Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Nepal and India have agreed to lower the projected Saptakoshi High Dam's height due to concerns in Nepal about the probable inundation of a huge swath of land upstream of the dam.
- After the high dam project had been stalled for several years due to local opposition, the two parties agreed to reduce the dam height.
- The change is expected to alleviate flooding concerns among Nepalis who may be relocated or affected by the project.
Details
- To evaluate the Saptakoshi High Dam Multipurpose Project and the Sunkoshi Storage and Diversion Project, a Nepal-India Joint Team of Experts was formed.
- It will lower hydropower generation to roughly 2,300MW, down from the 3,000MW originally anticipated for the multipurpose project.
Proposed hydropower projects between India- Nepal:
- Saptakoshi High Dam Multipurpose Project
- Sunkoshi Storage and Diversion Project
- A 756MW Tamor Storage Hydroelectric Project on the Tamor River.
- The 635MW Dudh Koshi Hydropower Project.
- The 683MWSunkoshi 3 Hydropower Project.

About Saptakoshi High Dam:
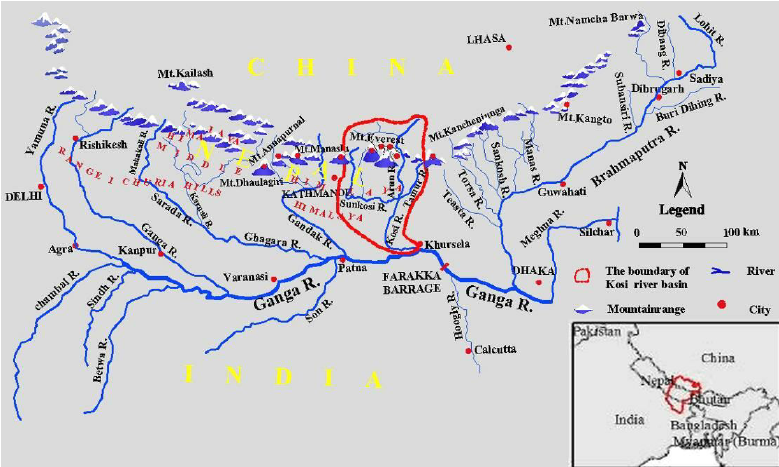
- It is a multipurpose project proposed to be built on Nepal's Saptakoshi River (known as the Koshi River in India).
- The project's primary goal is to prevent floods in southeast Nepal and northern Bihar while also generating hydropower.
- the Koshi Accord, is a bilateral initiative of the Indian and Nepalese governments.
- The planned location is 1.6 kilometers upstream from the Barahakshetra Temple in Nepal's Sunsari district.
River Saptakoshi:
- The Kosi, sometimes known as the Koshi, is a transboundary river that flows through China, Nepal, and India. It drains the northern Himalayan slopes of Tibet and the southern Himalayan slopes of Nepal.
- The Kosi River is also known as Saptakoshi for its seven upper tributaries from a major confluence of rivers north of the Chatra Gorge onwards. These include the Tamur River, which flows from the Kanchenjunga region in the east, and the Arun and Sun Kosi rivers, which flow from Tibet.
- From east to west, the Sun Koshi's tributaries are the Dudh Koshi, LikhuKhola, Tamakoshi River, Bhote Koshi, Tamor, and Indravati.
- The Saptakoshi enters northern Bihar, India, and splits several distributaries before entering the Ganges near Kursela in Katihar district.
- Kosi is the 3rd largest tributary of the Ganges by water discharge after Ghaghra and Yamuna.
Other Recent Developments in India-Nepal Relations
BOOT (Build Own Operate and Transfer):
- In 2008, the Government of Nepal and Sutlej Jal Vikas Nigam (SJVN) Limited signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for the project's execution on a Build Own Operate and Transfer (BOOT) basis for a duration of 30 years, including the five-year construction period.
Hydropower Initiatives:
- Nepal has also encouraged Indian firms to invest in the West Seti hydropower project.
.jpg)
Cross-border Rail Connection:
- The 35-kilometer cross-border train link between Jayanagar (Bihar) and Kurtha (Nepal) will be expanded to Bijalpura (Nepal) and Bardibas (Nepal).
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Evaluate India’s foreign policy towards its neighbors and how it has evolved over time. (250 words)
|
















