Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Dozens of people have died in a tribal dispute in Papua New Guinea's remote Highlands region.
Details
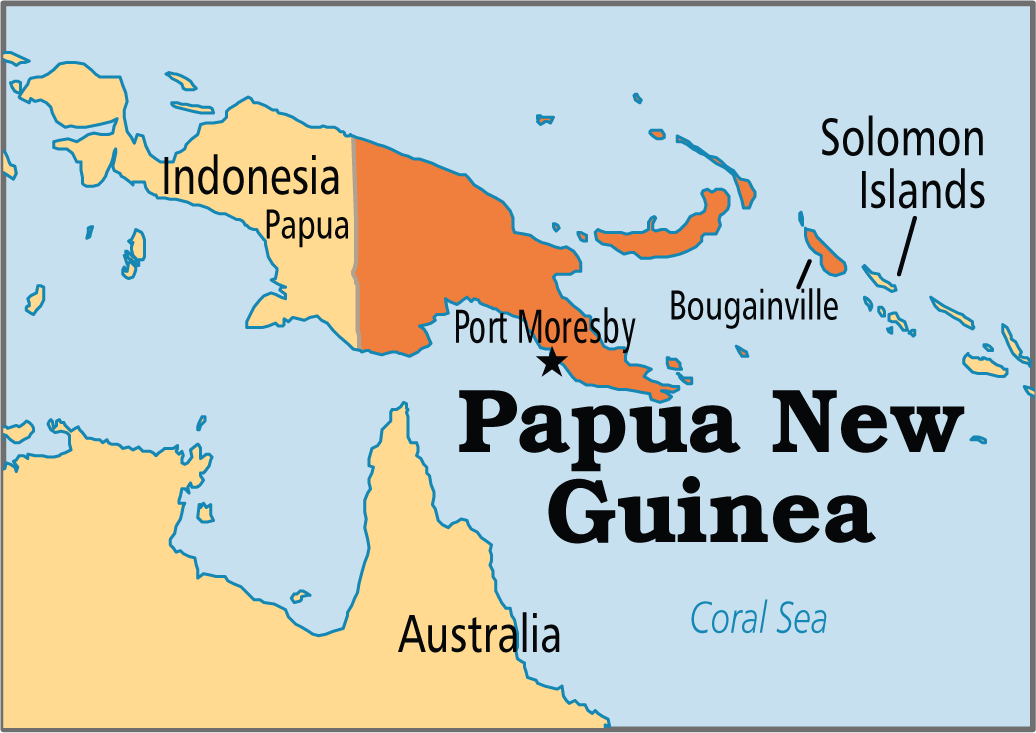
Papua New Guinea
- Situated just north of Australia and to the east of Indonesia, Papua New Guinea is part of the region known as Melanesia. It shares a border with Indonesia's Papua province to the west, with the remainder of the island belonging to Indonesia.
- It encompasses the eastern half of New Guinea, the world’s second largest island (the western half is made up of the Indonesian provinces of Papua and West Papua) the Bismarck Archipelago (New Britain, New Ireland, the Admiralty Islands, and several others); Bougainville and Buka (part of the Solomon Islands chain); and small offshore islands and atolls.
- The national capital, Port Moresby, is located in southeastern New Guinea on the Coral Sea.
Terrain
- The landscape of Papua New Guinea is incredibly diverse, ranging from dense rainforests and rugged mountains to coastal plains and coral reefs.
- The central part of the island is dominated by the rugged Central Highlands, with peaks exceeding 4,000 meters (13,000 feet) in elevation. The country is also home to active volcanoes, including Mount Tavurvur and Mount Ulawun.

Climate
- Papua New Guinea has a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures and humidity throughout the year. The coastal regions experience hot and humid conditions, while the highlands enjoy cooler temperatures.
- The country receives significant rainfall, especially in the central and northern regions, contributing to its lush rainforests and rich biodiversity.
Biodiversity
- Papua New Guinea is renowned for its exceptional biodiversity, with a vast array of plant and animal species found nowhere else on Earth.
- Its rainforests are home to countless species of birds, mammals, reptiles, and insects, including unique creatures such as tree kangaroos and birds of paradise.
- The country's marine environment is equally diverse, with vibrant coral reefs teeming with life.
Rivers
- Papua New Guinea is crisscrossed by numerous rivers, many of which are vital transportation arteries for remote communities. The Sepik River, one of the country's longest rivers, meanders through the northern lowlands, while the Fly River flows through the southwestern region.
- These waterways are not only important for transportation but also support diverse ecosystems and traditional fishing practices.
Cultural Diversity
- Papua New Guinea is one of the most culturally diverse countries in the world, with over 800 distinct languages spoken by its indigenous population.
- Each region boasts its own unique traditions, customs, and artistic expressions, including elaborate rituals, dances, and art forms.
- Traditional village life remains significant in many parts of the country, alongside modern urban centers.
Recent Development
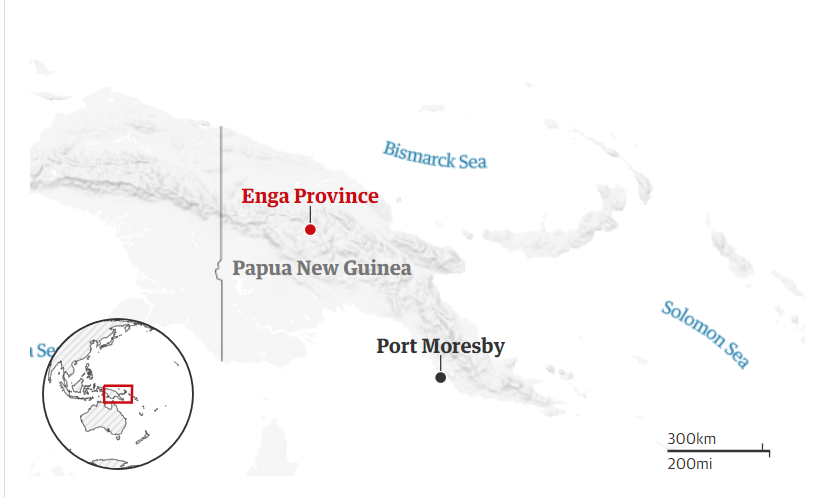
- Dozens of people have died in a tribal dispute in Papua New Guinea's remote Highlands region.
- The victims were shot dead during an ambush in the Enga province over the weekend.
- Escalating tribal conflict - often over the distribution of land and wealth - led to a three-month lockdown in Enga 2023 July, during which police imposed a curfew and travel restrictions.
- Papua New Guinea is home to hundreds of distinct ethnic groups, each with its own language, customs, and traditions. While many communities coexist peacefully, competition for resources, land disputes, and historical grievances can sometimes escalate into conflicts between tribes or clans.
Other Challenges
- Despite its natural beauty and cultural richness, Papua New Guinea faces various challenges, including poverty, limited infrastructure, and environmental conservation issues.
- Rapid population growth, coupled with urbanization and resource extraction activities, has placed pressure on the country's natural resources and traditional ways of life.
- Additionally, Papua New Guinea is prone to natural disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis, and tropical cyclones. Efforts to address these challenges and promote sustainable development are ongoing, both domestically and with international assistance.

Conclusion
Tribal conflict in Papua New Guinea remains a complex and multifaceted issue that requires comprehensive and sustainable approaches to address underlying grievances, promote social cohesion, and build resilient communities.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Bismarck Archipelago recently seen in news is located in which ocean/ Sea?
- Pacific Ocean
- Atlantic Ocean
- Indian Ocean
- North Sea
Answer A
|















