Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
What is a Payment Aggregator/Merchant Aggregator?
- A payment aggregator (also known as a merchant aggregator) is a third-party service provider that allows merchants to accept payment from customers by integrating it into their websites or apps.
- In other terms, a payment aggregator (PA) bridges the gap between merchants and acquirers.
- Under the payment aggregator model, merchants can process transactions through the aggregator’s Merchant Identification Number (MID). This means, your business doesn’t require a separate merchant account as the payment aggregator takes care of everything while levying a moderate fee. Thus, the PA receives payments from customers on the behalf of merchants. Finally, it transfers the payments to the merchant in batches after a period of time. This step is known as the settlement. The settlement may be standard i.e. it requires T+ 2 to 4 days. On the other hand, the settlement can be instant which can be as fast as 15 minutes.
.jpeg)
Laws and regulations pertaining to Payment Aggregators
- A payment aggregator in India is incorporated under the Companies Act, 1956 / 2013. Now, it can be a bank or a non-bank entity.
- Since a PA handles funds, it requires a license from the Reserve Bank of India.
- However, only non-bank payment aggregators require unique authorization from RBI. This is because ‘handling funds’ is considered a part of the normal banking relationships for bank PAs.
Eligibility
- According to RBI rules, a company applying for aggregator authorization must have
- A minimum net worth of Rs 15 crore in the first year of application, and
- At least Rs 25 crore by the second year.
- It also must fulfill the “fit and proper” criteria, and be compliant with global payment security standards.
Payment Gateway vs Payment Aggregator
- A payment gateway is a Payment Processing Software. Payment Gateways only deal with online transactions and are equipped with restricted payment options.
- Examples of payment gateways include Axis bank, HDFC, Union Bank of India, etc., as in India, most banks act as payment gateways.
- The key difference between a Payment Gateway & Aggregator is that while a Payment Gateway only provides the technology, a Payment Aggregator would also receive payments from consumers on the business/merchant’s behalf and then settles the same in their account.

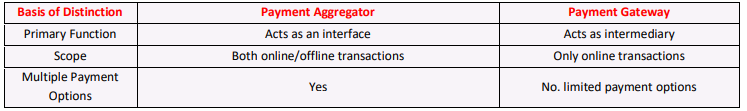
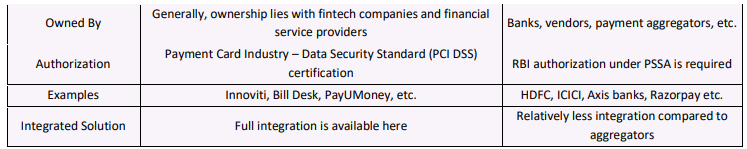
Payment Aggregator vs Payment Gateway
- While your business needs both payment services to function properly, here are some of the subtle differences between payment aggregator and payment gateway. Check out the given table to get a clear understanding of the differences.


https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/amazon-google-rbi-payment-aggregators-meaning-explained-8448767/#:~:text=Who%20are%20payment%20aggregators%3F,such%20entities%20in%20March%202020.
Array
(
[0] => daily-current-affairs/payment-aggregator
[1] => daily-current-affairs
[2] => payment-aggregator
)











