



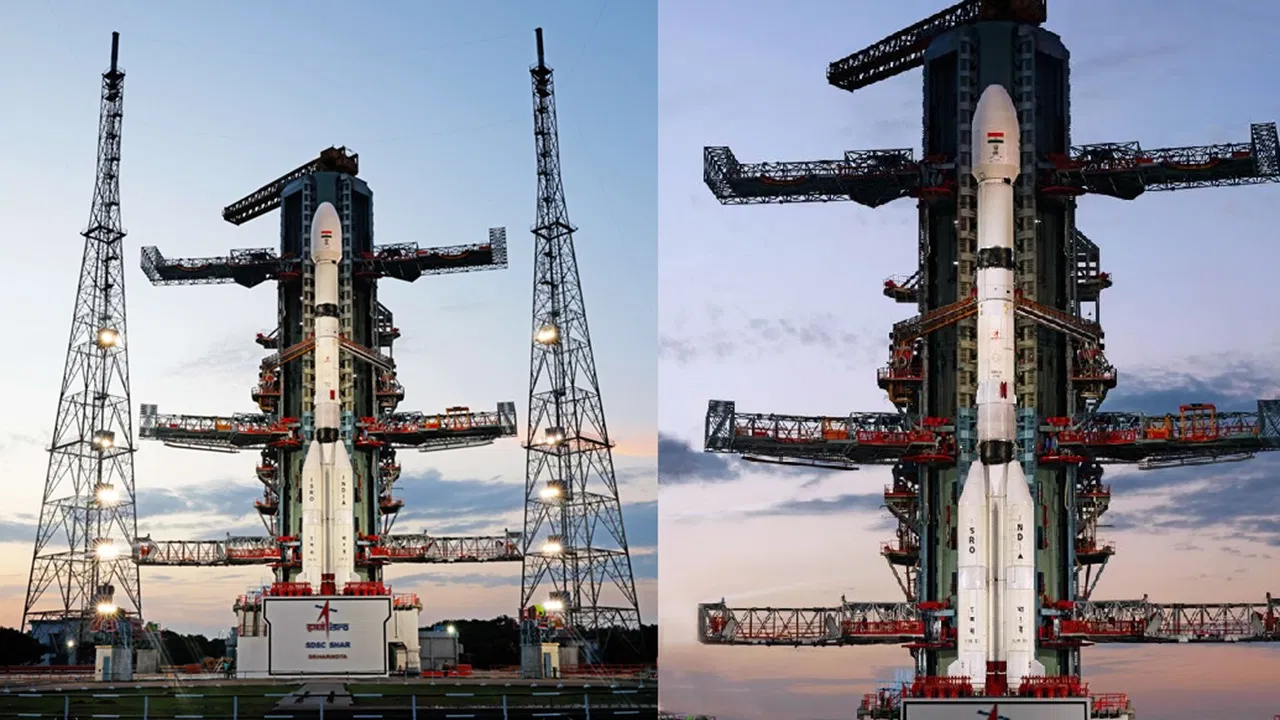
The Union Cabinet has approved the establishment of a third launchpad at India's Satish Dhawan Space Center in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh. The third launchpad will support ISRO's plans to use the Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV). Sriharikota's location and uninhabited status make it an ideal launch site.

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: Deccanheralnd
The Union Cabinet has approved the setting up of a third launchpad at the Satish Dhawan Space Center (SDSC) in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh.
It is India’s only spaceport, where spacecraft and satellites are launched.
It became operational in October 1971, with the flight of ‘Rohini-125,’ a small-sounding rocket.
Initially called SHAR (Sriharikota Range), the space center was renamed in 2002 to honor Satish Dhawan, the former ISRO Chairman.
The third launchpad will support ISRO’s future plans to use the Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV), which is under development. This will help ISRO become more capable and ready for upcoming space missions.
Apart from its location, Sriharikota was largely uninhabited and near the sea, which ensured that the flight path of rockets would be over the sea, minimizing risk. Any rocket hardware that separated during the launch could safely fall into the high seas.
Satish Dhawan was a renowned Indian rocket scientist, often called the 'Father of Experimental Fluid Dynamics Research' in India.
He was appointed Chairman of ISRO in 1972, and he guided significant achievements in the Indian space program, including the development of the INSAT and IRS satellites.
Following his death in 2002, the space centre was renamed in honour of his contributions to the country's space exploration.

A Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV) is a rocket-powered vehicle that transports satellites or spacecraft from Earth's surface into space.
It is designed to overcome Earth's gravitational pull and deliver payloads into various orbits, such as Low Earth Orbit (LEO) or Geostationary Orbit (GEO).

Launch vehicles work based on the principles of rocket propulsion, which involve action and reaction (Newton's Third Law). The vehicle’s propulsion system generates the necessary thrust to lift off the ground.
It consists of multiple stages that drop off as the vehicle ascends. These stages contain their own engines and propellants. The payload is protected by a fairing during launch, and once the vehicle reaches space, the fairing is jettisoned, allowing the satellite to be inserted into orbit.
ISRO has played a key role in advancing India's space capabilities. From launching its first satellite, SLV-3, in 1980, to developing more advanced launch vehicles like PSLV, GSLV, and GSLV Mk III, ISRO has significantly contributed to satellite deployments. These vehicles have launched various satellites for communication, Earth observation, and scientific research.
Launch vehicles generally have multiple stages. Each stage is designed to provide a certain amount of thrust to carry the vehicle further into space.


Sounding rockets are short-range, one or two-stage solid-propellant rockets used to explore the upper atmosphere and conduct space research. ISRO began using sounding rockets in 1965, and they continue to provide valuable data for atmospheric research.
ISRO is also working on human-rated launch vehicles and reusable technology to reduce costs in future space missions.
Must Read Articles:
Source:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q.Explain the concept of “Space Diplomacy” and its relevance to India’s space programme. 150 words |





© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved