Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Context: Ayushman Bharat, the world's largest health insurance scheme, aims to provide universal health coverage to the poor and vulnerable in India. However, official data revealed that more than a third of the hospitals empanelled under the scheme are inactive, raising concerns about its effectiveness and accessibility.
Details
- The Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY) is the world's largest health insurance scheme aimed at providing universal health coverage in India. However, official data has revealed a worrying trend of inactivity among the empanelled hospitals under the scheme. Out of the 27,000 hospitals empanelled since its launch in 2018, only 18,783 are currently active.
- The inactive hospitals can be categorized into two groups: 4,682 hospitals have been inactive since the beginning and have never treated a single PM-JAY beneficiary, and an additional 3,632 hospitals turned inactive in the last six months. This brings the total number of inactive hospitals to 8,314.
- The reasons for hospital inactivity may vary, but they could include dissatisfaction with the pricing packages for medical services or delayed payments. Some hospitals may also lack the necessary facilities for secondary and tertiary care hospitalization, leading to their inactivity under the scheme.
- The responsibilities for addressing the issue of hospital inactivity are with the state health authorities (SHAs) rather than the National Health Authority (NHA), which is implementing the scheme. NHA has set stringent guidelines to de-empanel hospitals that fail to raise even a single pre-authorization within six months of empanelment.
- The level of inactivity varies across states, with Andhra Pradesh and Rajasthan having the highest number of inactive hospitals.

Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY)
About
- It is a flagship health insurance program launched by the Government of India in 2018. The scheme aims to provide financial protection to vulnerable and economically weaker sections of society by offering health coverage for secondary and tertiary hospitalization.
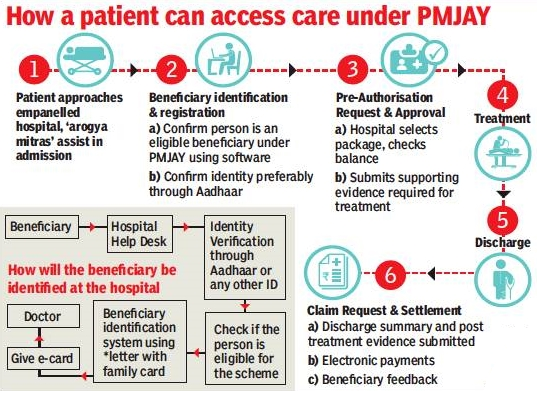
Features
- Universal Health Coverage: PM-JAY aims to cover over 100 million poor and vulnerable families, approximately 500 million beneficiaries, with a health insurance cover of up to ₹5 lahks per family per year for specified secondary and tertiary care treatments.
- Cashless Treatment: Beneficiaries can avail of cashless and paperless treatment at empanelled public and private hospitals across India.
- Empanelled Hospitals: The scheme has a network of both public (government) and private hospitals. As of the data mentioned earlier, around 15,000 private and 12,000 government hospitals are empanelled under PM-JAY.
- No Cap on Family Size: The scheme covers the entire family, including up to five members, and there is no cap on the family size or age of family members.
- Pre-existing Conditions: PM-JAY covers pre-existing conditions from day one of enrollment, ensuring access to treatment for existing health issues.
- Portability: The scheme is portable across India, meaning beneficiaries can avail treatment in any empanelled hospital in any state or union territory.
Significances
- Financial Protection: PM-JAY provides a crucial safety net to vulnerable sections of society by protecting them from catastrophic health expenditures that can push families into poverty.
- Improved Access to Healthcare: By providing cashless treatment at empanelled hospitals, PM-JAY enhances access to quality healthcare for millions of beneficiaries who may not have had access to it otherwise.
- Reduced Out-of-Pocket Expenditure: The scheme reduces the burden of out-of-pocket expenses for medical treatments, making healthcare more affordable for the poor.
- Health Outcomes: PM-JAY aims to improve health outcomes by facilitating timely access to appropriate medical care, especially for serious illnesses that require secondary and tertiary care services.
- Strengthening Healthcare Facilities: The scheme incentivizes hospitals to participate and improve their facilities to meet the standards required for empanelment, thus contributing to the overall improvement of healthcare infrastructure.
Challenges
- Inactivity of Empanelled Hospitals: As mentioned earlier, a significant number of hospitals empanelled under PM-JAY are inactive, which poses a challenge in ensuring adequate healthcare access for beneficiaries.
- Quality of Care: While the scheme focuses on financial protection, ensuring the quality of care delivered at empanelled hospitals is essential to achieve positive health outcomes.
- Information and Awareness: Some eligible beneficiaries might not be aware of the scheme or how to access it, leading to underutilization of the benefits.
- State Disparities: The level of implementation and participation may vary across states, leading to disparities in healthcare access among beneficiaries.
By addressing these challenges and building on their significance, the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana can continue to make significant strides in providing universal health coverage and financial protection to millions of vulnerable families across India.

Way Forward
- Addressing Hospital Inactivity: The authorities should work with state health authorities (SHAs) to identify the reasons behind hospital inactivity and take measures to incentivize and engage hospitals in the scheme.
- Quality Assurance: Regular monitoring and evaluation of empanelled hospitals' performance are necessary to ensure quality care and patient satisfaction.
- Awareness Campaigns: Launching targeted awareness campaigns to reach potential beneficiaries and educate them about the scheme and its benefits can increase participation.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly analyzing data and feedback from beneficiaries and healthcare providers can help identify areas for improvement and make necessary policy changes.
- Collaboration with States: Collaborating with state governments to address state-specific challenges and disparities will strengthen the implementation of the scheme.
Must Read Articles:
AYUSHMAN BHARAT PRADHAN MANTRI JAN AROGYA YOJANA (AB-PMJAY): https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/ayushman-bharat-pradhan-mantri-jan-arogya-yojana-ab-pmjay
PM-JAY SCHEME: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/pm-jay-scheme
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. What is the Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY), and what are its significance, impact, challenges, and the way forward for the scheme in providing universal health coverage and financial protection in India?
|
https://www.livemint.com/news/india/over-a-third-of-hospitals-empanelled-under-ayushman-bharat-scheme-in-new-delhi-are-inactive-official-data-11690305764552.html















