Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: uinewz.com
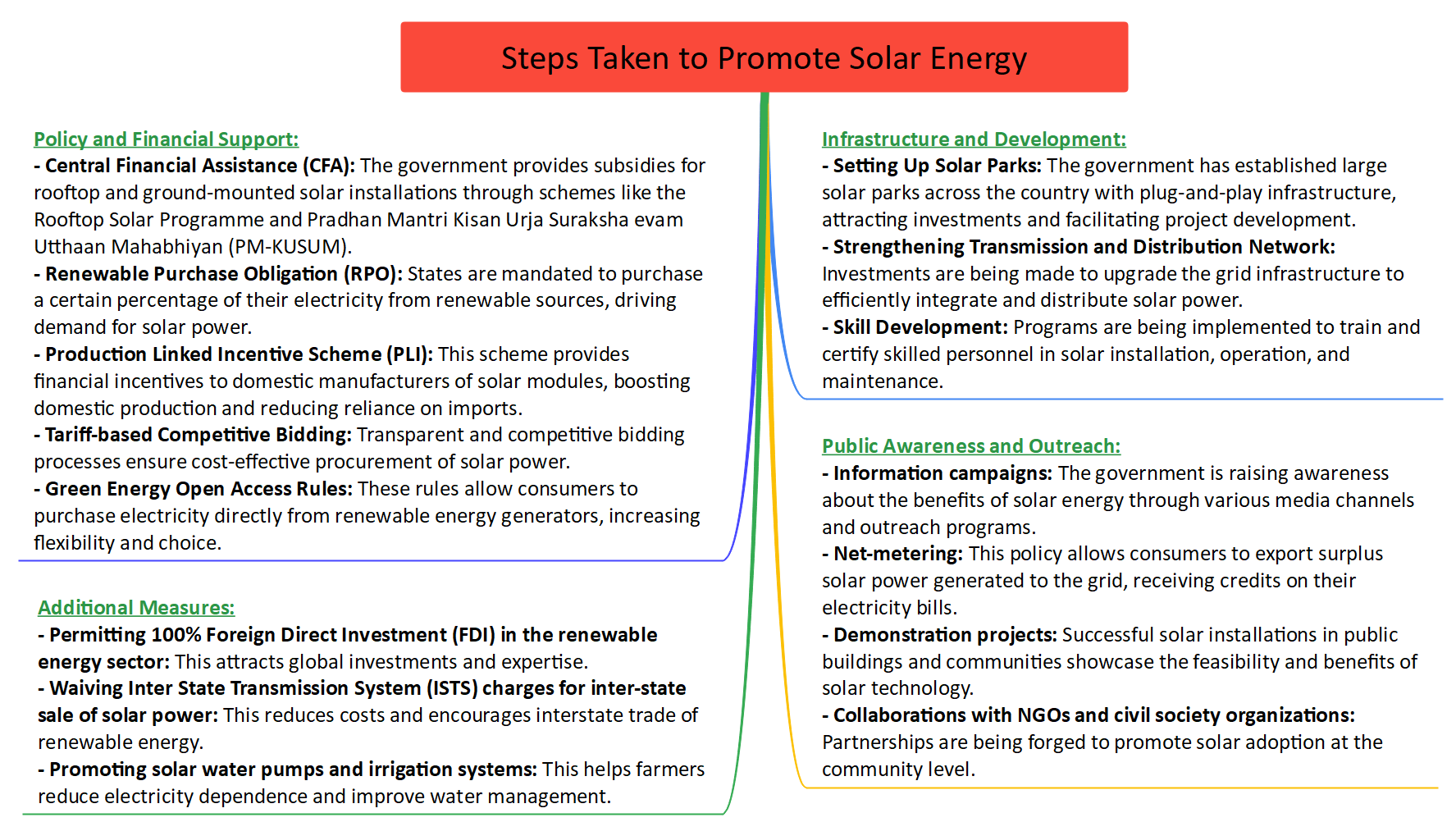
Context: The Pradhan Mantri Suryodaya Yojana, launched by the Prime Minister, aims to install solar power systems on the rooftops of residential buildings, with a specific target of covering 1 crore (10 million) houses across India.
Key Highlights
- The primary goals of the scheme include reducing electricity bills for the poor and middle class while contributing to India's self-reliance in the energy sector.
- By encouraging widespread adoption of solar power at the household level, the government aims to boost renewable energy usage and decrease reliance on traditional energy sources.
India's Current Solar Capacity
- As of December 2023, India's total solar capacity stands at approximately 73.31 gigawatts (GW), with rooftop solar contributing around 11.08 GW. This solar capacity is distributed across states, with Rajasthan leading in total solar capacity (18.7 GW) and Gujarat topping the list in rooftop solar capacity (2.8 GW).
- Solar power plays a significant role in India's total renewable energy capacity, which stands at around 180 GW. The country's commitment to renewable energy is evident in its efforts to achieve ambitious targets, aiming for 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030.
Importance of Solar Energy Expansion
- India is expected to experience the largest energy demand growth globally over the next 30 years, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). To meet this increasing demand, a reliable and sustainable source of energy is crucial, necessitating a shift away from traditional sources like coal.
- While India has increased its coal production, it is also committed to reaching 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030. Solar energy, in particular, has seen significant growth, rising from less than 10 MW in 2010 to 70.10 GW in 2023.
Rooftop Solar Programme
- Launched in 2014, the Rooftop Solar Programme focuses on expanding rooftop solar installed capacity in the residential sector. It provides Central Financial Assistance and incentives to distribution companies (DISCOMs).
- The programme's goal is to achieve 40 GW of rooftop solar installed capacity by March 2026. Noteworthy progress has been made, with rooftop solar capacity increasing from 1.8 GW in March 2019 to 10.4 GW in November 2023.
- Consumers can benefit from the scheme through DISCOM tendered projects or the National Portal (www.solarrooftop.gov.in). The scheme empowers consumers to choose vendors and solar equipment based on their preferences. After installation and inspection, subsidies are directly transferred to consumers' bank accounts.
- Consumers have the opportunity to export surplus solar power to the grid, receiving monetary benefits in accordance with prevailing regulations set by State Electricity Regulatory Commissions (SERCs) or Joint Electricity Regulatory Commissions (JERCs).

Pradhan Mantri Suryodaya Yojana
- To promote the adoption of rooftop solar systems in India, the Prime Minister announced the Pradhan Mantri Suryodaya Yojana (PMSY).
- The PMSY is a government scheme that aims to install rooftop solar systems in 1 crore (10 million) households across the country.
Features
- The scheme will target low and middle-income households who can benefit from reduced electricity bills and additional income from surplus electricity generation.
- The scheme will provide financial assistance to eligible households in the form of subsidy, loan or incentive, depending on their category and location.
- The scheme will also provide technical assistance to the households in terms of installation, operation and maintenance of the rooftop solar systems.
- The scheme will be implemented by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) in collaboration with state governments, distribution companies, banks and other stakeholders.
Significances
- The scheme will also help India meet its commitment under the Paris Agreement to reduce its emissions intensity by 33-35% by 2030 from 2005 levels.
- The scheme will contribute to India's vision of becoming self-reliant (aatmanirbhar) in the energy sector by reducing its dependence on imported fossil fuels and enhancing its energy security.
- The scheme will also support India's social and economic development by providing clean and affordable electricity to millions of households, especially in rural and remote areas where grid access is limited or unreliable.
Challenges in scaling up rooftop solar in the country
- Lack of awareness and information among consumers about the benefits and procedures of rooftop solar installation.
- High upfront cost and lack of easy financing options for consumers to invest in rooftop solar systems.
- Regulatory hurdles and policy uncertainties regarding net metering, grid connectivity, tariff structure, etc. vary across states and regions.
- Technical issues such as poor quality of equipment, installation and maintenance services, grid integration and management, etc. affect the performance and reliability of rooftop solar systems.
Way forward
- Increasing awareness and outreach among consumers through mass media campaigns, workshops, exhibitions, etc. that showcase the benefits and success stories of rooftop solar.
- Providing financial incentives and subsidies to consumers, especially low and middle-income households, to reduce the upfront cost and payback period of rooftop solar systems.
- Streamlining and harmonizing the regulatory and policy framework across states and regions to ensure uniformity, clarity and stability for rooftop solar installation and operation.
- Improving the technical standards and quality control of rooftop solar equipment, installation and maintenance services, grid integration and management, etc. to ensure safety, efficiency and durability of rooftop solar systems.

Conclusion
- The Pradhan Mantri Suryodaya Yojana is a welcome initiative by the government to boost the adoption of rooftop solar in India. The scheme can help India achieve its renewable energy targets and climate goals, as well as enhance its energy security and social and economic development. However, the scheme also faces several challenges that need to be addressed through effective implementation and coordination among various stakeholders. If done well, the scheme can usher in a new dawn for India's solar energy sector and make every household a part of the sun's power.
Must Read Articles:
SOLAR ENERGY IN INDIA: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/solar-energy-in-india
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. As India aims for a decentralized energy future with increased reliance on rooftop solar, what technological advancements or policy frameworks are needed to optimize grid integration and ensure efficient management of fluctuating energy supplies?
|














