




Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
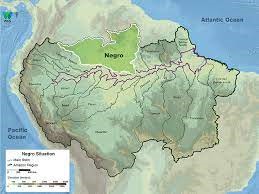
About
Geography
Upper Corse
Middle Corse
Lower Course
Major Tributaries
Fauna and Flora
|
PRACTICE QUESTION The Amazon River and its basin hold significant ecological and cultural importance, not only in South America but also globally. Discuss. (150 words) |











© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved