Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Context - The Prime Minister visited Jammu and Kashmir to celebrate National Panchayati Raj Day.
Details
- Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi visited Jammu and Kashmir to participate in the celebration of National Panchayati Raj Day.
- National Panchayati Raj Day is celebrated to mark the Panchayati Raj Systems in India.
- It is celebrated every year on the 24th of April.
- The day is also marked to honour the passing of the 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act in 1992.
- On this occasion, the Prime Minister addressed all the Gram Sabhas across the country.
- The Prime Minister has inaugurated and laid the foundation stone of multiple development projects.
- The Projects cost around Rs 20,000 crore and are related to connectivity and electricity.
- It will provide employment and promote socio-economic development in Jammu and Kashmir
- Prime Minister has also launched the Amrit Sarovar initiative.
- Aimed at developing and rejuvenating 75 water bodies in each district of the country as a part of the celebration of Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- PM urged that these sarovars should be lined with trees named after the martyrs and freedom fighters.
- Prime Minister has inaugurated the Banihal-Qazigund Road Tunnel, built at a cost of over Rs 3100 crore.
- The tunnel would provide an all-weather connection between Jammu and Kashmir.
- Prime Minister has laid the foundation stone of:
- 3 road development project Delhi-Amritsar-Katra Expressway, at a cost of over Rs. 7500 crore.
- The 850 MW Ratle Hydroelectric Project will be constructed on the Chenab river at a cost of around Rs 5300 crore.
- The 540 MW Kwar Hydroelectric Project will also be built on the Chenab river at a cost of over Rs. 4500 crore.
- Prime Minister Inaugurated 100 Jan Aushadi Kendras in J&K to make good quality generic medicines at affordable prices available,
- The Prime Minister handed over SVAMITVA cards to beneficiaries.
- On the occasion of the National Panchayat Raj Day, the following awards are being given to the best performing Panchayats.
- Deen Dayal Upadhyay Panchayat Sashaktikaran Puraskar
- Nanaji Deshmukh Rashtriya Gaurav Gram Sabha Puraskar
- Gram Panchayat Development Plan Award
- Child-friendly Gram Panchayat Award.
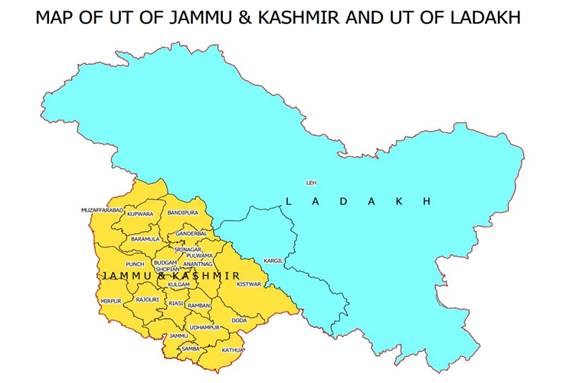
Status of Jammu and Kashmir
- Jammu and Kashmir lie to the north of the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab and to the west of Ladakh, which is also subject to the dispute as a part of Kashmir, and administered by India as a union territory.
- Some areas have been disputed between India and Pakistan since 1947 and between India and China since 1962.
- The Line of Control separates Jammu and Kashmir from the Pakistani-administered territories of Azad Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan in the west and north.
- The state of Jammu and Kashmir was accorded special status by Article 370 of the Constitution of India.
- Jammu and Kashmir had their constitution, flag and administrative autonomy.
- Indian citizens from other states were not allowed to purchase land or property in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Unrest and violence persisted in the Kashmiri Valley and, following a disputed state election in 1987, an insurgency persisted in protest over autonomy and rights.
- A resolution to repeal Article 370 was passed by both the houses of the Parliament of India in August 2019. At the same time, a reorganization act was also passed, which reconstituted the state into two union territories, Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. The reorganization took effect on 31 October 2019.
- This also suspended Article 35A.
- Article 35A had allowed J&K to define who its ‘permanent residents’ are and what rights and privileges are attached to such residency.
- At present, the union territory of Jammu and Kashmir is administered under the provisions of Article 239 of the Constitution of India.
- Article 239A, originally formulated for the union territory of Puducherry, will also apply to Jammu and Kashmir.
- The union territory is under the jurisdiction of the Jammu and Kashmir High Court, which also serves as the high court for Ladakh.
- In Parliament: Jammu and Kashmir now have 5 Lok Sabha Seats and 4 Rajya Sabha Seats.
Copyright infringement not intended
Key facts about Jammu and Kashmir
- Jammu and Kashmir is home to several valleys such as the Kashmir Valley, Tawi Valley, Chenab Valley, Poonch Valley, Sind Valley and Lidder Valley.
- The Himalayas divide the Kashmir valley from the Tibetan plateau while the Pir Panjal range, which encloses the valley from the west and the south, separates it from the Punjab Plain of the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
- The Jhelum River is the major Himalayan river which flows through the Kashmir valley. The Tawi, Ravi and Chenab are the other important rivers flowing through the region.
- The union territory of Jammu and Kashmir is divided into 20 districts and consists of two divisions: the Jammu Division and the Kashmir Division.
- Important Tribes; Gujjar, Bakerwal, and Gaddi.
- The most widely spoken language in Jammu and Kashmir is Kashmiri, the mother tongue of 52.72% of the population according to the 2011 census. The second most spoken language is Dogri, spoken by 20% of the population.
- According to the 2011 census, the literacy rate in Jammu and Kashmir was 67.17%.
Step by the Government to promote rural development
- Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushal Yojna
- It is a placement linked skill development scheme for rural poor youth.
- Swachchh Bharat Mission
- To provide access to every person to sanitation facilities including toilets, solid and liquid waste disposal systems, village cleanliness and safe and adequate drinking water supply.
- Sansad Adarsh Gram Yojna
- Each Member of Parliament will take the responsibility for developing physical and institutional infrastructure in selected villages.
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS)
- Provide ‘right to work' to the people falling Below Poverty Line.
- It guarantees 100 days of employment in a year to the village people.
- 50 workers should be women.
- National Rural Livelihood Mission
- Under this scheme, the government provides loans up to 3 lakh rupees at the rate of 7% which could be lowered to 4% on the timely repayment.
- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojna
- To provide all-weather road connectivity to the rural areas whose population is more than 500 persons and in terms of hilly areas, it is 250 persons.
- Antyodaya Anna Yojna (AAY)
- The scheme provides food grains to Below Poverty Line (BPL) families at a very subsidized rate.
- A total of 35 kg of food grains is provided to a family. Rice is provided at the rate of Rs. 3/kg and wheat at 2 Rs.2/kg.
- National Rural Health Mission
- To provide accessible, affordable and accountable quality health services even to the poorest households in the remotest rural regions.
- Aam Aadmi Bima Yojna
- Under this scheme, one member of the family is covered.
- The premium of Rs. 200 per person per annum is shared by the state and central governments.
- The insured person need not pay any premium if his/her age is between 18 years to 59
- Sarva Siksha Abhiyan
- Its main aim is to make free and compulsory education for children between the ages of 6 to 14, a fundamental right.
- The right to education is related to the 86th Amendment to the Constitution of India.
https://indianexpress.com/article/india/narendra-modis-palli-kashmir-youths-7884971/














