





Disclaimer: Copyright infringement is not intended.
Context:
Details of the study on trends of sea level rise:
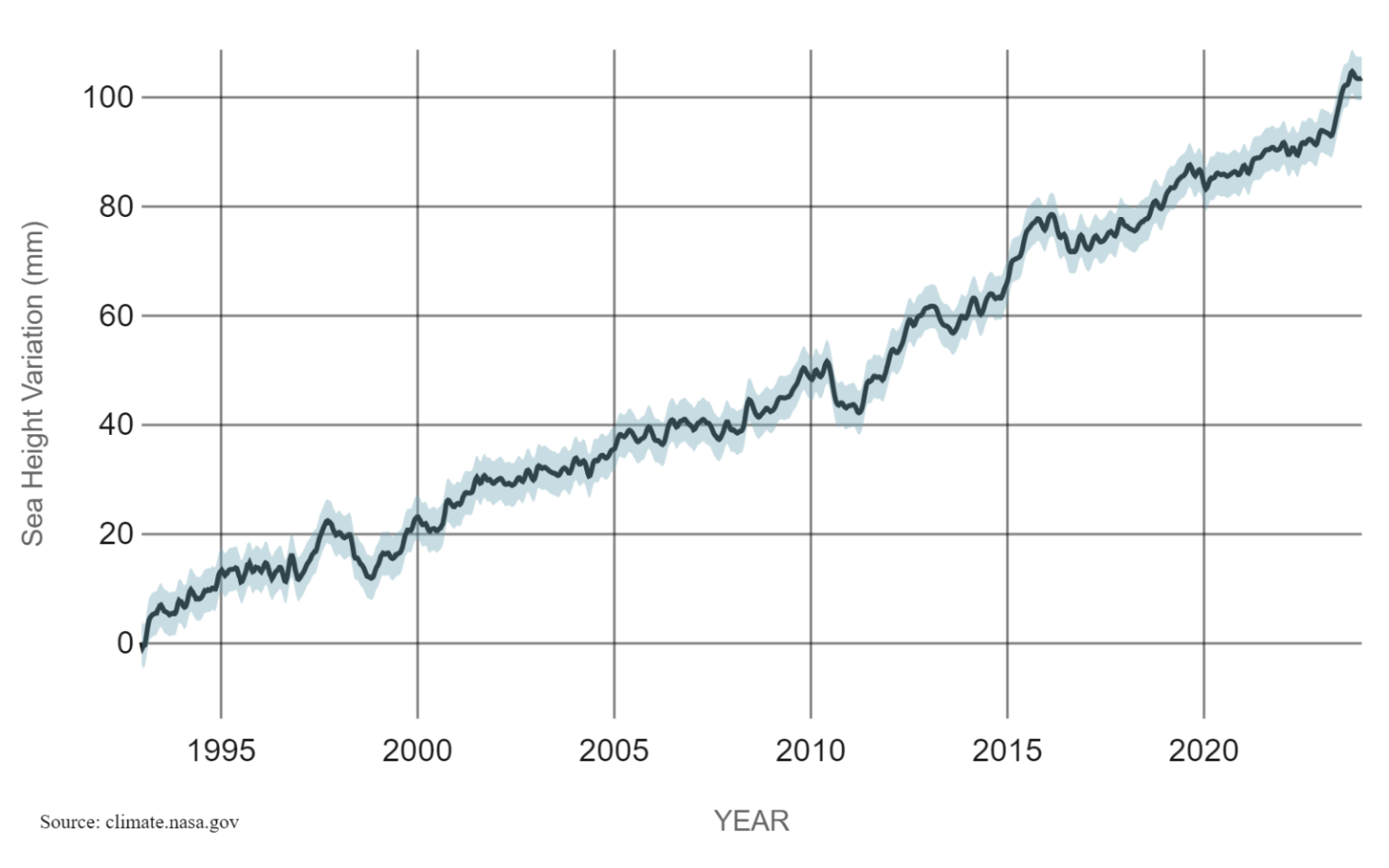
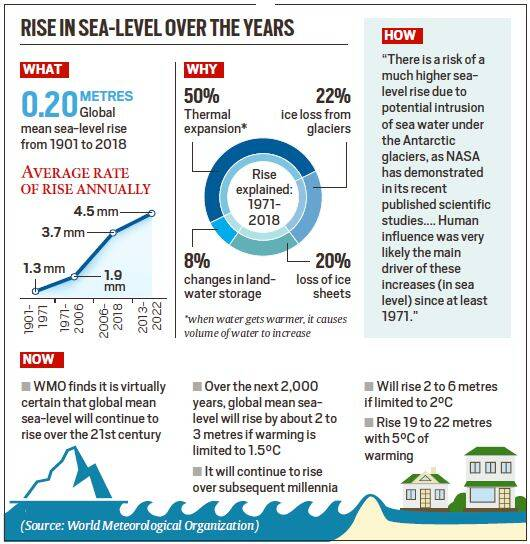
How climate change is leading to sea level rise?
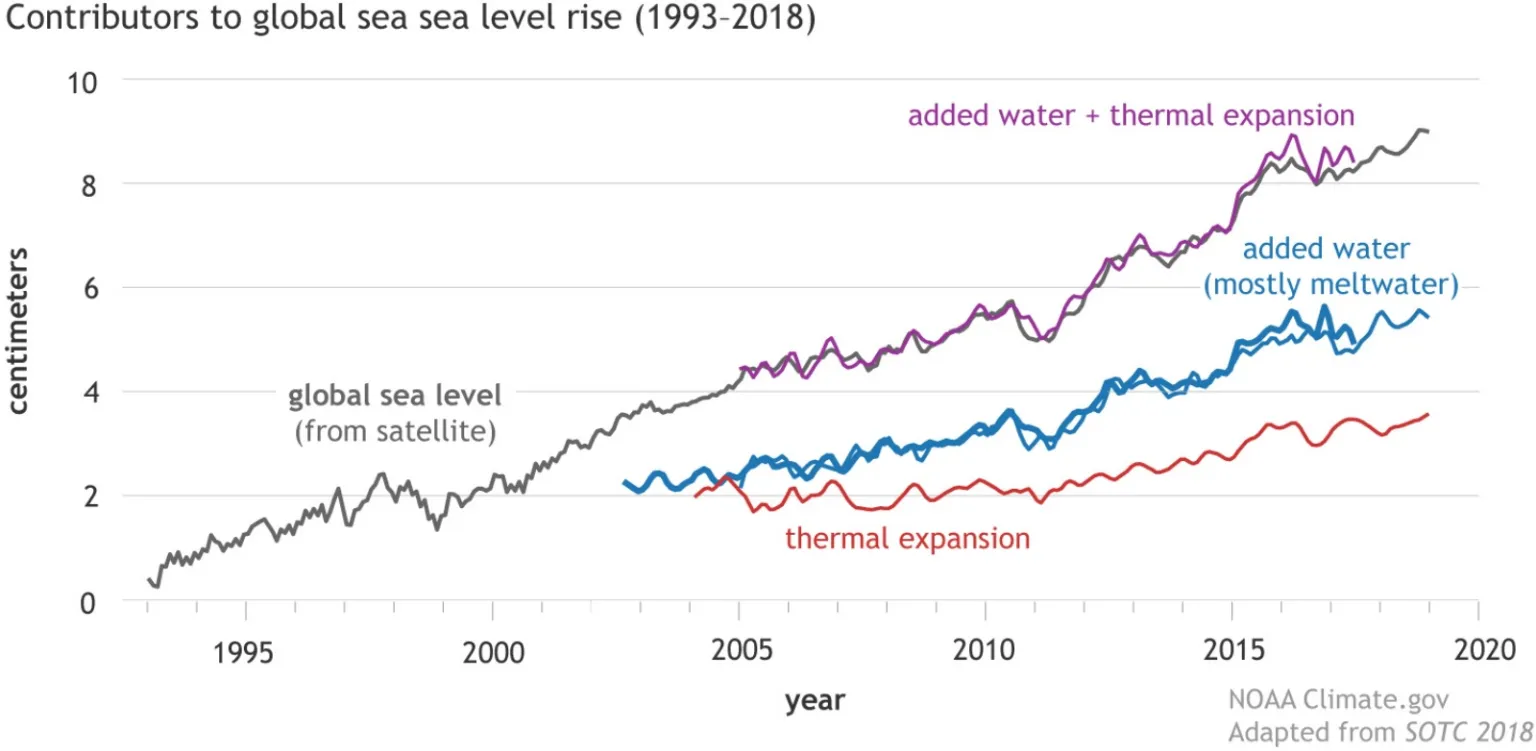
|
India's Coastal Vulnerability: ●Coastline Statistics: ●India's coastline spans 7,516 kilometers, encompassing 5,422 kilometers on the mainland and 2,094 kilometers across islands belonging to nine states and four Union Territories. ●This coastline supports 90% of the country's trade and encompasses 3,331 coastal villages and 1,382 islands. ●According to an analysis, about 43.5 of the coastline is under highly vulnerable zone and about 1 is under a very highly vulnerable zone. |
Impact of Sea Level Rise:
|
Initiatives to Address Sea Level Rise International: ●Relocation Strategies: ○Coastal cities like Kiribati Island and Indonesia's capital Jakarta are planning relocation to mitigate the impacts of sea level rise. Kiribati plans to shift to Fiji, while Jakarta is relocating to Borneo. ●Construction of Sea Walls: ○Indonesia initiated the construction of a Giant Sea Wall, also known as "Giant Garuda," in 2014 to protect coastal areas from flooding. ●Implementation of Enclosures: ○Researchers have proposed projects like the Northern European Enclosure Dam (NEED) to enclose bodies of water like the North Sea, Persian Gulf, Mediterranean Sea, Baltic Sea, Irish Sea, and Red Sea to shield Northern European countries from rising seas. ●Innovative Architectural Solutions: ○Cities like Rotterdam in the Netherlands have adopted innovative architectural features such as barriers, drainage systems, and "water squares" with temporary ponds to manage water flow and mitigate flooding. National: ●Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ): ●The Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) was established in 1991 to regulate coastal areas within 500 meters from the high tide line (HTL) and the land between the low tide line (LTL) and HTL. ●Recent regulations under CRZ consider the impact of rising sea levels due to global warming. ●National Action Plan on Climate Change: ●Launched in 2008 by the Prime Minister's Council on Climate Change, this plan aims to raise awareness among various stakeholders about climate change threats and mitigation strategies. |
Source:
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-climate/sea-level-rise-9284789/
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q) Discuss the factors contributing to sea level rise, its impact on coastal regions, and measures to mitigate its effects. Examine the role of international cooperation in addressing the challenges posed by increasing sea levels.. (250 Words) |











© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved