Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now



Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ring_of_Fire
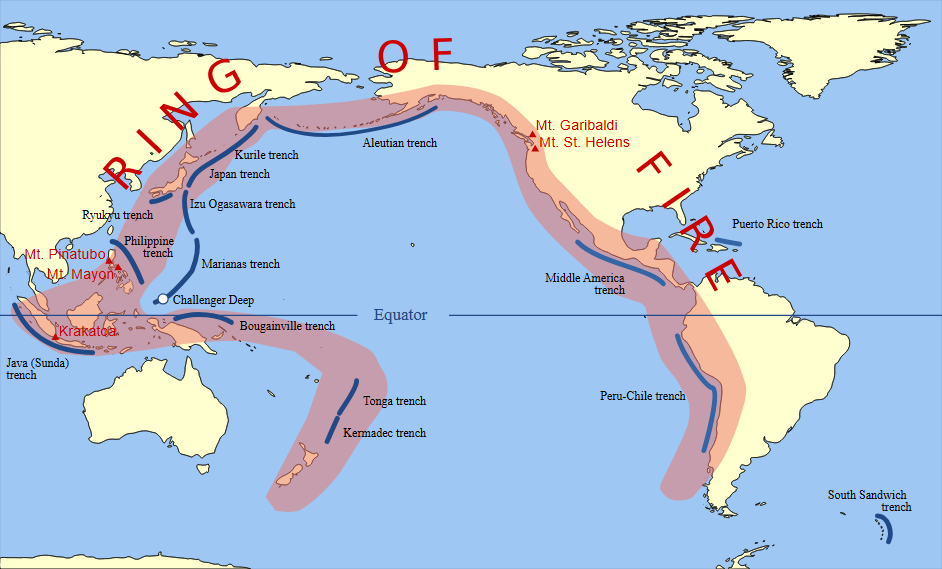
Context: The recent earthquake in Taiwan has highlighted the island's vulnerability to seismic activity. The vulnerability originates from its location on the Ring of Fire, a region that hosts a large proportion of the world's earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
|
Taiwan, officially known as the Republic of China (ROC), is an island nation situated in the western Pacific Ocean, approximately 100 miles off the southeastern coast of China. |
About Ring of Fire
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Which of the following countries is NOT part of the Ring of Fire? A) Indonesia B) Japan C) Brazil D) Chile Answer: C |










© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved