Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
The Panama Canal and the challenges it is facing due to a prolonged drought and the impact of climate change.
Details
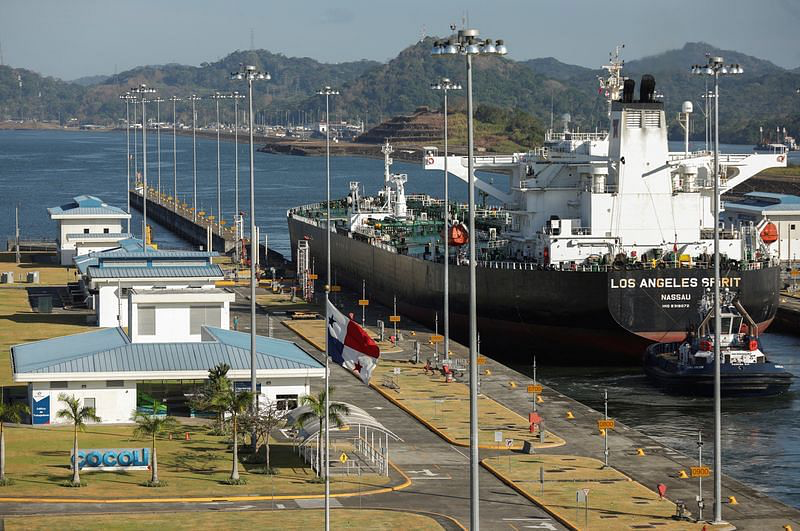
- The Panama Canal is one of the world's busiest trade passages, connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
- The canal authority faces challenges due to a prolonged drought and the impact of climate change.
Extended Restrictions and Limited Crossings
- The Panama Canal Authority (ACP) extends restrictions on ships' maximum depth and limits average crossings to 32 ships per day.
- The ACP maintains a depth limit of 44 feet for neo-Panamax container ships and postpones further restrictions that would have increased depth limits.
- During the rainy season, an average of 35-36 ships typically cross the canal each day, using 51 million gallons of water.

Significance of the Panama Canal
- Approximately 5% of the world's maritime trade passes through the 80-kilometer inter-oceanic waterway.
Impact of Prolonged Drought and Climate Change
- The canal authority faces an extended dry season with high evaporation rates and historically unprecedented lack of precipitation.
- Weather conditions and the potential El Nino condition may influence the depth limit in the future.
- The canal has implemented water-efficiency measures in response to climate change.
Outlook and Long-Term Planning
- The depth limit will remain at the current level as long as weather conditions do not drastically change.
- The ACP prepares for the long-term effects of climate change on the canal's operations.
About Panama Canal
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
- The Panama Canal is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean.
- The canal is 82 kilometers (51 miles) long and cuts across the Isthmus of Panama.
- The canal was built by the United States between 1904 and 1914.
- The canal is a vital economic asset for Panama and a major tourist attraction.
History
- The idea of a canal across the Isthmus of Panama was first proposed in the 16th century.
- Several attempts were made to build a canal in the 19th century, but they were all unsuccessful.
- The United States began construction of the Panama Canal in 1904.
- The canal was officially opened on August 15, 1914.
Construction
- The construction of the Panama Canal was a massive undertaking.
- Over 25,000 workers died during the construction of the canal.
- The canal was built using a system of locks, which raise and lower ships as they pass through the canal.
Operation
- The Panama Canal is operated by the Panama Canal Authority.
- The canal is open 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
- The canal can accommodate ships up to 120,000 deadweight tons.
Economic Importance
- The Panama Canal is a vital economic asset for Panama.
- The canal generates billions of dollars in revenue each year.
Tourism
- The Panama Canal is a major tourist attraction.
- Millions of people visit the canal each year.
- The canal offers a variety of tours and activities.
Future
- The Panama Canal is expected to continue to be a vital economic asset for Panama.
- The canal is undergoing a major expansion project, which will allow larger ships to transit the canal.
- The Panama Canal is a marvel of engineering and a testament to the ingenuity and determination of the people who built it.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q) Discuss measures to address the water scarcity issue and enhance the Panama canal's resilience in the context of climate change. (150 words)
|
.jpg)
https://theprint.in/environment/drought-hit-panama-canal-restricts-daily-crossings-in-water-saving-move/1686133/















