Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
Earlier this month, a sudden atmospheric warming event caused the Arctic's polar vortex to reverse its trajectory.
Details
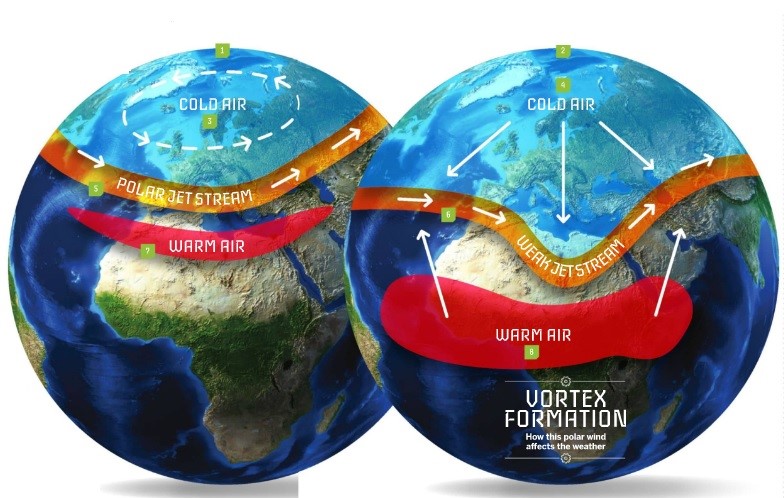
Polar Vortex
- The polar vortex is a large area of low pressure and cold air surrounding both of the Earth’s poles.
- It ALWAYS exists near the poles, but weakens in summer and strengthens in winter.
- The term "vortex" refers to the counter-clockwise flow of air that helps keep the colder air near the Poles.
How does the polar vortex work?
- The vortex is constantly spinning in a counter-clockwise direction around the North Pole.
- During the summer months in the Northern Hemisphere, the edge of the vortex sits at a higher latitude, and in winter months, it edges south.
- At the bottom edge of the vortex is the polar front, or polar jet stream.
- The polar jet stream moves from west to east, which is why the northeastern portions of North America are often hit the hardest by polar vortex weather.
- Jet streams are propelled forward by temperature differences and the Earth's rotation. Wider temperature differences create faster-moving winds.
- A strong polar jet stream moving roughly along the same latitude as the vortex makes the vortex more stable and traps cold Arctic air within the Arctic Circle.
- But occasionally the polar jet stream weakens, moving around the globe in a wavy pattern called arctic oscillations with peaks and troughs that allow warmer southern air to move north, and cold Arctic air to rush south.

Climate change and the polar front
- Scientists are studying how warming temperatures will influence weather patterns like winter storms in USA and Canada region.
- Scientists are now finding that the Earth is warming more quickly at the poles than at the mid-latitude regions, meaning the temperature contrast that drives jet streams has decreased.
- A study linked warmer-than-average Arctic temperatures to cold weather outbreaks in the eastern U.S. and another study found Arctic warming may increasingly disrupt the polar vortex itself, rather than the jet stream.
What caused the polar vortex reversal?
- Polar vortices occasionally reverse temporarily. These events can last for days.
- The prevailing west-to-east "screaming-fast winds" circling the North Pole have completely reversed twice this year.
- The culprit for the disruption lies on a sudden atmospheric warming caused by planetary waves that jostle the stratosphere from below and can reverse a vortex's flow.
.jpg)
Possible consequences of this reversal
- In the past, disruptions to the polar vortex — a rotating mass of cold air that circles the Arctic — have triggered extremely cold weather and storms across large parts of the U.S..
- The current change in the vortex's direction probably won't lead to a similar "big freeze." But the sudden switch-up has caused a record-breaking "ozone spike" above the North Pole.
- The change in air temperature around the Arctic has sucked up large amounts of ozone from lower latitudes, creating a temporary ozone spike — the opposite of an ozone hole.
|
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
How does climate change impact extreme weather events? Discuss 150 words
|











