Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- According to a new study, no matter how much carbon emissions are reduced, rapid melting of West Antarctica's ice sheet owing to warm waters surrounding it is now unavoidable.
Details
- The study, titled 'Unavoidable future increase in West Antarctic ice-shelf melting over the twenty-first century,' was published last week in Nature.
- If the ice sheet melted completely, it would raise global mean sea level by 5.3 meters (17.4 feet).
- If this occurs, it could have disastrous consequences for millions of people living in vulnerable coastal cities around the world, including India.
What is an Ice Sheet?
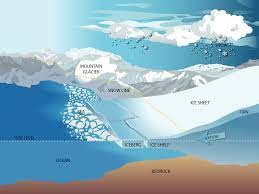
- An ice sheet is a mass of glacial ice that covers more than 50,000 square kilometers of land — roughly the size of Uttarakhand.
- Today, the planet has two large ice sheets: the Greenland ice sheet and the Antarctic ice sheet.
- They contain almost two-thirds of all freshwater on the planet.
- This means that as ice sheets gain mass, they contribute to a decrease in global mean sea level while losing mass contributes to a rise in global mean sea level.
What is the melting rate of the West Antarctic ice sheet?
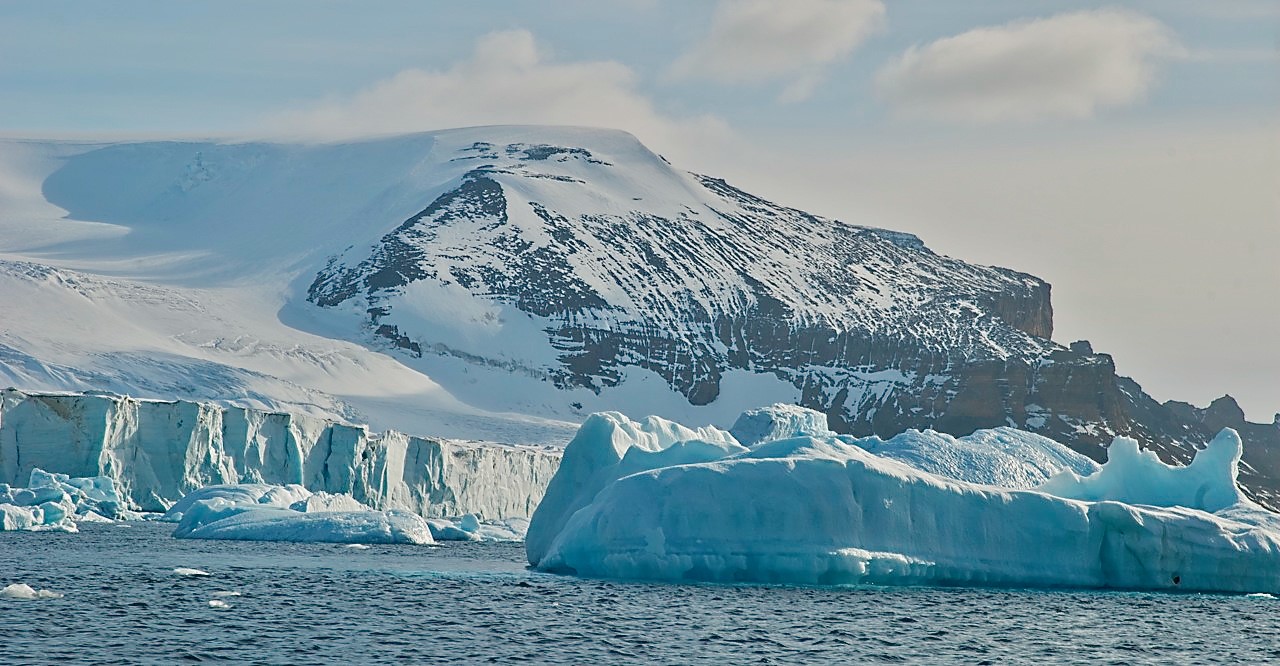

- Ice sheets melt through a variety of methods. One of these is when warm ocean waters melt ice shelves, which are the borders of floating ice sheets.
- Ice shelves help to stabilize the land-based glaciers behind them.
- When an ice shelf thins or disappears, glaciers accelerate, dumping more ice into the ocean and raising sea levels.
- Sea ice, the free-floating ice that surrounds the polar regions, is distinct from both ice shelves and ice sheets.
- Sea ice forms when seawater freezes.
- The same thing is happening in West Antarctica.
- For decades, the region's ice shelves have been dwindling, glaciers have been melting faster, and the ice sheet has shrunk.
Findings of the Study
- The study predicts severe and extensive future warming of the West Antarctica Sea, as well as greater melting of ice shelves.
- This will very certainly result in greater sea-level rise, affecting coastal towns around the world, including India.
- India is vulnerable to sea level rise due to its vast coastline and dense population.
- If coastal communities cannot afford to defend themselves against increasing sea levels, such as by erecting walls, residents will have to relocate or become refugees.
Is there any hope left?
- Although the findings are dismal, the report emphasizes that they should not deter attempts to minimize the effects of climate change.
- The melting West Antarctic ice sheet, according to the experts, is just one component of sea level rise, which is just one effect of climate change.

Way Forward
- There are many other impacts that we can still avoid or limit: like the loss of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet, or the severity of heatwaves, droughts, and extreme rainfall.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Discuss the potential consequences of ice sheet melting on global sea levels and climate patterns.
|


















