





Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.outlooktraveller.com/whats-new/schengen-visa-process-to-go-digital-heres-all-you-need-to-know
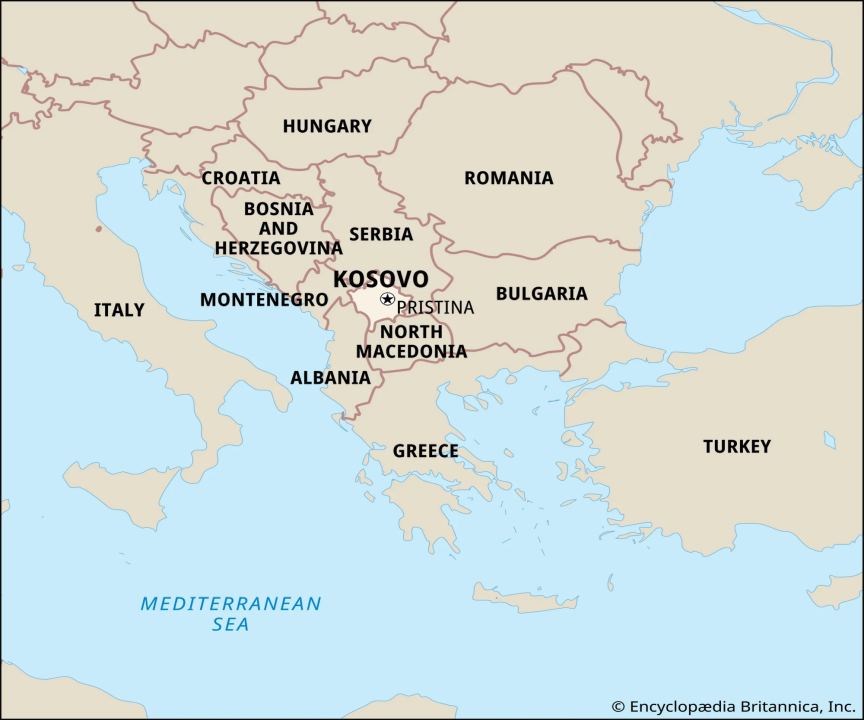
Context: Kosovo, a non-EU Western Balkan nation, has faced delays in obtaining visa-free access to the Schengen Zone, despite meeting preconditions related to illegal migration and corruption in 2018, which are prerequisites for Schengen entry.
Details
Schengen
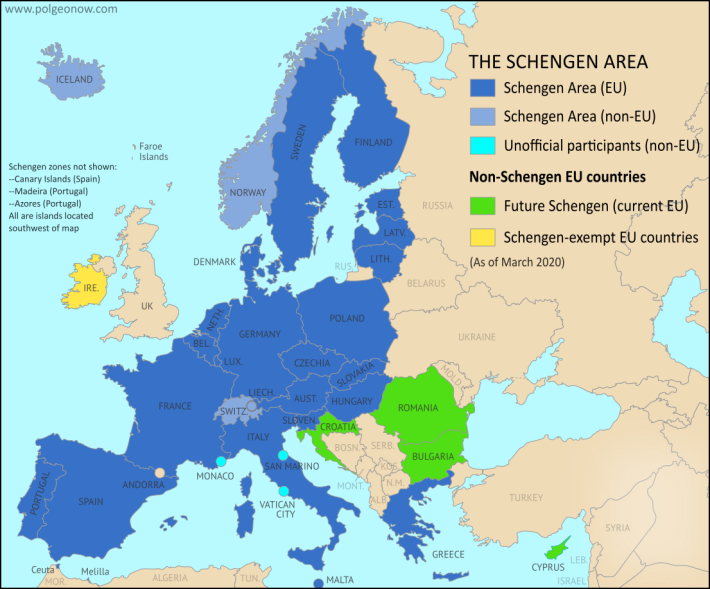
Internal Functioning
External Border Management
Impact and Significance
|
Kosovo ●Kosovo is a partially recognized state in southeastern Europe. It declared independence from Serbia in 2008, but its sovereignty is not recognized by all countries, including Serbia itself. ●Kosovo is a landlocked country bordered by Serbia to the north and east, North Macedonia to the southeast, Albania to the southwest, and Montenegro to the northwest. The landscape is mostly mountainous, with the highest point being Gjeravica at 2,656 meters. The climate is continental, with hot summers and cold winters. ●The economy of Kosovo is based on agriculture, mining, and manufacturing. The main agricultural products are wheat, maize, potatoes, and fruits. The main mineral resources are coal, lead, zinc, and nickel. The main manufactured goods are textiles, food products, and furniture. |
Must Read Articles:
SCHENGEN VISA: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/schengen-visa#:~:text=A%20Schengen%20visa%20is%20an,identity%20checks%20at%20the%20border.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. What is the main benefit of the Schengen Zone for citizens of member states? A) Cheaper flights within the zone B) Access to exclusive tourist destinations C) Freedom of movement without passport checks at internal borders D) Reduced visa fees for travel outside the zone Answer: C Explanation: The most significant advantage of Schengen is the ability to travel freely within the zone without the hassle of border checks. This facilitates easier travel, business activity, and social connections. While other options might offer specific benefits, they aren't core aspects of the zone. So, the answer is (C). |










© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved