



Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
About OSA
Impact
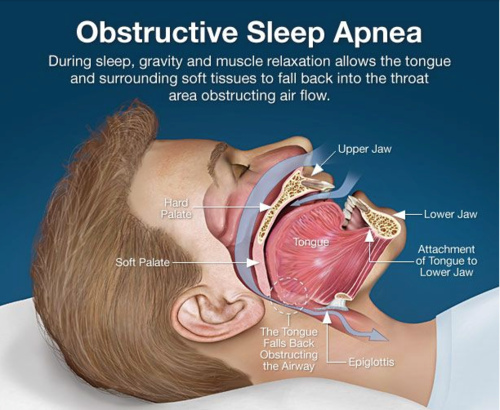
Cause
Symptoms
Aftermath
Treatment











© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved