Description
Copyright infringement not intended
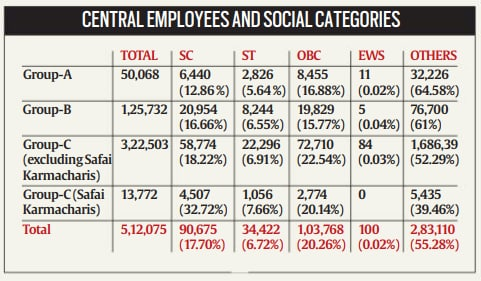
Context - The Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT) has released the data on the social categories of Central employees.
Details
- Recently the Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT) circulated a message to all Union ministries and departments asking them about the social categories of employees.
- According to the released data:
- 70 % of employees belong to SC categories.
- 72 % of employees belong to ST categories.
- 26 % of employees belong to OBC categories.
- 02% of employees belong to the EWS category.
- 28% of employees belong to the Unreserved/Others/General categories.
- The published data highlighted the huge vacancies:
- More than 8.70 lakh posts are vacant.
- The sanctioned strength of the IAS post is 6,746 and occupancy is 5,231, showing a vacancy of 1,515 posts.
Reservation System in India
- The Reservation system is an arrangement of affirmative action where a certain percentage of seats are reserved in Public employment and educational institutions.
- In India, the Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs), Other Backward Classes (OBCs) and socially and economically backward communities who were earlier poorly represented in the Public sector and educational institutions are now covered under the reservation facility.
Copyright infringement not intended
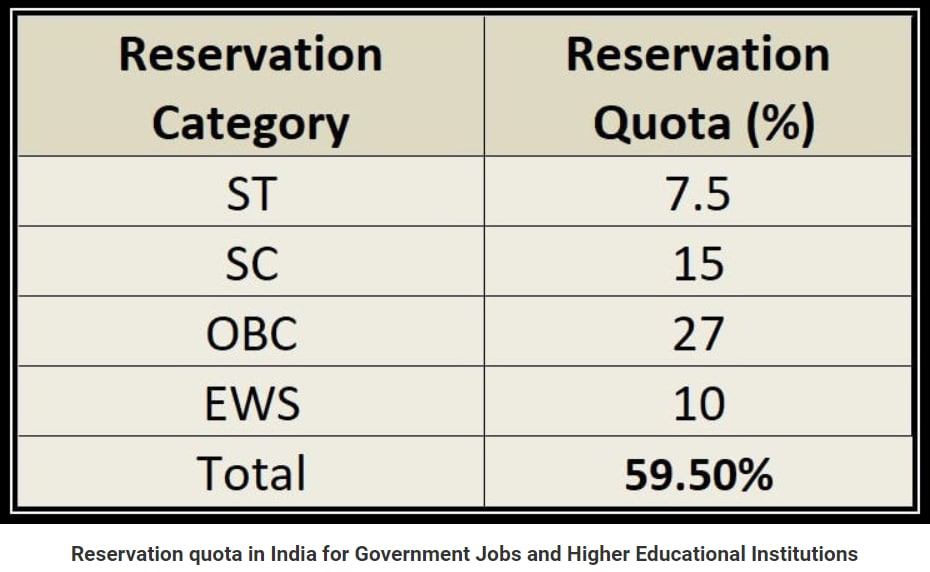
- In India, about 60% of seats are reserved for various sections like ST, SC, OBC, and EWS in Government jobs and Higher Education Institutions.
- 3% of seats are also reserved for differently-abled persons across all categories.
- The reservation policy is also enforced for the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes for representation in the Indian Parliament.
- The reservation issue has also remained a cause of conflict between the reserved and the non-reserved sections of society.
Arguments in the favour of Reservation System
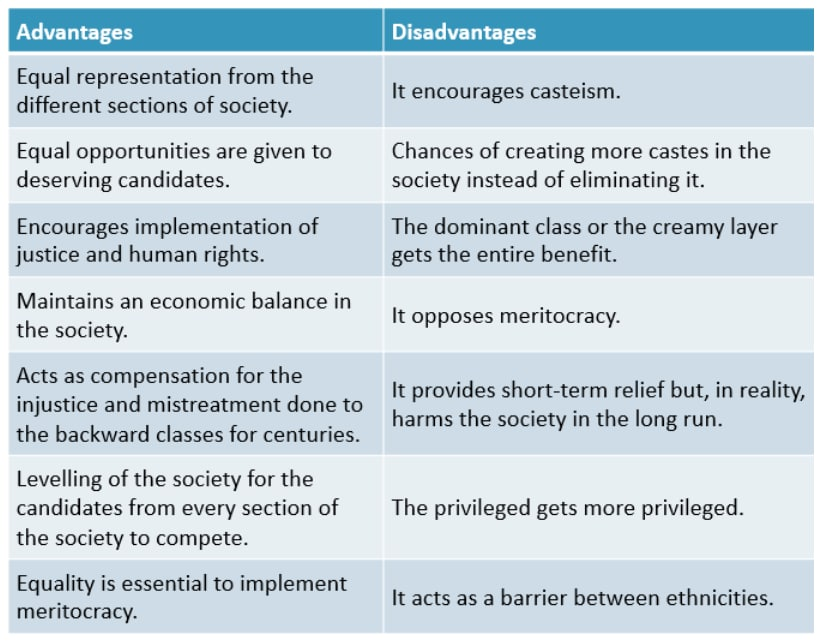
- It ensures equality, by providing opportunities to people from backward classes.
- It promotes justice and human rights.
- Decreasing inequality by promoting economic opportunities for the lower section of Society.
- Correcting historical injustice
- Reservation provides a level playing field as it is challenging for people from backward sections that were historically deprived of education, skills, and wealth to all of a sudden start competing with those who had access to those resources for years.
Arguments against Reservation System
- It Promotes Casteism and creates division in our society, and also encourages caste-based Politics.
- Beneficiaries of reservation are mostly from the dominant class in backward castes. Thus, the marginalized section still remains marginalized.
- Affects the productivity of an organization if unfit candidates get the opportunities.
- A reservation only provides a limited and short-term solution to historical injustice issues.
- Many deserving people from the upper castes are also affected by poverty and illiteracy.
- Reservation demands by various groups may cause social turmoil, such as during the Mandal Commission (1990).
Copyright infringement not intended
About Economically Weaker Section (EWS)
- Economically Weaker Section (EWS) in India is a subcategory of people belonging to the Economy Based Un-Reserved Category having an annual family income less than ₹8 lakh and who do not belong to any category such as SC/ST/OBC across India.
- Candidates who do not fall under SC/ST/OBC and fulfil the EWS economic criteria are to be part of the EWS category.
- In January 2019, the Union Council of Ministers approved a 10% reservation in government jobs and educational institutions for the Economically Weaker Section (EWS) in the General category.
- The cabinet decided that this would be over and above the existing 50% reservation for SC/ST/OBC categories.
- In January 2019, The Constitution (124th Amendment) Bill, 2019, was tabled in the Lok Sabha and it was passed on the same day.
- President Ram Nath Kovind gave assent to the bill on 12 January 2019, and a gazette was released on the bill, which turned it into law.
- The 103rd Amendment of the Constitution of India amended articles 15(6) and 16(6) of the Constitution of India to permit 10% reservations to the EWS category students among the unreserved category or General category students.
- A number of state cabinets approved the law and announced their intention to implement the 10% EWS reservations.
Eligibility Criteria under EWS Reservation
- The eligibility to get the EWS certificate is not only purely based on annual family income but also based on the held property.
- The income limit has been set by the central government for admission to central government-owned colleges and jobs offered by the central government.
- State governments are given the authority to change the eligibility criteria and also to extend the income limit further for candidates seeking reservation under the EWS category, which will be valid only in state-owned colleges and state government jobs as deemed fit for the respective states.
- Criteria for identifying EWS quota
- The candidate's annual family income must be less than Rs. 8 lakhs per annum.
- Their family must not own more than 5 acres of agricultural land.
- The residential flat area should be below 1000 sq ft.
- The residential plot's area should be below 100 square yards if in a notified municipality sector.
- The residential plot's area should be below 200 square yards if in a non-notified municipality sector.
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/scs-sts-obcs-in-central-govt-what-data-on-posts-and-vacancies-show-7881047/















