
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Capital markets regulator Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has introduced a regulatory framework to facilitate providers of online bond platforms that are selling listed debt securities.
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
- About:The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is a statutory body established under the SEBI act of 1992.
- Formation:It was formed in response to prevent malpractices in the capital markets that were negatively impacting people’s confidence in the market.
- Objective: Its primary objective is to protect the interest of the investors, preventing malpractices, and ensuring the proper and fair functioning of the markets.
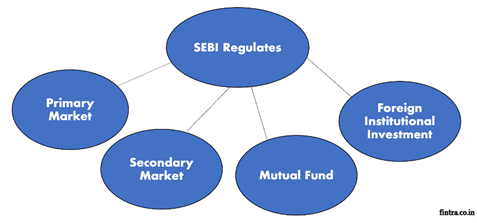
Functions of SEBI
SEBI has many functions, they can be categorized as:
- Protective functions:To protect the interests of the investors and other market participants. It includes – preventing insider trading, spreading investor education and awareness, checking for price rigging, etc.
- Regulatory functions:These are performed to ensure the proper functioning of various activities in the markets. It includes – formulating and implementing code of conduct and guidelines for all types of market participants, conducting an audit of the exchanges, registration of intermediaries like brokers, investment bankers, levying fees, and fines against misconduct.
- Development functions:These are performed to promote the growth and development of the capital markets. It includes – Imparting training to various intermediaries, conducting research, promoting self-regulation of organizations, facilitating innovation, etc
Powers of SEBI
- To perform its functions and achieve its objectives, SEBI has the following powers:
- To change laws relating to the functioning of the stock exchange
- To access record and financial statements of the exchanges
- To conduct hearing and give judgments on cases of malpractices in the markets.
- To approve the listing and force delisting of companies from any exchanges.
- To take disciplinary actions like fines and penalties against participants who involve in malpractice.
- To regulate various intermediaries and middlemen like brokers.
Members
The SEBI is managed by its members, which consists of the following:
- The chairman is nominated by the Union Government of India.
- Two members, i.e., Officers from the Union Finance Ministry.
- One member from the Reserve Bank of India.
- The remaining five members are nominated by the Union Government of India, out of them at least three shall be whole-time members.
SEBI’s new regulatory framework
Pertaining to online bond platform provider
- Under the new rules, no person would act as an online bond platform provider without obtaining registration certificate as a stock broker from SEBI.
- Such a person would have to comply with the conditions of registration and such other requirements specified by the regulator from time to time.
- A person acting as an online bond platform provider without registration certificate prior to the date of this regulation coming into force can continue to do so for a period of three months.
Note: The regulator has defined online bond platform as any electronic system, other than a recognized stock exchange or an electronic book provider platform, on which the debt securities which are listed or proposed to be listed, are offered and transacted. Further, online bond platform provider means any person operating or providing such a platform. In India, most of such bond platforms are fintech companies or are backed by brokers. These companies are GoldenPi, BondsIndia, Harmoney etc.
NCS Regulations
The NCS Regulations have prescribed certain parameters for identification and disclosure of risks in the offer document, such as: (i) risks in relation to the non-convertible debentures ('NCDs') , (ii) risk in relation to the security created, (iii) refusal by stock exchange for listing of any security in the previous three years, etc.
Applicability of the NCS Regulations
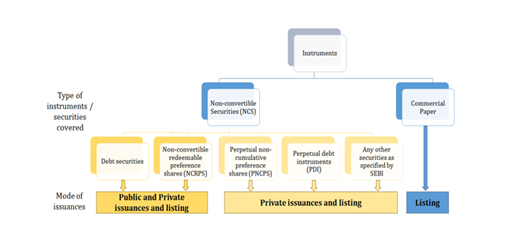
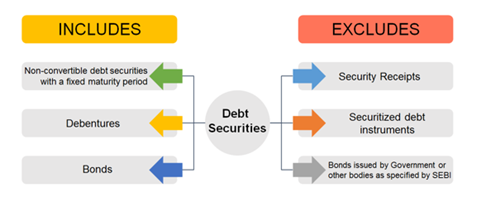
NCS Regulations Covers the following
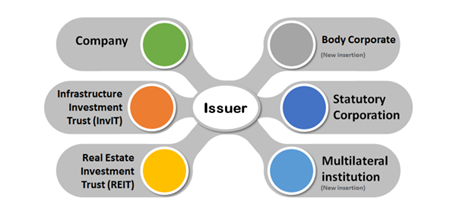
SEBI (Issue and Listing of Non-Convertible Securities) (Amendment) Regulations, 2022
- SEBI has amended NCS (Issue and Listing of Non-Convertible Securities) Regulations. The new norm has become effective from November 9, 2022.
- The amended regulation requires an issuer to ensure that the secured debt securities are secured by 100% security cover or higher security cover as per the terms of the offer document and/or Debenture Trust Deed sufficient to discharge the principal amount and interest. As per extant norms, the issuer is required to ensure that the secured debt securities are secured by 100% security cover.
- The amended regulation requires the lead manager to ensure that the secured debt securities are secured by 100% security cover or higher security cover as per the terms of the offer document and/or Debenture Trust Deed sufficient to discharge the principal amount and interest. As per extant norms, the lead manager is required to ensure that the secured debt securities are secured by 100% security cover.
Pertaining to Real Estate Investment Trust (REITs)
|
REIT
A real estate investment trust (REIT) is a company that pools its capital to purchase properties and/or mortgage loans. Investors buy REIT shares and, in turn, receive dividends from investment income or capital gains distributions. REIT shares are traded on exchanges much like the stocks of other companies.
|
- SEBI notified rules reducing the minimum holding requirement of Real Estate Investment Trust (REITs) units by sponsors to 15 per cent from 25 per cent at present. This move is aimed at encouraging more companies to float REITs.
- The sponsor(s) and sponsor group(s) shall collectively hold a minimum of 15 per cent of the total units of the REIT for a period of at least three years from the date of listing of such units pursuant to initial offer on a post-issue basis.
- However, any holding of the sponsor and sponsor group exceeding the minimum holding, would be held for at least one year from the date of listing of such units.

Peraining to Infrastructure Investment Trust
|
InvITs
Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs) are investment instruments that work like mutual funds and are regulated by SEBI. Typically, such a vehicle is designed to pool money (small sums) from several investors to be invested in income-generating assets.
|
- SEBI has discontinued a separate regulatory framework for unlisted Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT). This would come into force from January 1 2023.
Significance
- All these moves will enhance the confidence among investors, particularly non-institutional investors, as the platforms would be provided by SEBI-regulated intermediaries.

https://www.thehindu.com/business/markets/sebi-introduces-regulatory-framework-to-facilitate-online-bond-platform-providers/article66124013.ece




















