Description
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.theirishroadtrip.com/northern-ireland/
Context: After two years of deadlock, Northern Ireland finally has a functioning government with Michelle O'Neill of Sinn Féin as First Minister and Emma Little-Pengelly of the Alliance Party as Deputy First Minister.
Details
- The resolution of the long-standing deadlock in Northern Ireland and the formation of a functional government after two years are significant developments with several implications:
Background and Unique Governance System
- Creation of Northern Ireland (1921): In 1921, Northern Ireland was established through the partitioning of Ireland, comprising six northeastern counties. This division was a response to the complex religious and political dynamics on the island.
- Good Friday Agreement (1998): The Good Friday Agreement, signed in 1998, marked the end of decades of violence and conflict in Northern Ireland. It established a power-sharing system to ensure representation for both unionists (those loyal to the British Crown) and nationalists (those advocating for a united Ireland).
- Power-sharing in Stormont: Stormont, the seat of the devolved government in Belfast, was designed to accommodate both unionist and nationalist communities. The power-sharing arrangement involves the appointment of a First Minister and Deputy First Minister from the two largest political factions, with equal powers.

Collapse of Parliament in 2022
- Brexit and Northern Ireland Protocol: The implementation of the Northern Ireland Protocol, a consequence of the UK's departure from the European Union, introduced checks between Great Britain and Northern Ireland to avoid a hard border with the Republic of Ireland.
- Sir Jeffrey Donaldson's Decision: Sir Jeffrey Donaldson, the leader of the Democratic Unionist Party (DUP), opposed the Northern Ireland Protocol, believing it undermined Northern Ireland's position within the UK. As a response, he refused to allow the formation of a government after the May 2022 elections, resulting in the collapse of the Parliament.
Resolution Efforts and the New Deal
- Windsor Framework (February 2023): In an attempt to address unionist concerns, the Windsor Framework was introduced in February 2023. It included measures like green lanes for goods staying in Northern Ireland and red lanes for those going to the EU, along with the 'Stormont Brake' to provide lawmakers the ability to veto unfavourable EU regulations.
- Inadequacy for the DUP: The DUP, particularly under the leadership of Sir Jeffrey Donaldson, considered the measures in the Windsor Framework insufficient, leading to a prolonged political deadlock
- 'Safeguarding the Union' Deal (February 2024): The UK government presented a new deal named 'Safeguarding the Union.' This deal included significant changes to the Northern Ireland Protocol, such as renaming the green lane to the UK Internal Market channel, reducing checks to "risk and intelligence-based checks," and introducing an Internal Market Guarantee for 80% of goods. Additionally, a financial package of £3.3 billion was pledged to support Northern Ireland's finances.
Challenges for the New Government
- Diverse Responsibilities: While certain matters like security, foreign policy, tax laws, and immigration are overseen by the UK government, the devolved government in Northern Ireland has powers over local matters such as health and social services.
- Impact of Prolonged Deadlock: The extended political deadlock adversely affected public services, with public sector employees protesting delayed salary hikes.

Significance of the Resolution
- Restoration of Governance: The resolution of the deadlock is essential for restoring effective governance in Northern Ireland. This allows the government to address pressing issues and deliver essential public services.
- Political Stability: The formation of a new government brings a degree of political stability, fostering cooperation between unionists and nationalists and potentially reducing tensions.
|
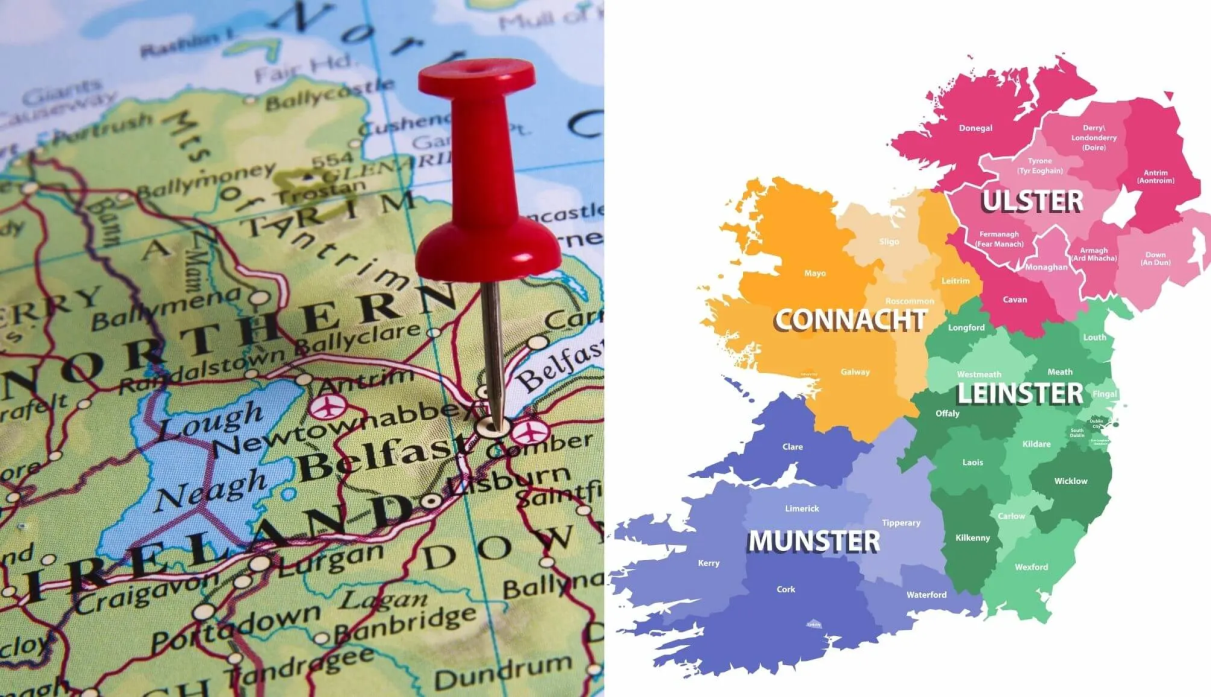
Northern Ireland
●Occupying roughly one-sixth of the island of Ireland, Northern Ireland shares its land border with the Republic of Ireland to the south and west.
●The Irish Sea borders its east and north, opening it up to maritime trade and connections with Great Britain.
●The Mourne Mountains are in the east, with Slieve Donard as the highest peak. The Sperrin Mountains in the west.
●The mighty River Bann, the longest river in Northern Ireland, cuts through the heart of the region, eventually flowing into the Atlantic Ocean.
|
Conclusion
- The resolution of the Northern Ireland deadlock involves complex historical, political, and socio-economic factors. The appointment of Michelle O'Neill as the First Minister and the new deal present steps toward overcoming challenges and ensuring effective governance in the region.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. With the rise of China and the ongoing war in Ukraine, how can India and the EU cooperate more effectively on global security challenges? Explore the potential for joint initiatives in areas like maritime security, counterterrorism, and cybersecurity, while acknowledging their differing perspectives on issues like NATO and the Indo-Pacific.
|