Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Tens of thousands of civilians have fled, and the United Nations has warned of a catastrophic humanitarian crisis, which could spill over into neighboring countries.
Present situation
Humanitarian crises worsening across the region
- There were humanitarian emergencies in Somalia, Sudan and South Sudan even before fighting broke out, and that relief efforts were underfunded.
- The has put neighboring nations under pressure.
- Some of these states are under military rule, an unstable security situation and economic trouble — or a combination thereof.
- Now, thousands of refugees from Sudan are streaming across the border to South Sudan, Chad, or the Central African Republic (CAR).
More support needed for the region’s countries
- The UN High Commission for Refugees (UNHCR) is bracing itself to support around 800,000 refugees in the region if the fighting does not end soon.
- But for many countries, there are severe challenges to hosting the incoming refugees.
- Local governments cannot support them financially.
Sudan’s leadership battle concerns neighbors
- Sudan has seven land borders.
- All those neighboring countries will be looking to influence outcomes and have interest in who will be leading Sudan.
Deep ties with Chad
- Sudan’s western neighbor, Chad, is politically unstable, having gone through its own civil wars and uprisings.

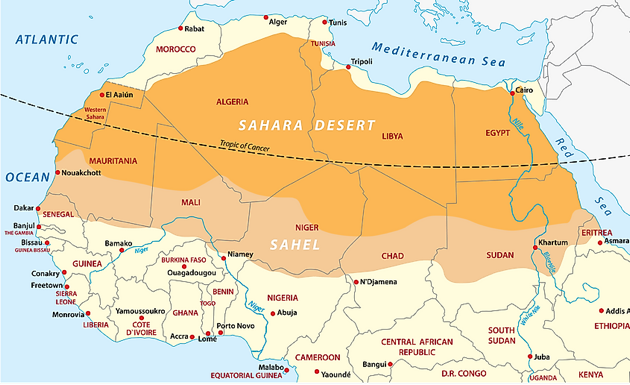
About Sahel region
- The Sahel is a region in Africa.
- It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south.
Location
- Having a hot semi-arid climate, it stretches across the south-central latitudes of Northern Africa between the Atlantic Ocean and the Red Sea.
Countries covered
- The Sahel part of Africa includes – from west to east – parts of northern Senegal, southern Mauritania, central Mali, northern Burkina Faso, the extreme south of Algeria, Niger, the extreme north of Nigeria, Cameroon and Central African Republic, central Chad, central and southern Sudan, the extreme north of South Sudan, Eritrea and Ethiopia.
History
- Historically, the western part of the Sahel was sometimes known as the Sudan region.
- This belt was located between the Sahara and the coastal areas of West Africa.
Conditions
- There are frequent shortages of food and water due to the dry harsh climate.
- This is exacerbated by the population increasing rapidly due to very high birthrates across the region; Niger has the world's highest fertility rate.
- Jihadist insurgent groups including Boko Haram, Islamic State and al-Qaeda frequently carry out major attacks in some parts of the western Sahel.
Flora and fauna
- The Sahel is mostly covered in grassland and savanna, with areas of woodland and shrubland.
- Species of acacia are the dominant trees, with Acacia tortilis the most common, along with Acacia senegal and Acacia laeta.
- The Sahel was formerly home to large populations of grazing mammals, including the scimitar-horned oryx, gazelle etc.
- The larger species have been greatly reduced in number by over-hunting and competition with livestock, and several species are vulnerable (Dorcas gazelle, cheetah, lion and red-fronted gazelle), endangered (Dama gazelle and African wild dog), or extinct (the Scimitar-horned oryx is probably extinct in the wild, and both Pelorovis and the Bubal hartebeest are now extinct).
- The seasonal wetlands of the Sahel are important for migratory birds moving within Africa and on the African-Eurasian flyways.
Climate
- Ennedi Plateau is located at the border of the Sahara and the Sahel
- The Sahel has a tropical semi-arid climate.
People
- Traditionally, most of the people in the Sahel have been semi-nomads, farming and raising livestock in a system of transhumance, which is probably the most sustainable way of utilizing the Sahel.
- In Western Sahel, polygamy and child marriage are common.
- Female genital mutilation is also practiced across the Sahel.
Etymology
- The term "Sahel" is borrowed from the Arabic name for the region. Sāḥil literally means "coast, shore".
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q) Tens of thousands of civilians have fled, and the United Nations has warned of a catastrophic humanitarian crisis, which could spill over into neighboring countries. Discuss how this id creating a dangerous security situation in the Sahel region. (150 words)
|

MUST READ ARTICLES:
Sudna crisis: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/crisis-in-sudan
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-global/sudan-crisis-sahel-8601520/













