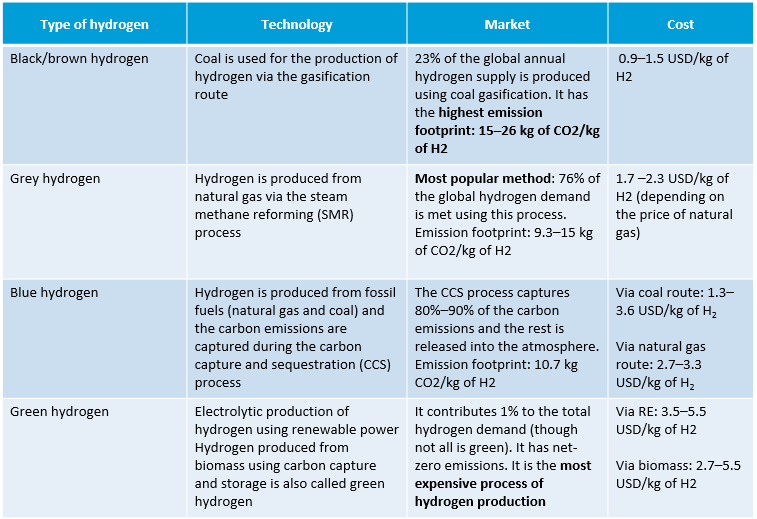
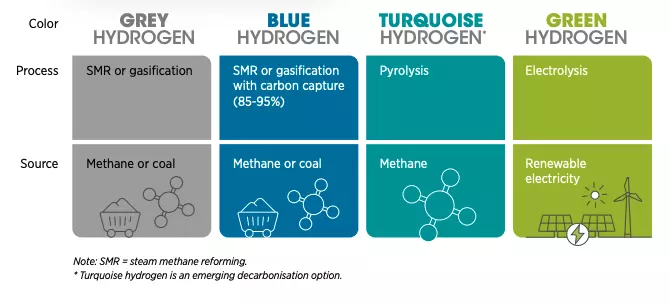
What is green hydrogen?
- Green hydrogen is produced by electrolysis of water using renewable energy and has a lower carbon footprint.
- By 2030, the cost of green hydrogen is expected to compete with that of hydrocarbon fuels.
- Hydrogen will make up 12 per cent of the energy mix by 2050, according to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA).
- At present, less than 1 per cent of hydrogen produced is green hydrogen, according to IRENA's World Energy Transitions Outlook.
India and green hydrogen
- Under the Paris Climate Agreement, India pledged to reduce the emission intensity of its economy by 33-35 per cent from 2005 levels by 2030.
- India consumes about six million tonnes of hydrogen every yearfor the production of ammonia and methanol in industrial sectors, including fertilisers and refineries.
- India has favourable geographic location and abundance of sunlight and wind for the production of green hydrogen.
- Green hydrogen production will reduce the country’s dependence on imports while also staving off climate change.
- India will become a net exporter of green hydrogen by 2030 due to its cheap renewable energy tariffs, according to the Global Hydrogen Council.
- In some sectors, the purchase of green hydrogen can be made mandatory, similar to renewable purchase obligations.
Why to opt for Green Hydrogen?
- Adoption of Green hydrogen technologies is favorable in those sectors where direct electrification isn't feasiblefor example in Heavy duty, long-range transport and long-term storage in the power sector.
- With technological improvements, green hydrogen will become more affordable and accessible.
- It can be used in a wide range of existing applications such as fertilisers, mobility, power, chemicals and shipping.
- It can be blended up to 10 per cent by city gas distribution networks for wider acceptance.
- It is a cross-cutting solution that will reduce emissions across a range of sectors.
Challenges in making Green Hydrogen
- Storing and transportation: H2 is a highly flammable gas, it takes up a lot of space and has a habit of making steel pipes and welds brittle and prone to failure.
- High Cost:The International Energy Agency put the cost of green hydrogen at $3 to $7.50 per kilo, compared to $0.90 to $3.20 for production using steam methane reformation.
- Loss of Efficiency in every process: Electrolyzer efficiencies range from around 60 percent to 80 percent.
What can be done to build a global-scale green hydrogen industry?
- As with renewable energy, India should announce ambitious national targets for green hydrogenand electrolyser capacity by 2030.
- Launch an incentive programme for the production of electrolysers.
- Implementing complementary solutionsthat create virtuous cycles for example building the hydrogen infrastructure for refueling, heating and generating electricity at airports.
- Optimizing distribution networksto decarbonise the gas grid.
Final Thoughts
- The implementation of National hydrogen Policy will provide clean fuel to the common people of the country.
- This will reduce dependence on fossil fuel and also reduce crude oil imports.
- The objective also is for our country to emerge as an export Hub for Green Hydrogen and Green Ammonia.
- Green hydrogen can play an important role in enhancing India’s decarbonisation efforts, particularly in its industrial, transport, and power sectors.
- The policy promotes Renewable Energy (RE) generation as RE will be the basic ingredient in making green hydrogen.
- This in turn will help in meeting the international commitments for clean energy.
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1812023


















