Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) announced its short-term rate lending decision.
Details
- RBI has kept the repo rate steady for the sixth time in a row.
- As of now, the repo rate stands at 6.5 percent after a 0.25 percent hike by RBI in February 2023.
- Inflation has remained largely above or at the upper end of RBI’s tolerance band of 2-6 per cent.
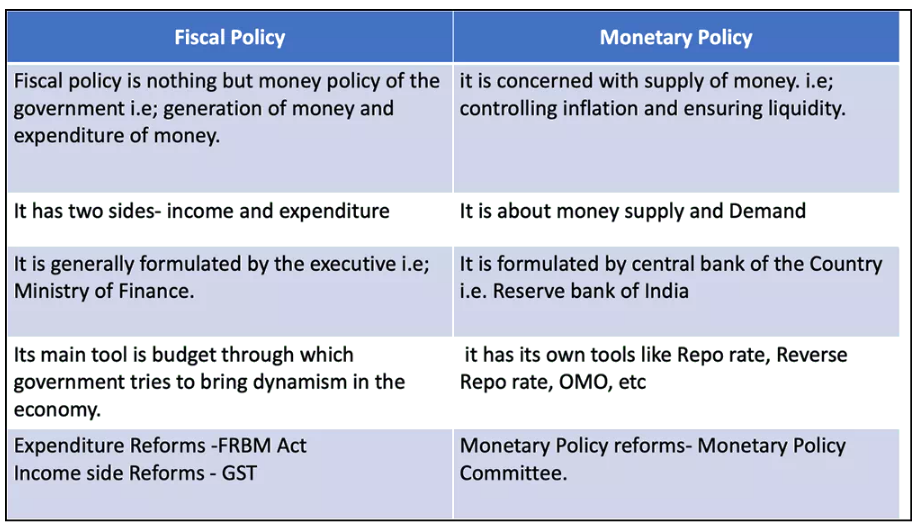
Monetary Policy:
- Definition: Monetary policy, managed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), is a key macroeconomic strategy aimed at regulating the nation's money supply and interest rates to foster sustainable economic growth.
- Objective: Its primary aim is to regulate the nation's money supply and interest rates to foster sustainable economic growth.
- Nature: This policy operates as a demand-side economic measure, influencing various aspects such as inflation, consumption, growth, and liquidity.

Expansionary and Contractionary Policies:
Expansionary Policy:
- Strategy: Focuses on increasing the money supply to stimulate economic activity.
- Measures: Lowering interest rates, purchasing government securities by central banks, and lowering the reserve requirements for banks.
- Effects: Aims to lower unemployment and stimulates business activities and consumer spending.
- Risks: May lead to higher inflation.
Contractionary Policy:
- Strategy: Aims to decrease the money supply to control inflation.
- Measures: Raising interest rates, selling government bonds, and increasing the reserve requirements for banks.
- Objective: Designed to curb inflationary pressures within the economy.
Objectives:
Inflation Management:
- Goal: To maintain stable inflation levels conducive to economic stability.
- Method: Utilizes various policy tools to target inflation rates within specified tolerance limits.
Unemployment Control:
- Impact: Monetary policies can influence the level of unemployment in the economy.
- Strategy: Expansionary policies generally decrease unemployment by stimulating economic activity.
Currency Exchange Rates:
- Role: Central banks regulate exchange rates between domestic and foreign currencies.
- Tool: By adjusting the money supply, central banks influence the strength of domestic currency relative to others.
Monetary Policy Tools:
Quantitative Tools:
Reserve Ratio:
- Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR): Banks are required to keep aside a set percentage of cash reserves with the RBI.
- Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR): Banks are required to keep aside a set percentage of reserves in liquid assets.
Open Market Operations (OMO):
- Buying and selling government securities to control the money supply.
Market Stabilization Scheme (MSS):
- Implemented to manage liquidity fluctuations in the market.
Policy Rates:
- Bank Rate: The interest rate at which RBI lends long-term funds to banks.
- Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF):
- Utilized through Repo and Reverse Repo rates to adjust liquidity
Monetary Policy Committee (MPC):
- Composition: Comprises officials from the RBI and external members nominated by the Government of India.
- Functions: Formulates monetary policy decisions, particularly regarding interest rates.
- Meetings and Decision Making: Hold regular meetings to determine policy interest rates aimed at achieving targeted inflation rates.
- Proposal: The Urjit Patel Committee was the first committee to propose the establishment of the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC).
- Mandate: The primary objective of the MPC, empowered by the RBI Act, of 1934, is to determine the policy interest rate required to achieve the inflation target.
- Meetings: The MPC holds meetings at least four times a year and publishes its decisions after each meeting.
- Composition: The committee comprises six members - three officials of the Reserve Bank of India and three external members nominated by the Government of India.
- Term: Each member has a tenure of four years.
- Confidentiality: Observe a "silent period" seven days before and after the rate decision for utmost confidentiality.
- Decision Making: Decisions are taken by majority vote, with the Governor having the casting vote in case of a tie.
Inflation Targets:
-
- Targeted consumer price index (CPI) inflation rate set at 4%.
- Upper tolerance limit: 6%, Lower tolerance limit: 2%.
Time Frame:
-
- Targets span from April 1, 2021, to March 31, 2026.
Trivia
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Which committee proposed the establishment of the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) in India, aimed at formulating and implementing monetary policies?
a) Rajan Committee
b) Raghuram Rajan Committee
c) Urjit Patel Committee
d) Y. V. Reddy Committee
Correct answer: c) Urjit Patel Committee
|














