Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Background
- In 2018 a team of researchers from Arizona State University (ASU) and MIT in the US detected a signal from stars emerging in the early universe.
- The team had claimed the discovery of a radio wave signalling the birth of the First Stars.
- However, the world awaited confirmation from independent researchers.
- Utilising SARAS 3 radio telescope, researchers from Raman Research Institute, an autonomous institute of the Department of Science & Technology, of India refuted this claim.
About SARAS 3
- SARAS 3 is an indigenously invented and built radio telescope that can detect extremely faint radio wave signals from the depths of time.
- It can detect faint cosmological signals, especially radiation emitted by hydrogen atoms at the 21-cm wavelength (1.4 GHz) arising from the depths of the cosmos.
Note: Detecting a faint signal from such an early period of the Universe is extremely difficult. The celestial signal is exceptionally faint - buried in sky radio waves that come to us from the gas in our own Galaxy, the Milky Way, which are a million times brighter.
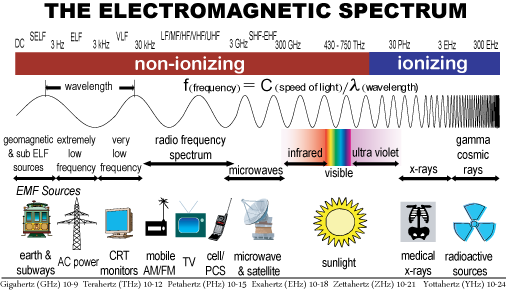
Radio Waves
- Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies of 300 gigahertz (GHz) and below.
- Like all electromagnetic waves, radio waves in a vacuum travel at the speed of light, and in the Earth's atmosphere at a close, but slightly lower speed.
- Radio waves are generated by charged particles undergoing acceleration, such as time-varying electric currents.
- Naturally occurring radio waves are emitted by lightning and astronomical objects, and are part of the blackbody radiation emitted by all warm objects.
- Radio waves are generated artificially by transmitters and received by radio receivers, using antennas.
- Radio waves are very widely used in modern technology for fixed and mobile radio communication, broadcasting, radar and radio navigation systems, communications satellites, wireless computer networks and many other applications.
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1802645














