Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: mapsofindia.com
Context: A new outbreak of the Nipah virus has been reported in Kerala. The state government has set up a control room to monitor the situation and has intensified surveillance and contact tracing measures. The district has been put on high alert to prevent the spread of the virus, which can cause severe respiratory and neurological complications.
Nipah virus
Origin
- The Nipah virus was first identified in 1998 during an outbreak in Malaysia and Singapore. The virus gets its name from the Malaysian village of Sungai Nipah, where one of the first major outbreaks occurred.
- It is classified as a zoonotic virus, meaning it can be transmitted from animals to humans.
- The natural reservoir hosts of Nipah virus are fruit bats (Pteropus species), which do not typically show symptoms of the disease but can shed the virus in their urine, saliva, and faeces.
- Human infections often occur through the consumption of contaminated fruit or close contact with infected animals.
Symptoms of Nipah Virus Infection
- Nipah virus infection can vary widely in its presentation, from mild to severe. This variability makes early diagnosis challenging.
- Initial Symptoms:
- Most patients with Nipah virus infection initially experience a high fever.
- Severe headaches are a common early symptom.
- Muscular aches and pain are often reported.
- Nausea and vomiting may occur.
- Sore throat is another early symptom.
- As the disease progresses, individuals may develop more severe symptoms, which can include:
- Altered mental state, confusion, and disorientation are common as the virus affects the central nervous system.
- Vertigo and a feeling of unsteadiness may be present.
- Patients with severe Nipah virus infection can experience a loss of consciousness or a coma-like state.
- Neurological signs may include seizures and focal neurological deficits.
- Encephalitis: Severe Nipah virus infection is characterized by encephalitis, which is the inflammation of the brain. This is a hallmark feature of the disease and contributes to the neurological symptoms.
- Respiratory Symptoms: In addition to the neurological symptoms, Nipah virus can also cause respiratory symptoms, including cough and difficulty breathing. These respiratory manifestations may become more pronounced in severe cases.
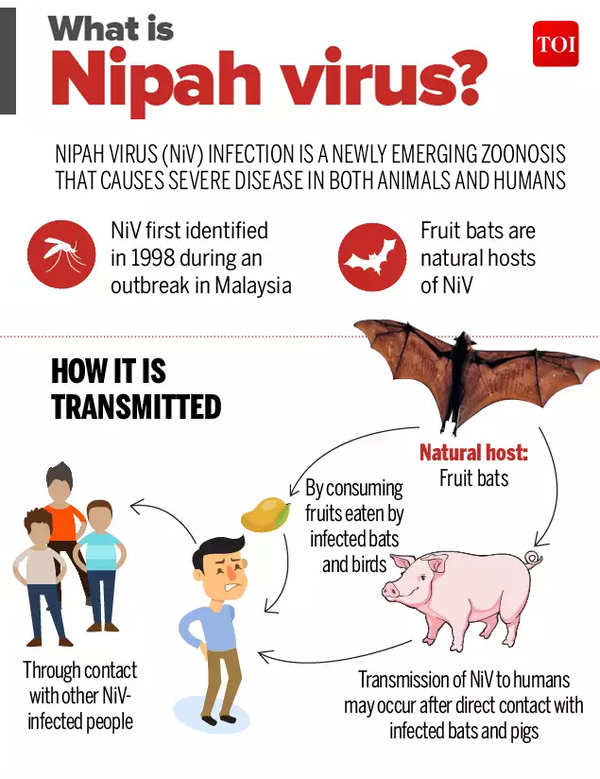
Picture Courtesy: The Times of India
Impact of Nipah Virus Outbreaks
Geographic Spread
- Nipah virus outbreaks have occurred in several countries in Southeast Asia and South Asia, including Malaysia, Singapore, Bangladesh, and India. These outbreaks have demonstrated the potential for the virus to re-emerge and spread to new areas.
High Case Fatality Rates
- One of the most concerning aspects of Nipah virus outbreaks is the high case fatality rates associated with the disease. The fatality rates often range from 40% to 100%, depending on the outbreak and the healthcare infrastructure in the affected region. This high mortality rate places a significant burden on healthcare systems.
Public Health Burden
- Healthcare Systems: Nipah virus outbreaks strain local healthcare systems, particularly in resource-limited regions. The need for specialized care, including intensive care for severe cases, places a heavy demand on medical resources.
- Community Impact: Outbreaks can cause fear and panic in affected communities. Public health authorities often need to implement strict isolation and quarantine measures to control the spread of the virus, which can disrupt daily life and create anxiety among the population.
- Travel and Trade Restrictions: Outbreaks can lead to travel restrictions and disruptions in trade, affecting the economy and livelihoods of people in the affected areas.
Economic Burden
- Agriculture: In some outbreaks, culling of pigs has been implemented as a control measure, leading to significant economic losses in the swine industry.
- Tourism: Outbreaks can deter tourists from visiting affected regions, impacting the tourism sector.
- Workforce: Illness and fear of infection can lead to absenteeism in the workforce, affecting productivity.
Global Concern
- Nipah virus outbreaks are a global health concern due to their potential to spread to new regions and the lack of specific treatments or vaccines. International cooperation and information sharing are critical in managing and preventing the global spread of the virus.

Challenges in Dealing with Nipah Virus
Diagnosis
- Nonspecific Symptoms: The initial symptoms of Nipah virus infection, such as fever, headache, muscle pain, and sore throat, are nonspecific and can be mistaken for other common illnesses like influenza or dengue fever. This can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
- Limited Diagnostic Resources: In many regions where Nipah virus outbreaks occur, there may be limited access to specialized diagnostic tests, making it challenging to confirm cases quickly.
Treatment
- Lack of Specific Antiviral Treatment: Currently, there is no specific antiviral medication approved for the treatment of Nipah virus infection. This means that patient care primarily involves supportive measures, such as maintaining hydration, managing symptoms, and providing respiratory support for severe cases.
- Limited Treatment Centers: Adequate facilities and expertise for managing severe cases of Nipah virus infection may be lacking in affected regions, further complicating patient care.
Prevention
- Zoonotic Transmission: The Nipah virus primarily spreads from animals to humans, with bats as the natural reservoir hosts. Preventing transmission from bats and other animals to humans is a complex challenge, as it involves modifying human-animal interactions and behaviours.
- Human-to-Human Transmission: During outbreaks, human-to-human transmission can occur, often within healthcare settings or among close contacts of infected individuals. Implementing effective infection control measures is crucial but can be challenging in resource-limited healthcare settings.
Vaccine Development
- Complexity of the Virus: The Nipah virus is a highly complex virus with multiple strains. Developing a safe and effective vaccine has proven challenging due to the need to target multiple strains and the limited resources available for research.
- Lack of Commercial Incentives: The Nipah virus primarily affects low-resource regions, which may not provide significant commercial incentives for vaccine development. This can result in limited investment from pharmaceutical companies.
Treatment of Nipah Virus Infection
- There is no specific cure or antiviral medication approved for the treatment of Nipah virus infection.
- The primary approach to managing Nipah virus infection is providing supportive care to patients. This includes:
- Maintain hydration and electrolyte balance.
- In severe cases, patients may require mechanical ventilation to assist with breathing.
- Medications may be used to alleviate specific symptoms such as fever, pain, and nausea.
- Researchers have been exploring experimental treatments for Nipah virus infection, including:
- Some antiviral drugs have shown promise in laboratory and animal studies. These drugs aim to inhibit the replication of the virus.
- Monoclonal antibodies that target the Nipah virus have also been under investigation. They may help the immune system combat the virus.
Way Forward for Dealing with the Nipah Virus
Prevention
- Enhanced Surveillance: Improved surveillance systems are crucial for the early detection of Nipah virus cases and outbreaks. This includes monitoring both animal populations, particularly fruit bats, and human cases.
- Early Case Identification: Early detection of cases, prompt isolation, and contact tracing are essential to prevent the further spread of the virus during outbreaks.
- Control Measures: Implementing control measures, such as quarantine and isolation of infected individuals, can help contain outbreaks.
Vaccine Development
- Research and Development: Continued research efforts are necessary to develop a safe and effective vaccine against the Nipah virus. Vaccine candidates should be rigorously tested in preclinical and clinical trials.
- Affordability and Accessibility: Ensuring that any developed vaccine is affordable and accessible to at-risk populations, especially in low-resource regions, is crucial.
Public Awareness and Education
- Community Engagement: Conducting public awareness campaigns and community engagement programs can help educate people in at-risk areas about the virus, its transmission, and preventive measures.
- Promoting Safe Practices: Encouraging safe practices when handling animals, consuming fruits, and during healthcare interactions can reduce the risk of Nipah virus transmission.
One Health Approach
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Promoting collaboration between human health, animal health, and environmental sectors is essential for a comprehensive One Health approach. This approach recognizes the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health and aims to prevent zoonotic diseases like the Nipah virus.
Research
- Understanding the Virus: Ongoing research into the biology, genetics, and transmission dynamics of the Nipah virus is critical for developing effective prevention and control strategies.
- Treatment Development: Research should continue to explore potential treatments, including antiviral drugs and monoclonal antibodies, with a focus on safety and efficacy.

Summary
- Nipah virus is considered a serious emerging infectious disease due to its potential for high morbidity and mortality, as well as its ability to cause outbreaks with person-to-person transmission. Public health measures, along with education and awareness, play a crucial role in preventing and controlling Nipah virus infections.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. What are the most significant socio-economic challenges that have emerged as a result of the pandemic, and what strategies can societies implement to address these challenges as they navigate their way forward in a post-pandemic world?
|
https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/nipah-alert-sounded-in-kerala-after-two-unnatural-deaths-all-you-need-to-know-101694479958878.html

















