Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: www.hindustantimes.com
Context: The Union Health Ministry notifies revised rules under Schedule M of the Drugs and Cosmetics Rules, 1945, aiming to align Indian guidelines with global standards and strengthen the quality of domestically manufactured drugs.
Details
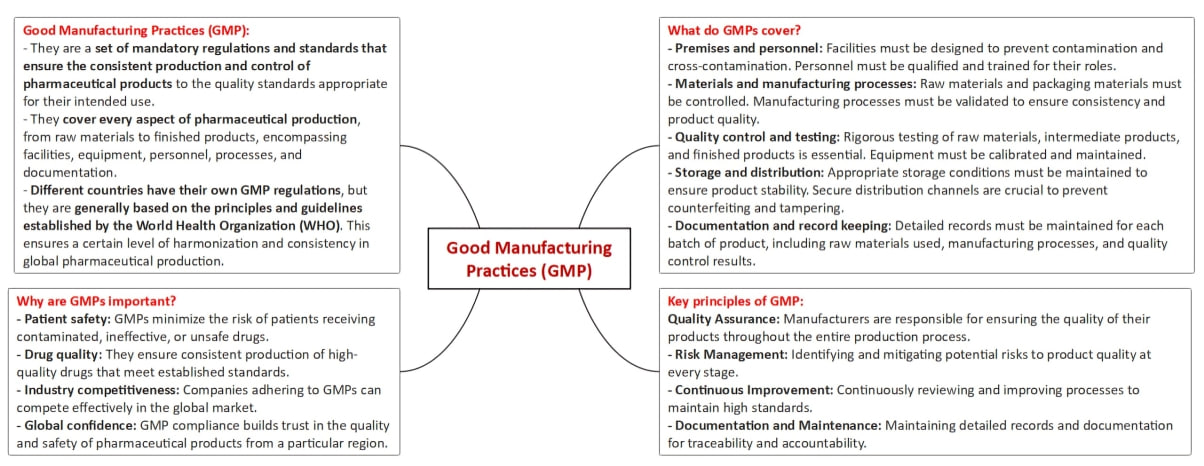
- The revised Schedule M under the Drugs and Cosmetics Rules, 1945, represents a significant update to pharmaceutical manufacturing regulations, particularly focusing on Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and the associated requirements for premises, plant, and equipment.
Objective and Scope
- The primary goal is to ensure robust quality control for pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical products in India.
- The revised Schedule M emphasizes adherence to GMP, which is essential for maintaining high-quality standards in the production of pharmaceuticals.
Evolution of GMP
- GMP was initially incorporated into Schedule M in 1988 and underwent its last amendment in June 2005.
- The recent amendment replaces the term 'Good Manufacturing Practices' with 'Good Manufacturing Practices and Requirements of Premises, Plant, and Equipment for Pharmaceutical Products.'
Alignment with Global Standards
- The revision is driven by the need to keep up with fast-changing manufacturing and quality standards globally.
- The aim is to bring Indian GMP recommendations on par with global standards, particularly those outlined by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Key Changes Introduced
- The revised Schedule M introduces several new elements, including a pharmaceutical quality system (PQS), quality risk management (QRM), product quality review (PQR), qualification and validation of equipment, and a computerized storage system for all drug products.
- These changes reflect a comprehensive approach to ensuring high standards in pharmaceutical manufacturing.

New Categories of Drugs
- The revised Schedule M introduces five new categories of drugs, including pharmaceutical products containing hazardous substances such as sex hormones, steroids (anabolic and androgenic), cytotoxic substances, biological products, and radiopharmaceuticals.
Manufacturer Responsibilities
- The notification emphasizes that manufacturers must take responsibility for the quality of pharmaceutical products, ensuring they are fit for their intended use, comply with licensing requirements, and do not pose risks to patients due to safety, quality, or efficacy issues.
Testing and Quality Assurance
- The notification stipulates that companies can market a finished product only after obtaining satisfactory results from tests of the ingredients.
- Manufacturers are required to retain a sufficient quantity of samples of intermediate and final products to allow for repeated testing or verification of a batch.
Implementation Timeline
- The revised rules set specific timelines for implementation based on company turnovers. Small manufacturers with an annual turnover of less than ₹250 crore are given 12 months, while large manufacturers with a turnover over ₹250 crore have six months to comply.
Industry Response
- Secretary General of the Indian Pharmaceutical Alliance (IPA), sees the revision as a positive step and an important milestone for the Indian pharmaceutical sector. It is expected to elevate and update the quality standards of medicines, contributing to India's global reputation in pharmaceutical quality.

Conclusion
- The revised Schedule M reflects a comprehensive and forward-looking approach to pharmaceutical manufacturing regulations in India, aligning them with global standards and aiming to enhance the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products.
Must Read Articles:
SCHEDULE-M: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/schedule-m#:~:text=Schedule%20M%20is%20a%20section,and%20efficacy%20of%20their%20products.
WHO Standard Good Manufacturing Practices: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/who-standard-good-manufacturing-practices
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. How does the World Health Organization influence and regulate the global healthcare system, and what key roles does it play in ensuring international health standards and coordination among member nations?
|












