




Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.cfr.org/backgrounder/what-hamas
Context: The resignation of the Palestinian Authority (PA) government in February 2024 was a significant event with several contributing factors and potential consequences.
Possible Reasons for Resignation
About Palestinian Authority (PA)
Formation and Oslo Accords
Jurisdiction
Government Structure
International Recognition
Relations with Israel
Hamas and Gaza
|
Palestine |
|
|
Key Points |
Description |
|
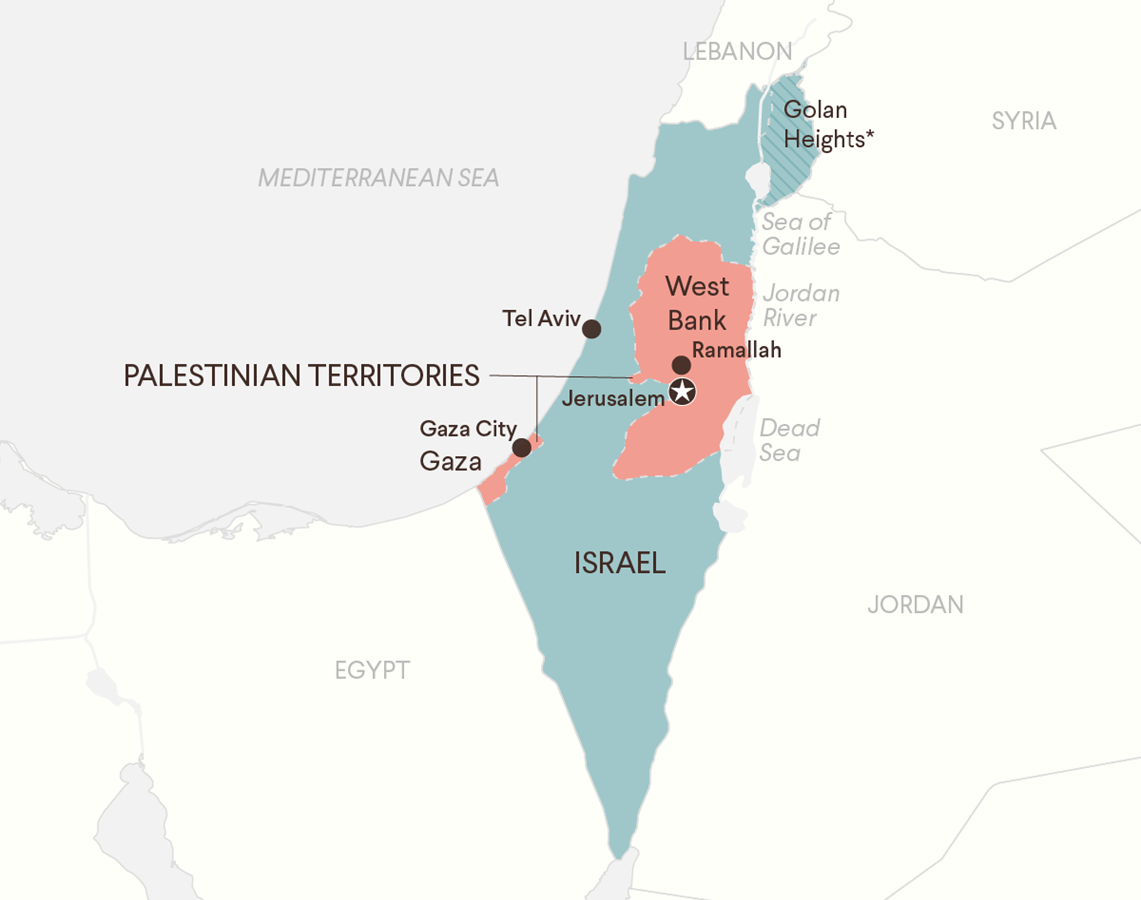
Geographical Location |
Palestine refers to a historical and present-day region in the Middle East, located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River. |
|
Governance & Status |
There is no single, unified Palestinian state. The Palestinian territories consist of: ●West Bank: Currently under Israeli occupation, but with limited Palestinian self-rule in certain areas. ●Gaza Strip: A coastal territory under the control of the Hamas government, blockaded by Israel & Egypt. The final status of both territories is highly disputed and the subject of peace negotiations. |
|
Demographics |
The primary ethnic group is Palestinian Arabs, who are predominantly Muslim with a Christian minority. A significant global Palestinian diaspora also exists. There is also a substantial Israeli population, mainly Jewish, living in settlements within the West Bank. |
|
Historical Context |
Palestine has a long and complex history marked by various empires and rulers. Key modern historical points include: ●Zionism: The late 19th-century nationalist movement for a Jewish homeland in the region. ●British Mandate: The period of British rule (1920-1948) saw rising tensions between Jewish and Arab populations. ●1948 War: Following Israel's declaration of independence, war erupted, leading to the displacement of many Palestinians (known as the Nakba). ●1967 War: Israel captured the West Bank, Gaza Strip, and other territories. ●Ongoing Occupation: Israel's ongoing presence in and control over the West Bank is a point of major dispute. |
|
Key Issues in the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict |
Borders: Disputes over the final borders of a potential Palestinian state and of Israel. Jerusalem: Both Israelis and Palestinians claim Jerusalem as their capital; the city has holy sites for Judaism, Islam, and Christianity. Palestinian Refugees: Millions of Palestinians were displaced in the 1948 conflict and their descendants; their right of return is disputed. Israeli Settlements: Israeli settlements in the West Bank are considered illegal by most of the international community and a major obstacle to peace. Security: Continuing violence and security concerns for both Palestinians and Israelis. |
|
Peace Efforts |
Decades of negotiations and peace proposals, including: ●Oslo Accords (1993): Set up the Palestinian Authority but failed to resolve final status issues. ●Two-State Solution: The most widely proposed solution, envisioning an independent Israel and Palestine existing side-by-side. However, prospects for this solution seem increasingly diminished. |
Conclusion
Must Read Articles:
INDIA’S STAND ON THE ISRAEL-PALESTINE ISSUE: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/indias-stand-on-the-israel-palestine-issue
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. How does India's stance on the Israel-Palestine issue impact it’s broader diplomatic relations, both in the Middle East and globally, and how does it influence India's standing in international forums? |


© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved