Description
GS PAPER III: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
Context: Indian Scientists have recently developed a theory that helps understand the complicated nature of Sun-Earth interaction's happening in the magnetosphere-- an area of space around Earth that is controlled by the Earth’s magnetic field.
- This new theory has opened up a plethora of opportunities to unlock the mysteries of the ion-hole structures (a localized plasma region where the ion density is lower than the surrounding plasma).
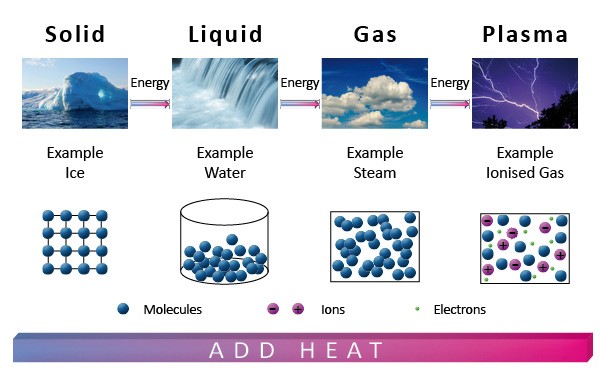
What is Plasma?
- Plasma is superheated matter – so hot that the electrons are ripped away from the atoms forming an ionized gas.
- It comprises over 99% of the visible universe.
- In the night sky, plasma glows in the form of stars, nebulas, and even the auroras that sometimes ripple above the north and south poles.
- That branch of lightning that cracks the sky is plasma and the neon signs along city streets.
- Plasma is often called “the fourth state of matter,” along with solid, liquid and gas.
- Just as a liquid will boil, changing into a gas when energy is added, heating a gas will form a plasma – a soup of positively charged particles (ions) and negatively charged particles (electrons).
Significance of knowing about plasma:
- Because so much of the universe is made of plasma, its behavior and properties are of intense interest to scientists in many disciplines.
- Researchers have used the properties of plasma as a charged gas to confine it with magnetic fields and to heat it to temperatures hotter than the core of the sun.
- Other researchers pursue plasmas for making computer chips, rocket propulsion, cleaning the environment, destroying biological hazards, healing wounds and other exciting applications.
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1720408










