Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Scientists from the Raman Research Institute (RRI) an autonomous institute of the Department of Science and Technology, have used quantum computers to perform some precision tests of the fundamental aspects of the quantum theory called Sorkin and Peres tests.
Details
- Sorkin is a test of the probabilistic aspect of quantum mechanics which helps calculate the chances of events happening.
- Peres is a test of an aspect of the superposition principle, which expresses the fact that quantum objects may behave as waves -- throwing two stones in a pond gives a wave pattern which is the sum of two waves.
- The scientists have also shown that quantum mechanics is true and the tests can be used as a benchmark to evaluate how well a quantum computer performs.
- These Tests helps to create well defined benchmarks for quantum computers so that it can be known exactly how error prone they are.
What is quantum computing?
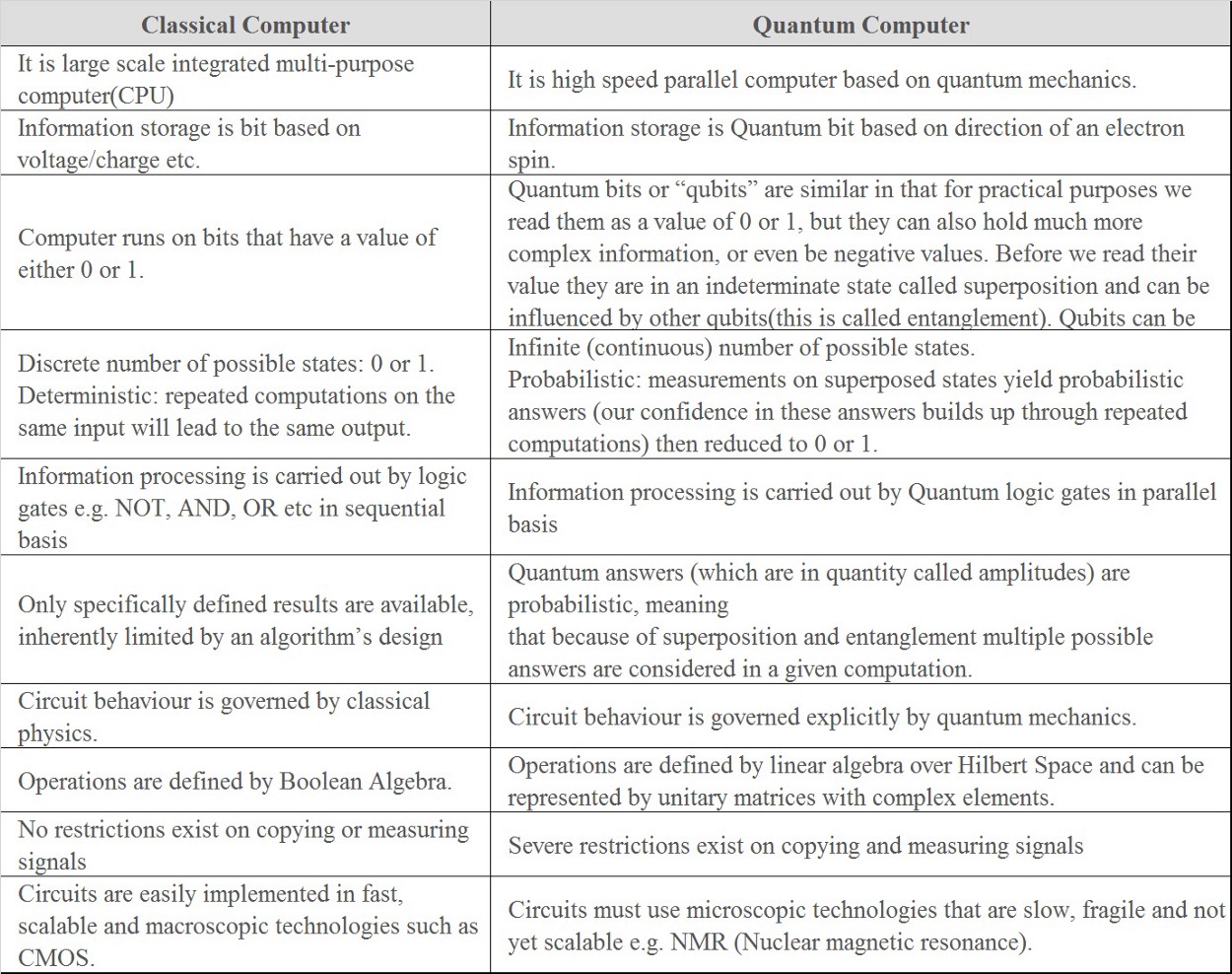
- An ordinary computer chip uses bits. These are like tiny switches that can either be in the off position – represented by a zero – or in the on position – represented by a one.
- Every app we use, website we visit and photograph we take is ultimately made up of millions of these bits in some combination of ones and zeroes.
- This works great for most things, but it doesn’t reflect the way the universe actually works.
- In nature, things aren’t just on or off. They’re uncertain. And even our best supercomputers aren’t very good at dealing with uncertainty. That’s a problem.
- So, for scientists to accurately simulate any of those things, they need a better way of making calculations that can handle uncertainty. Here enters the Quantum Computers.
- Quantum computing is a sophisticated approach to making parallel calculations, using the physics that governs subatomic particles to replace the more simplistic transistors in today’s computers.
- Quantum computers calculate using qubits, computing units that can be on, off or any value between, instead of the bits in traditional computers that are either on or off, one or zero.
- The qubit’s ability to live in the in-between state — called superposition — adds a powerful capability to the computing equation, making quantum computers superior for some kinds of math.
How do quantum computers work?
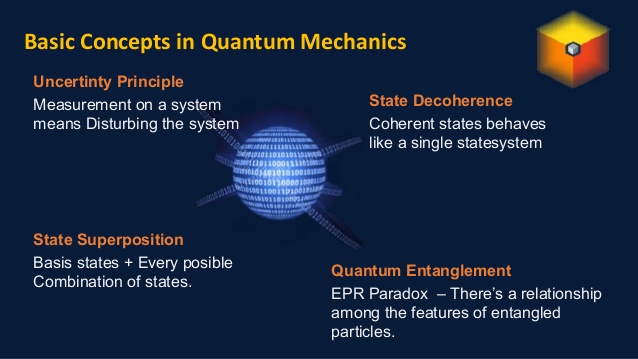
- Instead of bits, quantum computers use qubits. Rather than just being on or off, qubits can also be in what’s called ‘superposition’ – where they’re both on and off at the same time, or somewhere on a spectrum between the two. A qubit allows for uncertainty.
- The other thing that qubits can do is called entanglement. In entanglement, two particles are linked together, even if they’re physically separate.
Understanding Superimposition
- If we flip a coin, it can either be heads or tails. But if we spin it – it’s got a chance of landing on heads, and a chance of landing on tails. Until we measure it, by stopping the coin, it can be either.
- Superposition is like a spinning coin, and it’s one of the things that make quantum computers so powerful. A qubit allows for uncertainty.
- If we ask a normal computer to figure its way out of a maze, it will try every single branch in turn, ruling them all out individually until it finds the right one.
- A quantum computer can go down every path of the maze all at once. It can hold uncertainty in its head.
- For example, today’s computers use eight bits to represent any number between 0 and 255. Thanks to features like superposition, a quantum computer can use eight qubits to represent every number between 0 and 255, simultaneously.
- It’s a feature like parallelism in computing: All possibilities are computed at once rather than sequentially, providing tremendous speedups.
- So, while a classical computer steps through long division calculations one at a time to factor a humongous number, a quantum computer can get the answer in a single step.
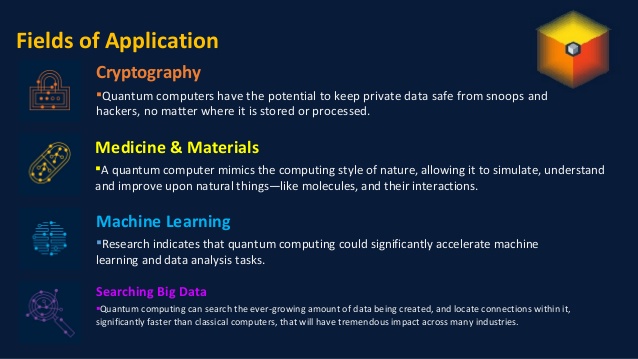
- That means quantum computers could reshape whole fields, like cryptography, that are based on factoring what are today impossibly large numbers.
Entanglement
- The other thing that quits can do is called entanglement. Normally, if we flip two coins, the result of one coin toss has no bearing on the result of the other one. They’re independent. In entanglement, two particles are linked together, even if they’re physically separate. If one comes up heads, the other one will also be heads.
- Quantum computing can be used to perform complex calculations. And if multiple qubits are stringed together, one can tackle problems that would take our best computers millions of years to solve.

|
Trivia
Chinese scientists claim to have built a quantum computer that is able to perform certain computations nearly 100 trillion times faster than the world’s most advanced supercomputer.
|
Quantum Entanglement
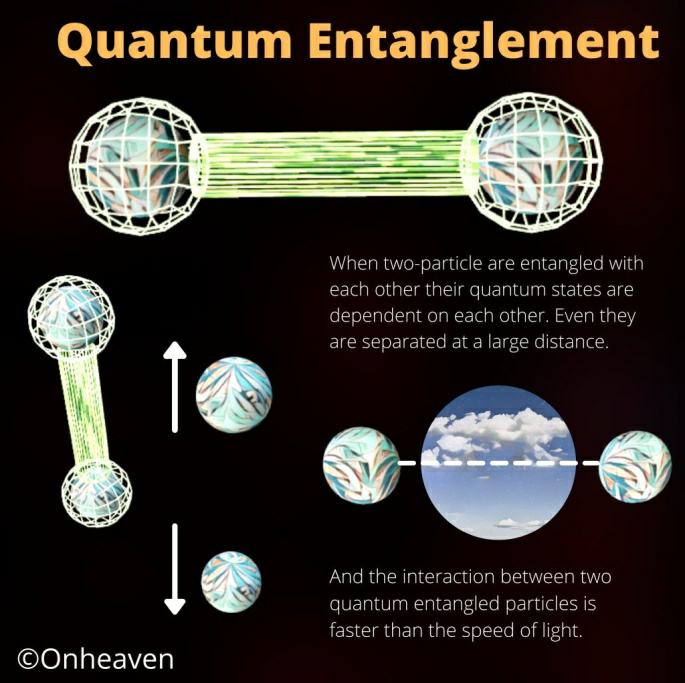
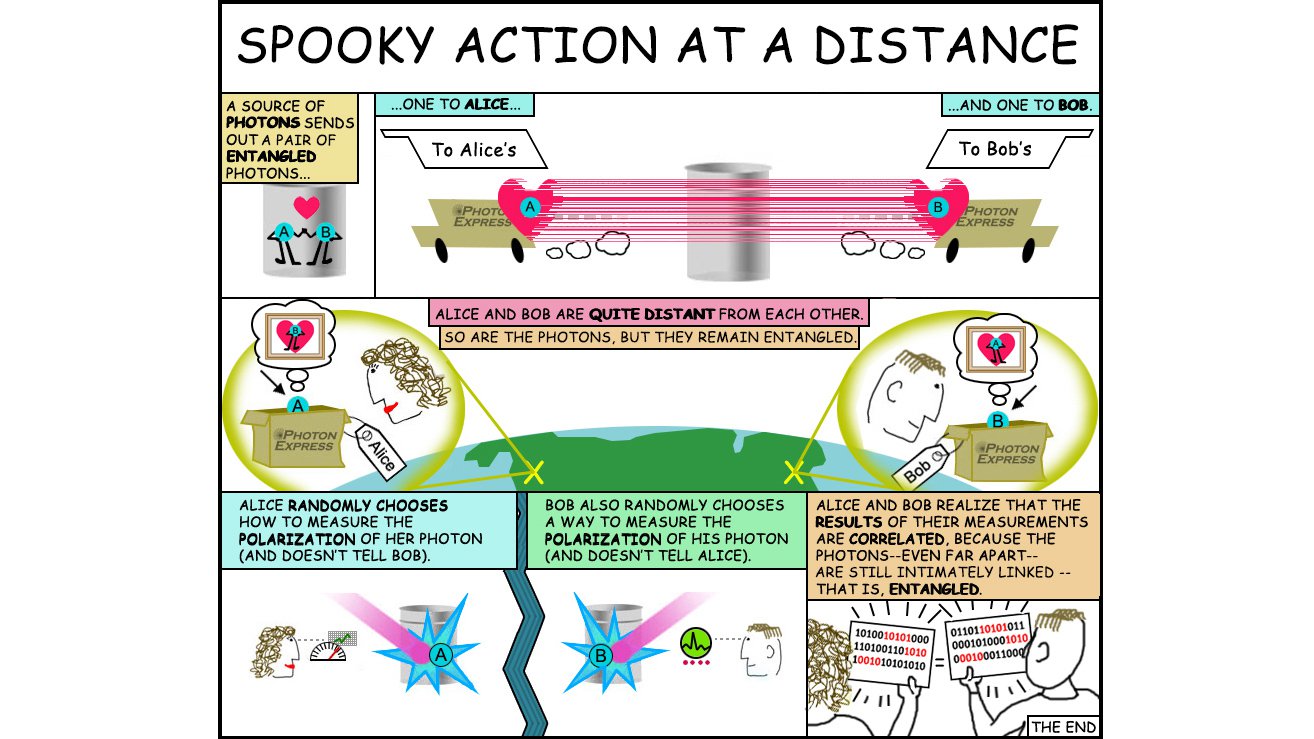
- Quantum entanglement is a physical phenomenon that occurs when a pair or group of particles is generated, interact, or share spatial proximity in a way such that the quantum state of each particle of the pair or group cannot be described independently of the state of the others, including when the particles are separated by a large distance.
- Measurements of physical properties such as position, momentum, spin, and polarization performed on entangled particles can, in some cases, be found to be perfectly correlated.
- Quantum entanglement has direct application in Quantum Computing.
India’s Efforts in this regard
QuEST Initiative
- The Department of Science and Technology launched the Quantum-Enabled Science and Technology (QuEST) initiative to invest INR 80 crores to lay out infrastructure and to facilitate research in the field.
QSim Toolkit
- Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) launched the ‘Quantum Computer Simulator (QSim) Toolkit’ to provide the first quantum development environment to academicians, industry professionals, students, and the scientific community in India.
Digital Partnership
- The digital partnership between the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) at Pune and Finland’s Aalto University has created a high probability of getting its first quantum computer.

Importance of Quantum Computing
- Developments in quantum computing will help India realize future expectations of various fields, including IT, health, ed-tech, finance, security, research, and many more Constant investment in R&D, autonomy, and hunger for new technologies hold the key to better prospects.
- Quantum computers are unbeatable when it comes to solving optimization problems with relevance in a variety of applications, from alleviating climate change to finding the best routes to a certain destination, or even when it comes to scheduling flights at airports.
Way Ahead
Developing a Knowledge Ecosystem
- Entrepreneurship, innovation, university courses at all levels, scholarships, fellowships, training programmes, and consulting in quantum technologywill be crucial towards developing a knowledge ecosystem and bridging the skill gap.
- This will lead to the creation of a dedicated quantum community in India, capable of collaborating with researchers and industry professionals worldwide.
Self-sufficiency in superconducting materials
- For developing a quantum computer at home, India will need superconducting materials, physical qubits, a data plane, chips, processors, and fabrication labs.Not enough impetus is given here.
- A few private companies and startups have started to develop these critical quantum components, but most hardware is still imported.
Boost to Investor Ecosystem
- India must give a boost to its investor ecosystem which can help amplify production of hardware components of a quantum computer and its applications.
Address implementation gaps
- Policy-level and implementation-level gaps need to be acknowledged and addressedin a timely manner, so as to ensure India emerges as a world leader in the quantum technology space.
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1816336























