Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context:
- The Government released the Theme for the "National Science Day 2023", titled "Global Science for Global Wellbeing".
History of National Science Day:
- In 1986, the National Council for Science and Technology Communication (NCSTC)asked the Indian government to observe February 28 as National Science Day.
- Since then, National Science Day has been celebrated all over India in schools, colleges, universities, and other academic, scientific, technical, medical, and research institutions.
- On this day, a well-known scientist of India C V Raman got the scientific breakthrough of the Raman Effect and that is why 28th Feb is celebrated as a National Science Day to praise the effort made by C V Raman in the field of Science. After the successful research of the Raman Effect, Indian scientist C V Raman was awarded a Nobel prize in 1930 for his brilliant effort and that was the debut Nobel prize received by any Indian in the field of Science.
Significance of National Science Day:
- National Science Day is held to raise awareness of the value of science and technology in everyday living.
- It is commemorated in order to showcase all operations, endeavours, and successes accomplished in science for the well-being of humans.
- It is a privilege to examine any topic and introduce additional technology into practice for the advancement of science in India.
- It provides a chance for India’s scientifically inclined populace to inspire individuals and promote awareness of science and technology.
.jpeg)
Raman Spectroscopy:
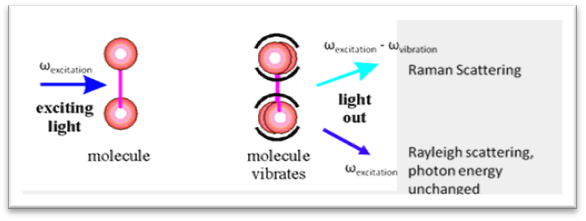
- Raman is a light scattering technique, whereby a molecule scatters incident light from a high-intensity laser light source.
- Most of the scattered light is at the same wavelength (or color) as ---- this is called Rayleigh Scatter.
- However a small amount of light (typically 0.0000001%) is scattered at different wavelengths (or colors), which depend on the chemical structure of the analyte – this is called Raman Scatter.
Important Applications:
The following are some important areas which use Raman spectroscopy to great effect.
Pharmaceutical Agents and Cosmetic Products
- The distribution of a compound within a tablet.
- The concentration of an API(Active Pharmaceutical Agent).
- Testing the content and purity of a powder.
- Verifying raw material quality.
- Identification of contaminants.
Geology and Mineralogy
- Identification of various minerals and precious/semiprecious stones.
- Studying the distribution of minerals and phases within a section of rock.
- Studying the behavior of minerals under harsh conditions.
- Identifying chondrite or achondrite meteorites.
Carbon Materials
- Study of single-walled carbon nanotubes.
- Testing hard disk drives.
- Detection of defects or disorder in carbon materials.
- Testing diamond quality and place of origin.
- Measuring the electrical properties and the number of layers of 2D materials like graphene.
Semiconductors
- Assaying the purity.
- Analysis of the composition of an alloy.
- Identifying contaminants.
- Analyzing defects in a structure.
- Microanalysis of photoluminescence

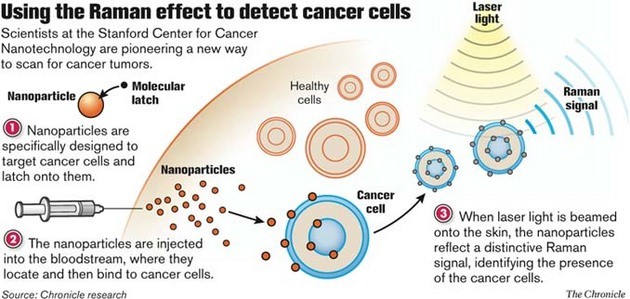
Life Sciences
- Analysis of biocompatibility of a material.
- Analysis of nucleic acids.
- Study of interactions between drugs and cells.
- Diagnosis of disease.
- Analysis of individual cells.
- Cell sorting applications.
- Analyzing the features of biomolecules.
- Study of bone structure.
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1889763













